14. Africa
Contents
14.1 The African continent
14.2 The map of Africa
14.3 Gallery: Different parts of Africa
14.4 African vegetation zones
14.5 Plants of the rainforest
14.6 Animals of the rainforest
14.7 Gallery: Rainforests
14.8 Animals of the savanna
14.9 Gallery: Birds of the savanna
14.10 Gallery: Bammals of the savanna
14.11 Desert
14.2 The map of Africa
14.3 Gallery: Different parts of Africa
14.4 African vegetation zones
14.5 Plants of the rainforest
14.6 Animals of the rainforest
14.7 Gallery: Rainforests
14.8 Animals of the savanna
14.9 Gallery: Birds of the savanna
14.10 Gallery: Bammals of the savanna
14.11 Desert
14.1 The African continent
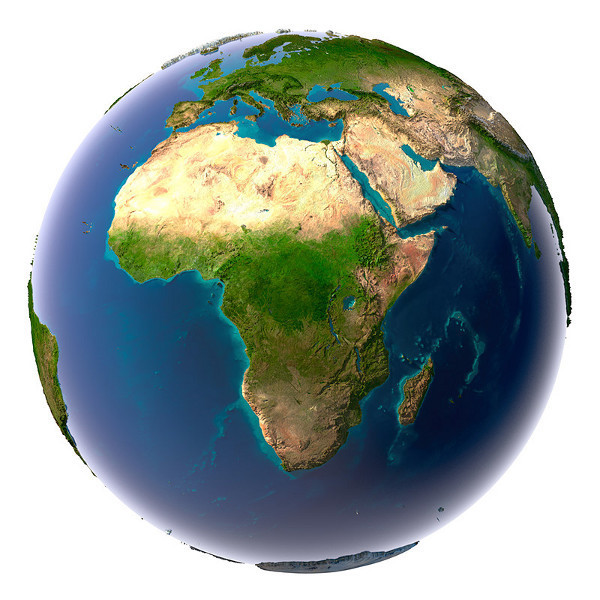
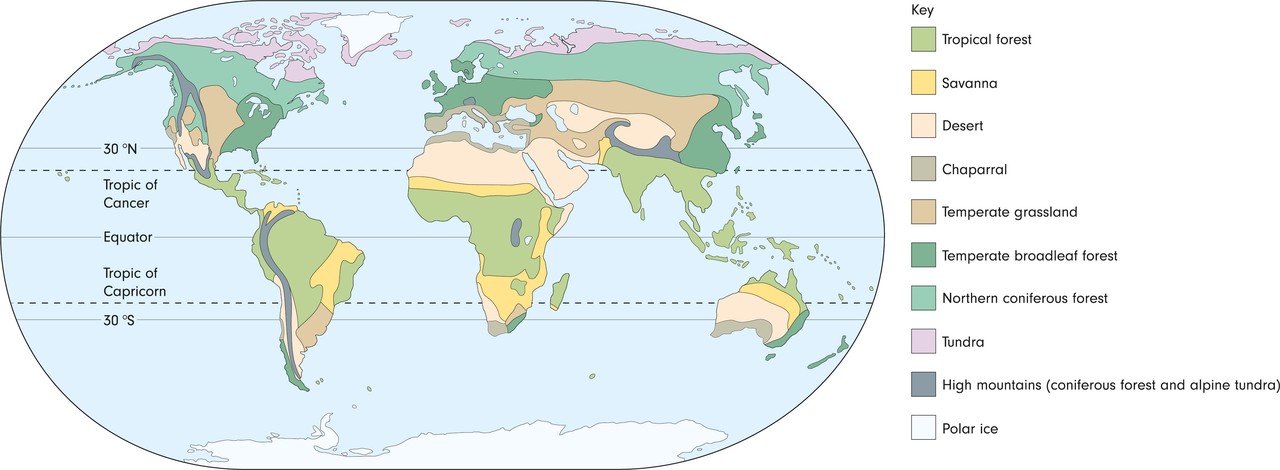
When looking at planet Earth from space, the African rainforest can be seen as vast regions of deep green. Rainforests are a lush vegetation type found in the tropical zone. Rainforests require plenty of warmth and precipitiation in order to thrive.
The African rainforest regions are surrounded by areas that are colored in a lighter shade of green. They consist of savanna. Savanna is a type of tropical grassland vegetation. Many large mammal species, such as lions and elephants, live on the savanna.
Deserts can be distinguished as vast regions of light brown. The northern parts of the African continent are covered by the vast Sahara desert. The conditions in the desert are so dry that almost no plants can thrive there.
The water near the African shoreline has a greenish shade. This color tells us that a lot of algae grow in the shallow shore waters. This is important for people living on the shores of the African continent, as fish eat algae. As a result, these shore regions are important fishing areas for many African nations.
14.2 The map of Africa
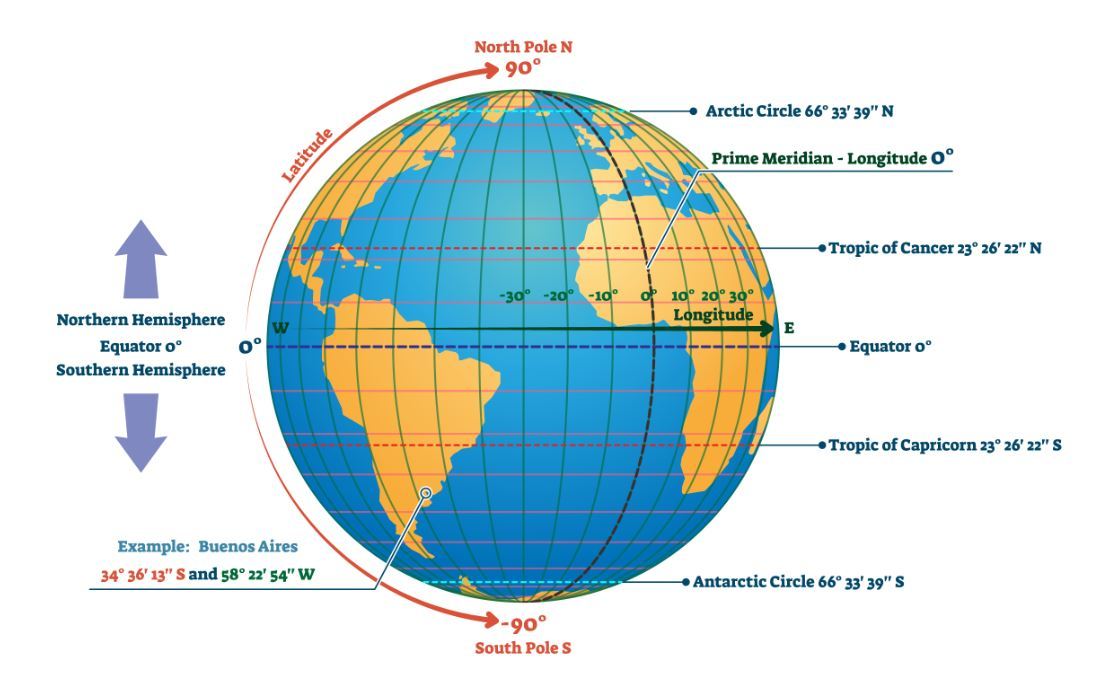
Africa is a long continent. In total, it covers an area of approximately eight thousand kilometers north and south of the equator.
The equator runs through the middle of the African continent. The Tropic of Cancer crosses through North Africa, whereas the Tropic of Capricorn runs through the southern part of the continent.
Africa is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea in the north, the Atlantic Ocean in the west, and the Indian Ocean in the east.
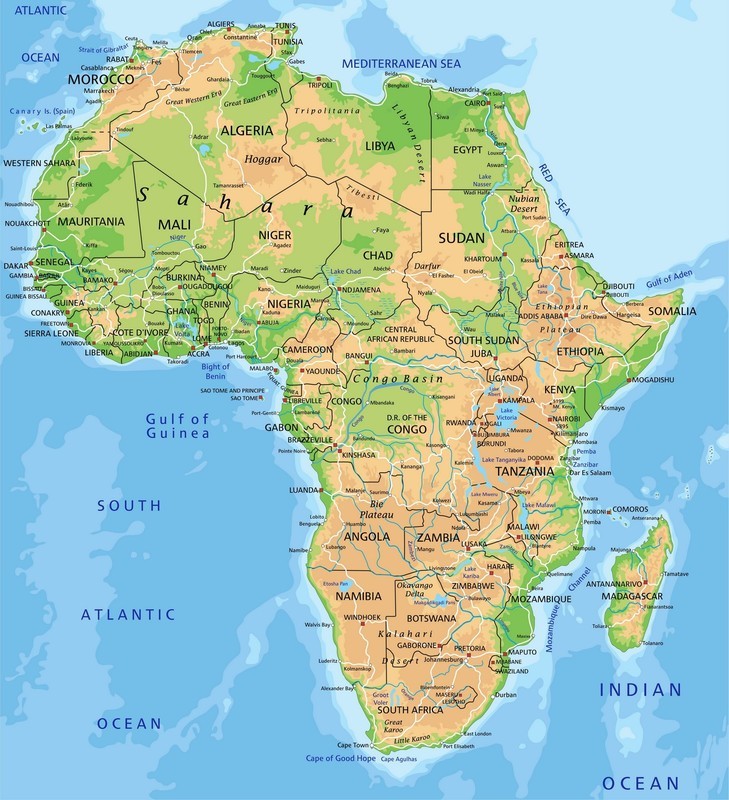 Africa consists mostly of highland regions, but it has no great mountain ranges. Lowland areas are found near the equator. The African rainforests are mostly concentrated to these lowland areas.
Africa consists mostly of highland regions, but it has no great mountain ranges. Lowland areas are found near the equator. The African rainforests are mostly concentrated to these lowland areas.
Africa does not have a great number of large lakes. The largest African lake is Lake Victoria, which is located on the border between Tansania and Kenya. However, the continent does have a large number of rivers. The most significant African rivers are the Nile and the Congo.
 Seterra
Seterra
The equator runs through the middle of the African continent. The Tropic of Cancer crosses through North Africa, whereas the Tropic of Capricorn runs through the southern part of the continent.

Africa is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea in the north, the Atlantic Ocean in the west, and the Indian Ocean in the east.
 Africa consists mostly of highland regions, but it has no great mountain ranges. Lowland areas are found near the equator. The African rainforests are mostly concentrated to these lowland areas.
Africa consists mostly of highland regions, but it has no great mountain ranges. Lowland areas are found near the equator. The African rainforests are mostly concentrated to these lowland areas. Africa does not have a great number of large lakes. The largest African lake is Lake Victoria, which is located on the border between Tansania and Kenya. However, the continent does have a large number of rivers. The most significant African rivers are the Nile and the Congo.
There are almost 50 independent nations in Africa. Their borders are mostly carried over from the period of European colonial rule. During the 19th and 20th centuries many European nations used African regions as colonies. The purpose of these colonies was to produce raw materials for the European economies. The borders that were drawn during this era are, for the most part, still in place today.
The largest African nations in terms of their surface area are Algeria, DR Congo and South Africa.
You can practice the names, locations, flags and capitals of the African nations on Seterra.The largest African nations in terms of their surface area are Algeria, DR Congo and South Africa.
14.3 Gallery: Different parts of Africa
14.4 African vegetation zones
14.5 Plants of the rainforest
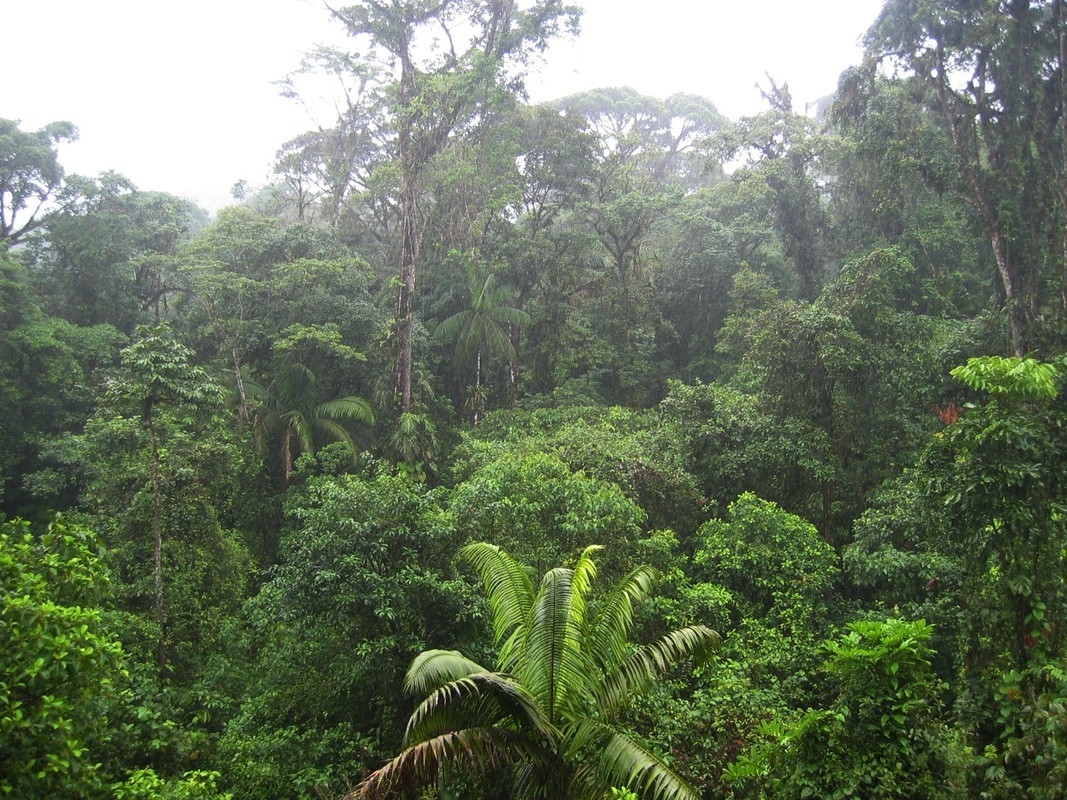
The African rainforests are found near the equator. These tropical rainforests are in a state of eternal summer. The monthly average temperature varies only a little through amount the year, staying between 25–27 degrees Celsius.
The vegetation of the tropical rainforests rises in thick layers. The trees often reach the height of tens of meters as they compete for sunlight. The plant life of the tropical rainforests is extraordinarily diverse. Over 50 percent of the world's known species of flora and fauna live in the tropical rainforests. Most of the animal life of the tropical rainforests is concentrated in treetops.
Many epiphytic plants, such as vine-like lianas and beautiful orchids, grow on the trunks of rainforest trees. The bottom of the rainforest rarely experiences sunlight, and as a result the vegetation there is quite scarce.
The vegetation of the tropical rainforests rises in thick layers. The trees often reach the height of tens of meters as they compete for sunlight. The plant life of the tropical rainforests is extraordinarily diverse. Over 50 percent of the world's known species of flora and fauna live in the tropical rainforests. Most of the animal life of the tropical rainforests is concentrated in treetops.
Many epiphytic plants, such as vine-like lianas and beautiful orchids, grow on the trunks of rainforest trees. The bottom of the rainforest rarely experiences sunlight, and as a result the vegetation there is quite scarce.
14.6 Animals of the rainforest
Because rainforest foliage is concentrated in the treetops, the animal life of the rainforests is also concentrated in the trees. There, you can find apes, snakes, and hundreds of bird species. The best-known African ape species are chimpanzee and gorilla.
Only a few large animals roam the lower areas of the rainforest. One of these is the leopard (pictured). Rainforests also contain a large number of insects. The larvae of these insects feed on tree leaves, and the insects themselves are the food of other insects and birds. If a leaf or a dead animal falls down on the ground, it is decomposed quickly by the small organisms living in the rainforest floor. As a result, it is rare to find dead leaves in the rainforest.
Rainforest rivers are also full of life. They are inhabited by species such as giant snakes and crocodiles.
Only a few large animals roam the lower areas of the rainforest. One of these is the leopard (pictured). Rainforests also contain a large number of insects. The larvae of these insects feed on tree leaves, and the insects themselves are the food of other insects and birds. If a leaf or a dead animal falls down on the ground, it is decomposed quickly by the small organisms living in the rainforest floor. As a result, it is rare to find dead leaves in the rainforest.
Rainforest rivers are also full of life. They are inhabited by species such as giant snakes and crocodiles.
14.7 Gallery: Rainforests
14.8 Plants and animals of the savanna
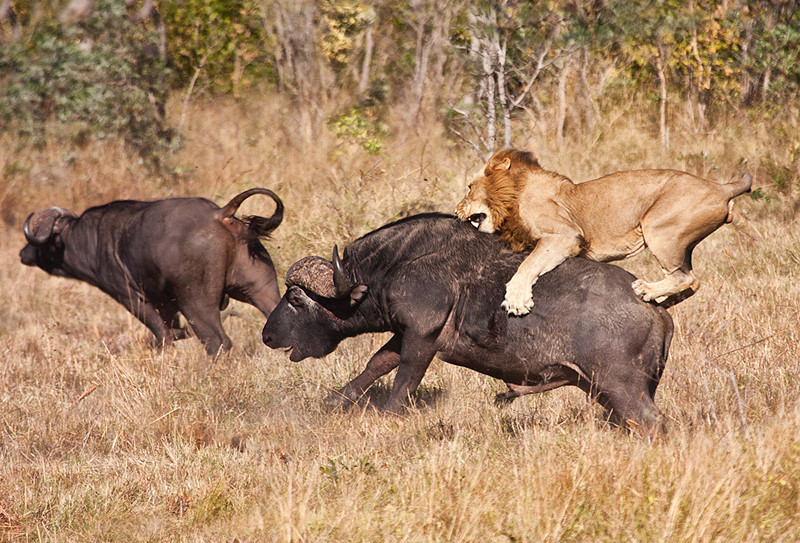 Savanna is a type of open grassland vegetation. Savannas can be found in the African tropical zone. They have formed in regions that experience both a rainy season and a dry season.
Savanna is a type of open grassland vegetation. Savannas can be found in the African tropical zone. They have formed in regions that experience both a rainy season and a dry season. The vegetation of the savanna consists of grasses, shrubs and trees. The long dry season is difficult for the flora of the savanna. During the dry season, the grass dries out and the trees and shrubs drop their foliage. The landscape becomes brown. Finally, as the dry season gives way to the rainy season, large thunderstorms bring large amounts of rainfall to the savanna. As a result of this, the landscape becomes green once again.
Savannas are suited for cattle farming. A number of nature reservations have been established in some savannas, for example in Kenya. In these reservations, hunting animals and raising cattle is prohibited. The reservations attract numerous tourists every year – who wouldn't want to see a lion or an elephant in the wild?
The grassland of the savanna accommodates a large variety of different animals. The largest herbivores include the buffalo, the giraffe and the rhinoceros. Savanna herbivores are very selective as to what kinds of grasses they eat. Different species eat different grasses, which means that there is no competition between them. The herbivores of the savanna provide food for the savanna's predators, the most well-known of which is the lion.
14.9 Gallery: Birds of the savanna
14.10 Gallery: Mammals of the savanna
14.11 Desert
The vast Sahara desert is located in North Africa. Due to the constant high air pressure in the area, the region receives only very little rainfall. However, this has not always been the case: during the time when the pyramids were built, the Sahara region received more rainfall than it does today. Water can also be found in the desert in the form of oases, which have formed as a result of underground water concentrations.
When looking at a satellite image of the Sahara desert, the importance of the river Nile becomes clear. The green color in the satellite image tells us that agriculture and plant life is concentrated along the shores of the river. The mouth of the river has accumulated loose soil. The water has carried this loose soil from upriver areas, finally forming a triangular delta near the river's mouth. The fertile soil of the delta is suitable for agriculture. The food grown in the Nile delta feeds millions of Egyptians.
Satellite image of the Egyptian desert.
When looking at a satellite image of the Sahara desert, the importance of the river Nile becomes clear. The green color in the satellite image tells us that agriculture and plant life is concentrated along the shores of the river. The mouth of the river has accumulated loose soil. The water has carried this loose soil from upriver areas, finally forming a triangular delta near the river's mouth. The fertile soil of the delta is suitable for agriculture. The food grown in the Nile delta feeds millions of Egyptians.
Satellite image of the Egyptian desert.