13.2 What is climate change?
Life on Earth relies on a moderate greenhouse effect in the planet's atmosphere. Atmospheric greenhouse gases, such as water vapor and carbon dioxide, prevent solar heat radiation from escaping into space from the Earth's atmosphere. As a result, the planet's lower atmosphere stays warm. In other words, greenhouse gases reflect some of the solar heat radiation back to the surface of the Earth.
The temperature of planet Earth would be approximately 30 degrees lower without greenhouse gases in its atmosphere. If this was the case, the conditions would be too cold for sustaining life at a similar level as with greenhouse gases in our planet's atmosphere.
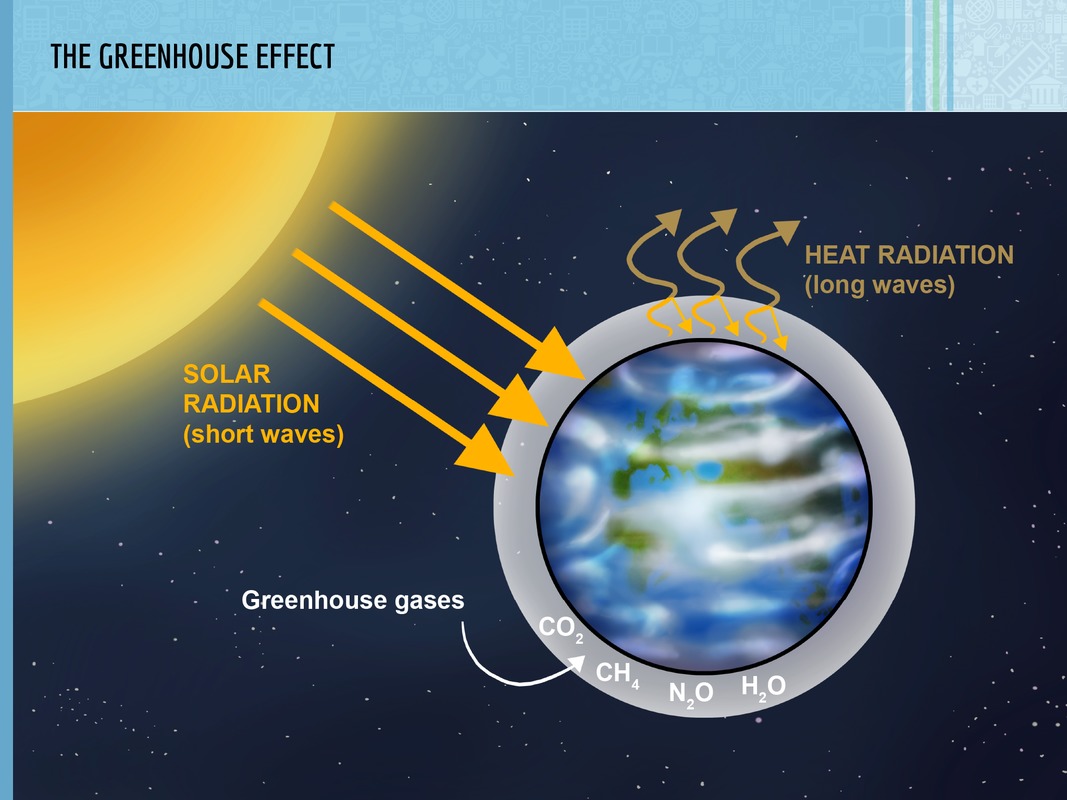
Human activity has increased the amount of greenhouse gases in our planet's atmosphere. This has resulted in an accelerated greenhouse effect. This, in turn, has resulted in global warming. The 1900s were the warmest century in a thousand years. This human-caused acceleration in the atmospheric greenhouse effect is called climate change. It has been proven by studying average temperatures all around the globe over long time frames. It is one of the defining global challenges of our time.
The temperature of planet Earth would be approximately 30 degrees lower without greenhouse gases in its atmosphere. If this was the case, the conditions would be too cold for sustaining life at a similar level as with greenhouse gases in our planet's atmosphere.

Human activity has increased the amount of greenhouse gases in our planet's atmosphere. This has resulted in an accelerated greenhouse effect. This, in turn, has resulted in global warming. The 1900s were the warmest century in a thousand years. This human-caused acceleration in the atmospheric greenhouse effect is called climate change. It has been proven by studying average temperatures all around the globe over long time frames. It is one of the defining global challenges of our time.