Objectives and evaluation criteria for heritage language teaching (grades 1-2)
Content area 1: Acting in interactive situations
- You can follow the instructions in your heritage language but you will not always answer in your heritage language.
- You participate in the group, but you do not always express yourself in words and need much encouragement.
Examples:
1. When writing, the student doesn’t copy the example, but will write with help of dots: writing with help of dots.pdf
2. When playing a game, the student understands what to do, but first wants to watch, before he/she really participates.
3. When listening to a story, students can follow what happend in the story, buty they might tell in Finnish, or they answer questions just by yes/no or nodding their heads.
Example excercise: When listening to a story, the studens have to make a sound or guesture with certain words. The class can also be devided in groups, each group has their own role in the story. Or sounds can be created with the story and the story can be turned into a radio play.
good performance
- You take part in familiar interaction situations and answer sometimes in Finnish or without words.
- You participate in class work.

–Drawing the word
–Describing without saying the word
–Acting out a verb
–Answering a question
Word or picture cards of different themes: can be used
- You take independently part in different interaction situations and use words appropriate for your age.
- You participate in the work of the group and encourage others.
Example: Student can tell in the group how his/her week has been, and ask question from the other students about what they have been doing. Student can explain the rules of a game that is being played. Or help the other students with their task if he/she already finished.
Content area 2; Interpreting texts
- You recognise the alphabet and the reading signs of your heritage language and voice / letter / character combinations.
- You can answer questions about texts you have heard.

Example:
- The student can fill the missing letters of the alphabet, knows how to pronounce the letters/combination of letters e.g.: oe/ui/au/ou/ei/ij/eu in Dutch
-
Student can answers general question about a text that he/she heard:
good performance
- You can put letters together to form words.
- You can read words and single sentences.
- You can answer questions about these sentences.

- You read simple texts.
- You answer the questions about texts you have heard or read independently, and you explain your own view on the story you heard or the text you have read.
Did they like it or not and why? What was weird, what was nice etc.
Example text: Mickey Mouse - Reading Comprehension
Content area 3: Producing texts
- You write singular words independently.
- You write simple sentences on dictation.
good performance
- You need support to write short sentences using the basic vocabulary.
- When using your heritage language, you write in the correct writing direction.
- You write short sentences using the basic vocabulary and need occasional support.
Example: Students can write a story about a picture(s) or they can finish a short story from a given beginning.

Content area 4: Understanding language, literature, and culture
- You can name some of the festive traditions and customs from your own culture.
- You can tell when and where you use your heritage language.
Example: student can name the (festive) traditions on the pictures.
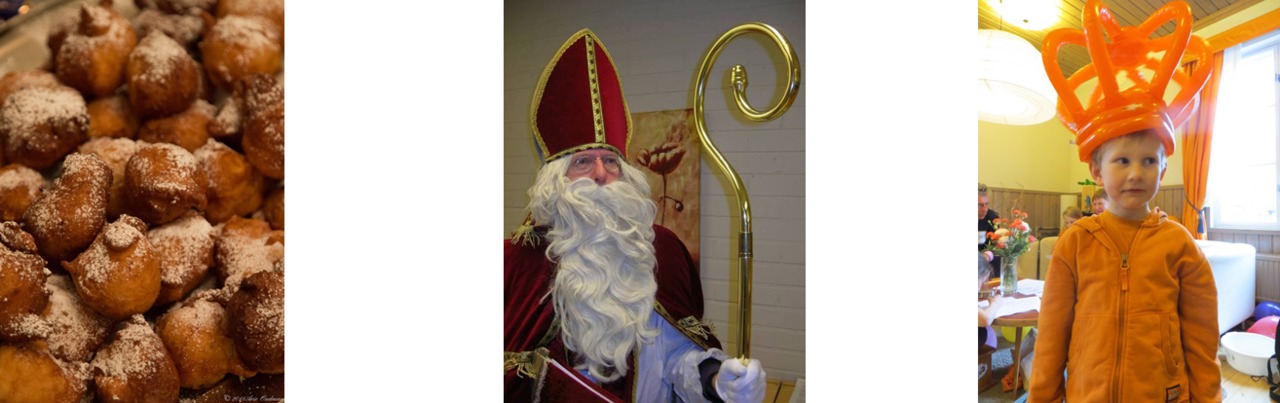

good performance
- You know the festive traditions and custom from your own culture.
- You use the appropriate language and customs in familiar situations.
Example: a year calendar with all the different celebration you celebrate in your family/ culutre group can be created

The student knows how to address people, knows the difference in speaking to friends/teachers/grand parents.

- You recognize differences between Finnish and your heritage culture and describe the ways of your heritage culture to other students.
- Your language use and cultural habits are appropriate for the situation.
- What are the difference in school systems
- What are difference in eating habits
- What are differences in celebrating (e.g. Christmas)
- What are differences in addressing people? (e.g. how to speak to your teacher)


