Objective 9: to encourage the pupil to recognise different linguistic registers, such as the differences between spoken and written language and the use of language in different situations
-
You know the most common Idioms and cultural-related expressions but do not actively use them.
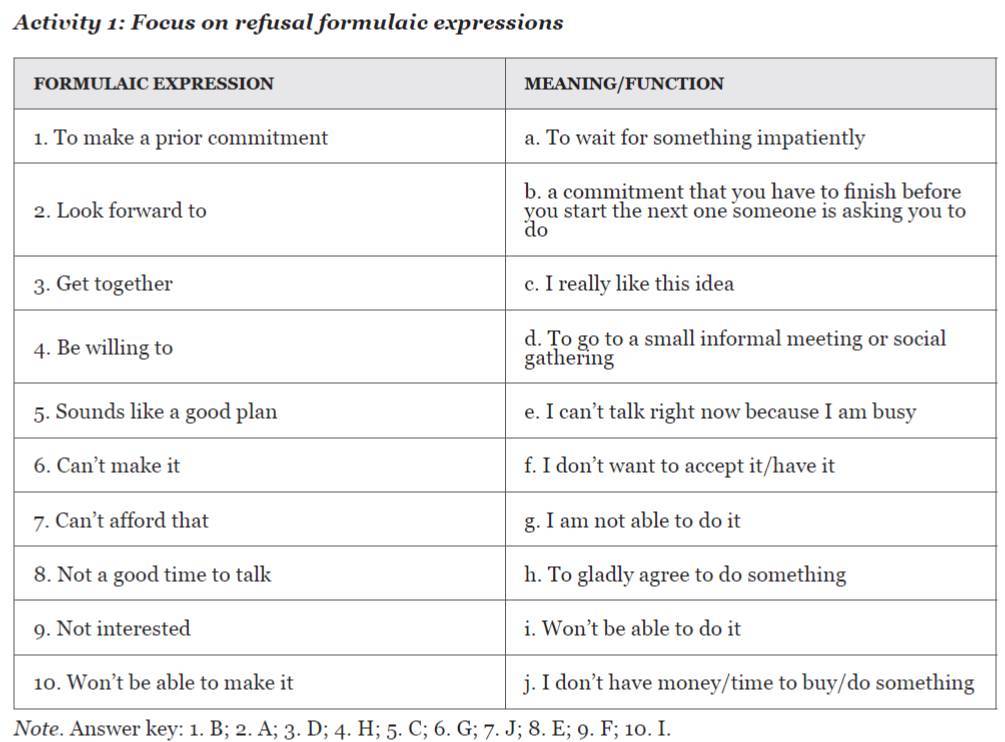
-
You know the difference between written and spoken language and can exchange them.
Example: Invite a person to a party by oral communication and by written communication. spoken and written language

-
You know the difference between formal and informal and in which situations to use them.
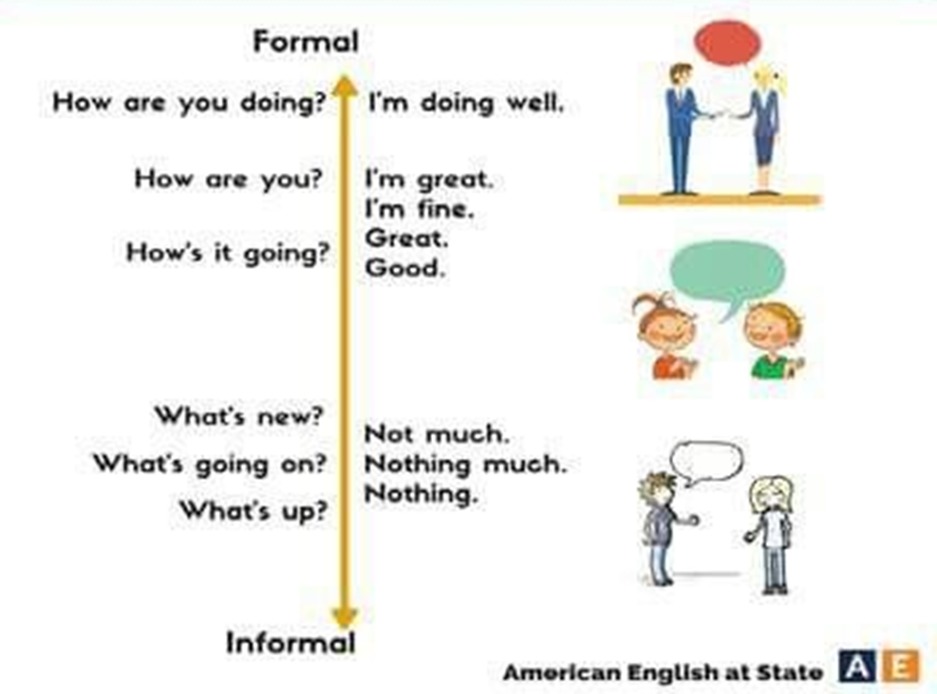 formal and informal speaking
formal and informal speaking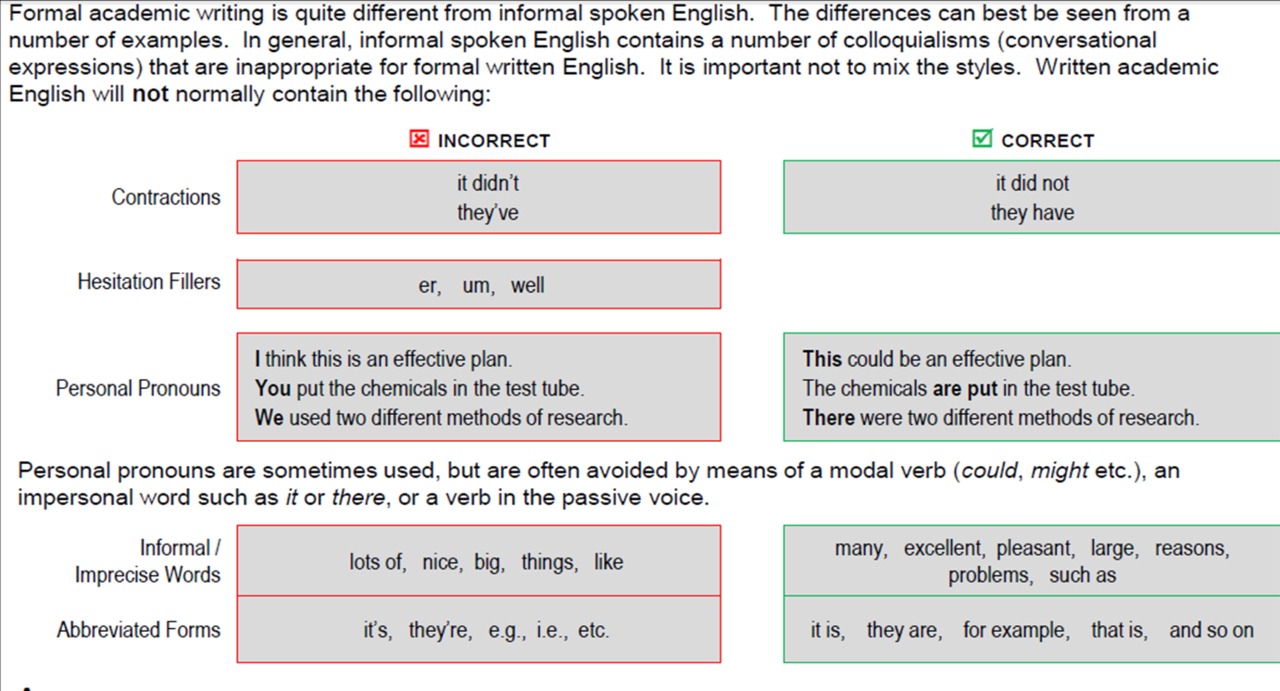
formal-and-informal-situations.pdfFormal & Informal Language.pdf
-
You are able to recognise different linguistic registers, differences between written and spoken language, and situation specific language.

Example: You can write an invitation for the same event to people form different linguistic registers.
- Text message to your friend
- Invitation email to your family/parents
- Invitation letter to the principle
- Invitation add for the newspaper
-
You can analyse different language registers, differences between written and spoken language and situation specific language.
Example: language registers
- Baby language
- Texting language
- Street language /slang
Example: You can write or direct a short play/movie in which the different linguistic registers have a role.
‘My Fair Lady’ could be used as an example in which different linguistic registers have a main role in the story.
