13. The changing climate
Contents
13.1 The temperature of planet Earth changes
The climate of planet Earth has changed a lot throughout its history. The climate has occasionally grown both warmer and colder, and these changes have been impossible to stop.
Currently, the planet's climate is warming at an unprecedented rate as a result of human activity. Our lifestyle is proving to be insustainable, as it takes an irreversible toll on the environment.
The climate of planet Earth was warm and humid during the Mesozoic era (approximately 100 million years ago).
13.2 What is climate change?
The temperature of planet Earth would be approximately 30 degrees lower without greenhouse gases in its atmosphere. If this was the case, the conditions would be too cold for sustaining life at a similar level as with greenhouse gases in our planet's atmosphere.
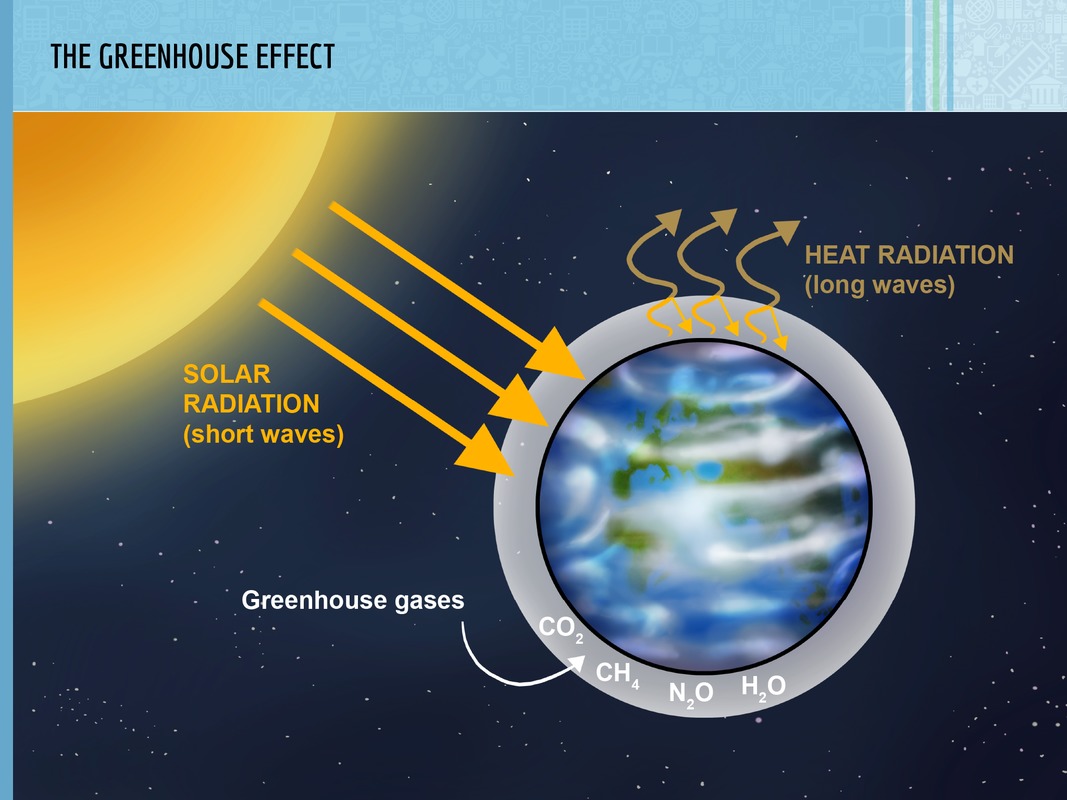
Human activity has increased the amount of greenhouse gases in our planet's atmosphere. This has resulted in an accelerated greenhouse effect. This, in turn, has resulted in global warming. The 1900s were the warmest century in a thousand years. This human-caused acceleration in the atmospheric greenhouse effect is called climate change. It has been proven by studying average temperatures all around the globe over long time frames. It is one of the defining global challenges of our time.
13.3 The effects of climate change
Climate change causes an increase in our planet's average temperature. It has been estimated that the current average temperature of planet Earth, approximately 15 degrees Celsius, will probably rise by a couple of degrees druing the next 100 years.
![]() NASA: Earth's surface temperature
NASA: Earth's surface temperature
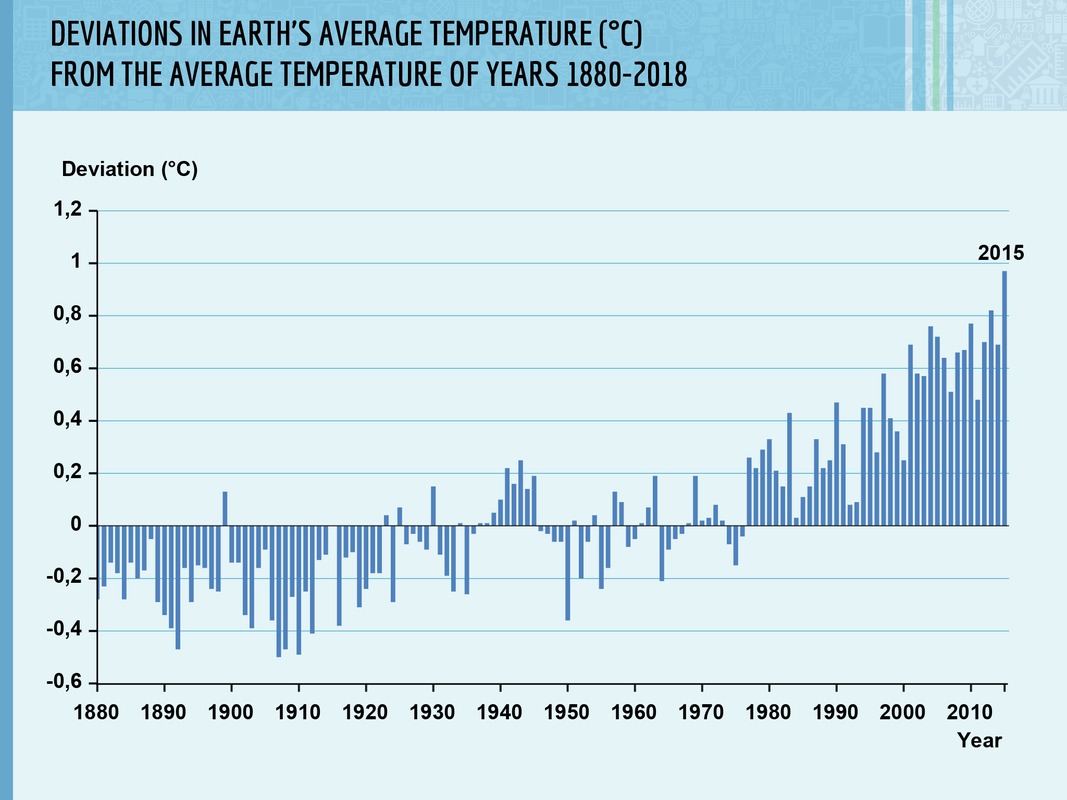
The average temperature of our planet increased by 0,74 degrees over the course of the 20th century. This increase in temperature has continued to the current century, and shows no signs of slowing down.
The temperatures will also rise in parts of the Earth that are currently in the frigid geographic zone. The average temperature of Arctic regions can increase almost twice as much as the temperature of other areas.

The polar bear is only one of the many species threatened by global warming.
Global warming causes a variety of changes in the chances of survival of animal and plant species. The most drastic changes can be seen near the Arctic Ocean, where species like the polar bear and the walrus are already threatened by shrinking habitats. If the planet's atmosphere continues to grow warmer, these species might become extinct.
Different extreme weather phenomena, such as storms, floods, droughts and forest fires, will also increase as the planet's atmosphere continues to grow warmer.
![]() Animations by NASA
Animations by NASA
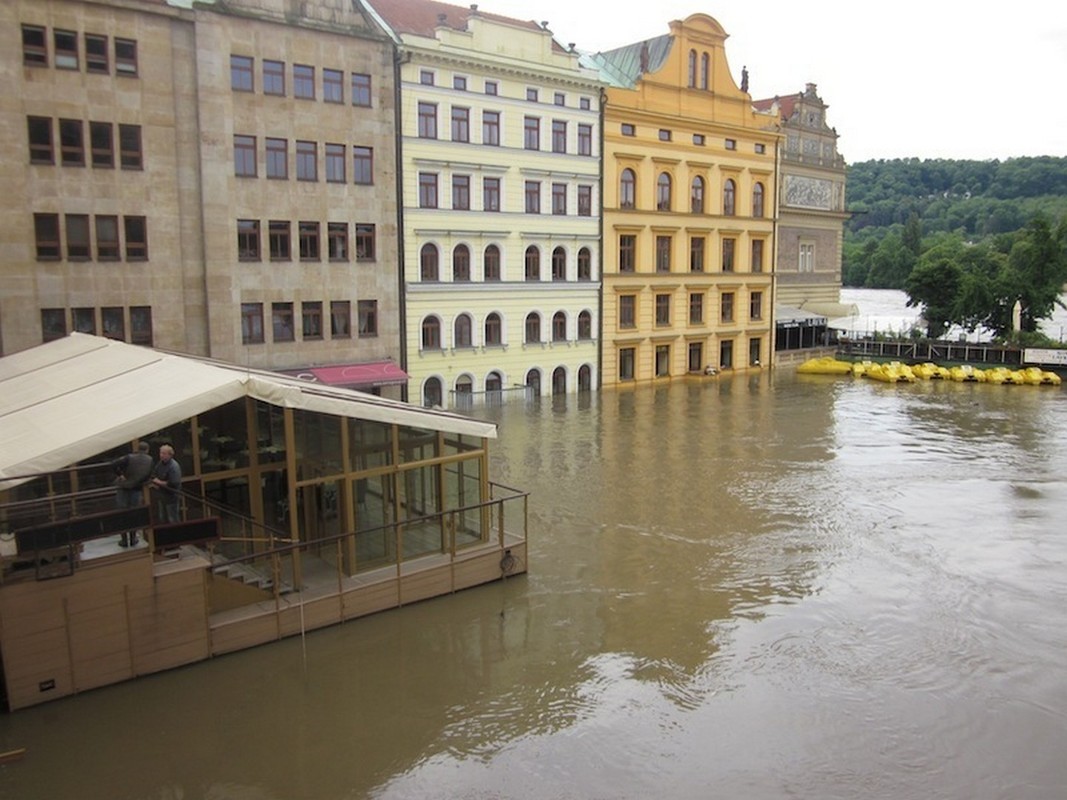

Extreme weather phenomena such as floods will increase as a result of global warming. Floods in Prague, Czech Republic during the summer of 2013.
As the Earth's oceans grow warmer as a result of climate change, the likelihood and strength of tropical storms will increase. Warmer oceans can also cause tropical storms to become more frequent even in areas where they previously were rare.
Droughts and heavy rains will also increase as a result of global warming, causing problems for farming and agriculture. Droughts also increase the risk of forest fires, which in turn release more greenhouse gases into the planet's atmosphere.
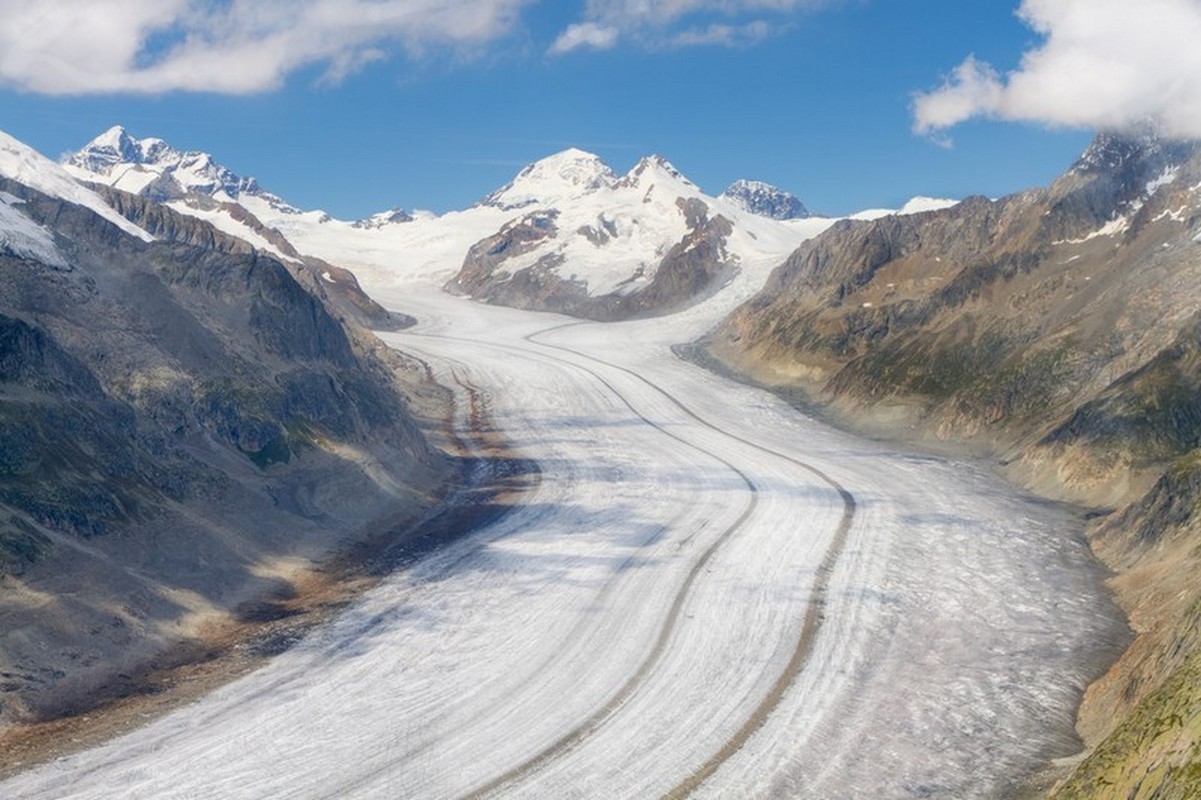

The famous Grossglockner glacier in Austria is shrinking at a rapid rate.
Mountain glaciers have already shrunk in size as a result of human-caused climate change. When the glaciers continue to melt, the planet's sea levels will slowly rise. This will cause shorelines to move further back, reducing the amount of land available for human habitation and agriculture.
13.4 Greenhouse gases
Greenhouse gases are atmospheric gases that accelerate the greenhouse effect. The most significant greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide (CO2) and methane (CH4).
The amount of greenhouse gases in the atmopshere has increased as a result of human activity. Our everyday lives generate endless amounts of greenhouse gases. They are produced in traffic, energy production and food production.
Carbon dioxide is the most significant greenhouse gas produced by humans. Carbon dioxide emissions are created when humans use fossil fuels, such as crude oil, coal or natural gas. The largest producers of carbon dioxide emissions are heavy industry, traffic, energy production and slash-and-burn forest clearing for agriculture production. Carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere by green plants, which use it during photosynthesis. Therefore, cutting down forests reduces the planet's ability to regulate the carbon dioxide condition of its atmosphere.
Methane is the second most significant greenhouse gas produced by humans. Methane is produced when carbon-based materials (such as dead plant parts) rot in anaerobic conditions. The most prominent sources of methane emissions are landfills, livestock farming and sewage treatment. The amount of methane emitted from landfills will continue to increase drastically if the production of unrecycable waste is not slowed down.

Rice fields emit methane into the atmosphere.
13.5 How to combat climate change?
As inhabitants of planet Earth, it is our collective duty to slow down climate change. We can all contribute to this goal by choosing more climate-friendly lifestyles and by making sustainable choices.
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is the most effective way to control climate change. Greenhouse gas emissions can be reduced by reducing consumption, using renewable sources of energy, increasing the amount of carbon sink forests and by developing environmentally sustainable technologies.Decreasing the amount of energy required by industry, traffic, housing and food production is an important way of slowing down climate change. These goals can be achieved by a combination of more efficient technologies and more environmentally sustainable living habits.

Renewable energy sources, such as wind power, help to slow down climate change.
Stopping climate change is impossible, as many human-produced greenhouse gases remain in the atmosphere for a long time after they are emitted. However, climate change can be slowed down with global cooperation. However, as climate change can neverbe stopped completely, it is also necessary for us to adapt to changing scenarios.
 Regular people can help to combat climate change in a variety of ways.
Regular people can help to combat climate change in a variety of ways.
The effects of climate change have been visible for a relatively long time, but concentrated efforts to reduce global emissions have only began in the 21st century. Different international agreements are the most powerful way to decrease greenhouse gas emissions and slow down global warming.

Using public transportation is more energy-efficient than driving a car.
Summary
 Life on Earth is based on a greenhouse effect, which prevents heat radiation from escaping into space.
Life on Earth is based on a greenhouse effect, which prevents heat radiation from escaping into space.- Human activity accelerates the greenhouse effect and causes climate change by increasing the amount of greenhouse gases in the planet's atmosphere.
- The most important human-produced greenhouse gases are carbon dioxide and methane.
- Climate change affects all parts of the planet. The glaciers will melt, extreme climate phenomena will increase, and local climates will experience drastic changes.
- Climate change also affects living organisms and threatens some species with extinctions.
- Reducing greenhouse gas emissions is the most effective way to control climate change. Greenhouse gas emissions can be reduced by reducing consumption, using renewable sources of energy, increasing the amount of carbon sink forests, and by developing environmentally sustainable technologies.