9. The world needs energy
Contents
9.1 Energy
 Nothing happens without energy. When you sit in the classroom, you need light energy. The computer or tablet you are using to read this book needs electric energy to work. Heat energy is needed to keep the classroom warm. You have arrived in the classroom by using kinetic energy. All the things you see around you are produced by using different kinds of energy.
Nothing happens without energy. When you sit in the classroom, you need light energy. The computer or tablet you are using to read this book needs electric energy to work. Heat energy is needed to keep the classroom warm. You have arrived in the classroom by using kinetic energy. All the things you see around you are produced by using different kinds of energy.
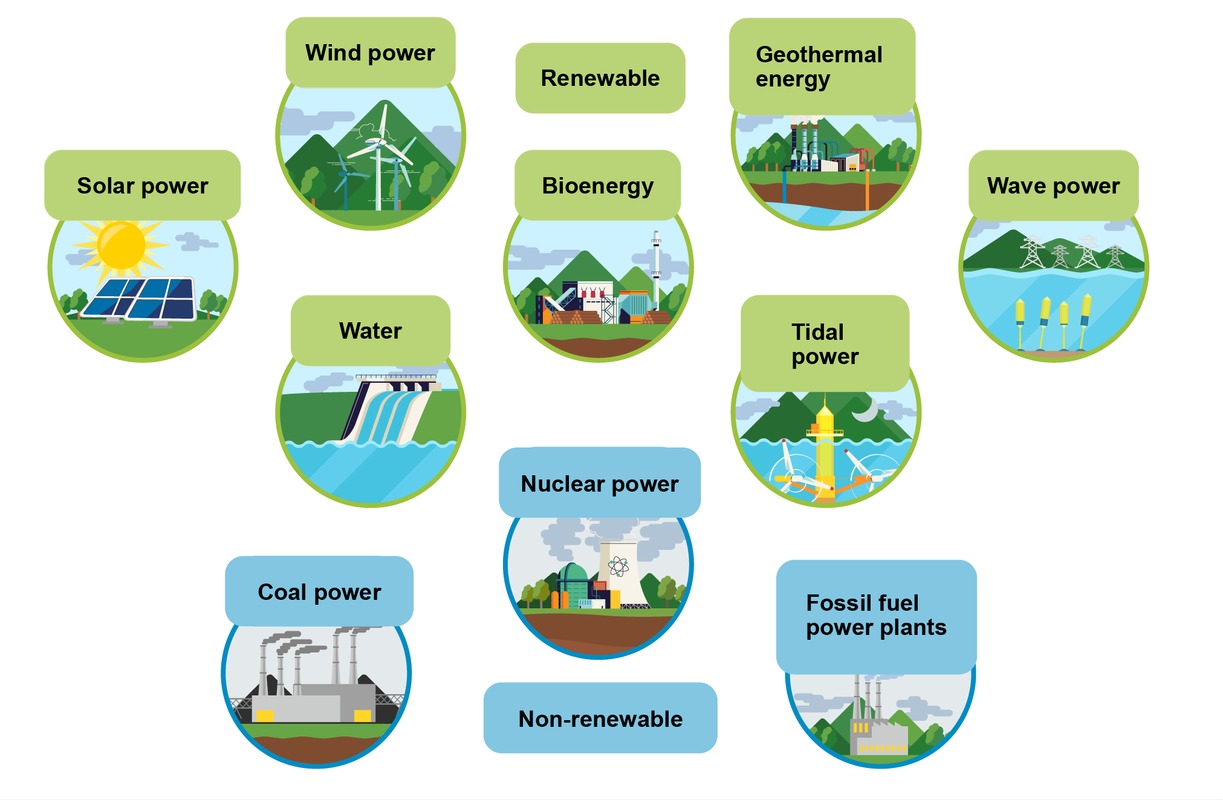
Energy sources can be either renewable or non-renewable. Renewable energy sources include water, wind, sunlight, and wood. They are share one common quality: the energy that is consumed when these energy sources are used will replenish. For example, new trees will grow as old trees are cut down and the sun radiates solar energy constantly.
Non-renewable energy sources include nuclear power and fossil fuels such as oil, coal, and natural gas. These energy sources are diminished as they are used. In addition to the limited supplies of these resources, non-renewable energy sources are also linked to significant environmental problems.

The picture contrasts different forms of non-renewable energy sources (on the left) with renewable energy sources (on the right). What kinds of energy sources can you identify from the picture?
9.2 Fossil fuels
| Source | Percentage of the planet's total energy production |
|---|---|
| Oil | 34 % (fossil fuel, largest producers: USA and Saudi Arabia) |
| Natural gas | 24 % (fossil fuel, USA, EU, and China) |
| Coal | 27 % (fossil fuel, e.g. USA, China) |
| Nuclear power | 4 % (e.g. USA, France, and China) |
| Water power | 7 % (e.g. China, Canada, Norway) |
| Other | 4 % (solar energy, wind power, etc.) (Source: Wikipedia) |
Like their name suggests, fossil fuels were formed when the remains of ancient organisms decomposed in anaerobic conditions under layers of other materials. The formation of fossil fuels has occurred over a long period of time. Because of this, fossil fuels are considered practically non-renewable.
Oil, natural gas and recently popularized shale gas have formed from the remains of ancient marine organisms. Some concentrations of these resources are still located in the ocean floor, while some have remained inside bedrock as a result of plate tectonics. Oil and natural gas are extracted by drilling into oil or gas pockets that are buried deep underground. Shale gas is extracted from rocks that contain organic substances with the help of pressurized water.
Oil is the most important energy source in the world. Approximately one third (33 %) of the total energy consumed on the planet is produced with oil. Crude oil contains a number of different hydrocarbons, and it can be refined into various kinds of fuels, lubricants, plastics and bitumen. In addition to its versatility, it is also easy to transport and store. Oil is especially important fuel in traffic and transportation. In contrast, natural gas covers approximately one quarter (24 %) of Earth's total energy consumption.

Crude oil is obtained through deepwater drilling, which is mostly concentrated in the Arctic Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico.
Coal has formed as the thick peat layers of ancient fern forests have decomposed in anaerobic conditions. It is a solid fuel that is mined from bedrock. Coal is a lasting, cheap and easy energy source. It is used especially in heavy industry and the production of electricity.

Coal is a fossil fuel.

The use of fossil fuels accelerates global warming. Because of this, efforts have been made to reduce the use of oil, coal, and natural gas.
9.3 Nuclear power
Nuclear power produces energy by splitting the cores of uranium atoms in a process known as fission. This process releases heat that is used to warm up a tank of water. As the water in the tank warms up, it releases water vapor, which rotates a turbine that converts the movement into electricity. Although the process itself is relatively simple, the radioactivity of the fuel used and the harmful isotopes produced during the process create technical challenges for nuclear power plants.

Nuclear power plant in Loviisa, Finland.
Nuclear power has many advantages. The production of nuclear energy is both efficient and stable, which means that it not reliable on external processes such as weather. As a result, the price of nuclear energy is always the same. Unlike fossil fuels, nuclear energy does not release combustion gases like carbon dioxide. This is one reason why nuclear power is often championed as the answer to stopping climate change.
However, nuclear power also has its disadvantages. First, uranium is a relatively rare element in bedrock. Second, uranium is also a radioactive element. This means that uranium atoms have a tendency to break off by themselves, which can release harmful radiation into the environment. Nuclear power also has a risk of nuclear accidents, which can be devastating for the areas near nuclear power plants.

Radiation remains strong near the Chernobyl nuclear power plant well after the accident that occured there in 1986.
9.4 Gallery: Non-renewable energy sources
9.5 Renewable energy sources
 Because the supplies of fossil fuels is limited, and because their use accelerates climate change, the methods of global energy production need to change.
Because the supplies of fossil fuels is limited, and because their use accelerates climate change, the methods of global energy production need to change.
One way to make energy production more sustainable is to base it on the use of renewable energy sources. These energy sources replenish themselves when they are used, which means that they never run out.
Most forms of renewable energy gain their energy from radiation from the Sun. This radiation can be directly transformed into electricity or used in heating water for service use. The use of solar radiation in energy production is called solar energy. Only one percent of global energy production is currently based on solar energy, but it is the most rapidly increasing form of energy production in the world.
In wind power, electricity is produced with generators. These generators are rotated by the wind, which itself occurs as a result of solar radiation.
| Year | Wind power (mostly electricity production) |
Solar energy (electricity production, heating, warming up water for service use, etc.) |
|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 31 TWh or terawatt hour | 1 TWh or terawatthour |
| 2005 | 105 TWh | 4 TWh |
| 2010 | 340 TWh | 31 TWh |
| 2018 | 840 TWh | 443 TWh |
In water power or hydropower, running water is directed to move through electricity-generating turbines. This process is also based on solar radiation: this is the case, because rivers are formed when the Sun causes water to evaporate to the atmosphere and to rain back down to the surface of the Earth. Water power is currently the most significant renewable energy source in the world. Approximately 7 % of the planet's total energy consumption is covered by water power.
In bioenergy, heat or electricity is produced by burning plant-, animal-, or microbe-based materials. Burning wood in a fireplace is a well-known example of bioenergy. Biogenic materials or biomass can nowadays be refined into other forms, as well. It can be used to produce liquid fuels and biogas, for example.
Geothermal heat and other similar forms of energy are also based on energy that has originally come from the Sun. In these methods, heat from water or air is used to produce thermal or heat energy. Geothermal energy, on the other hand, uses the heat contained inside the planet. Geothermal energy has traditionally been used especially in volcanic areas, such as Iceland, but its popularity is steadily growing in other regions, as well.
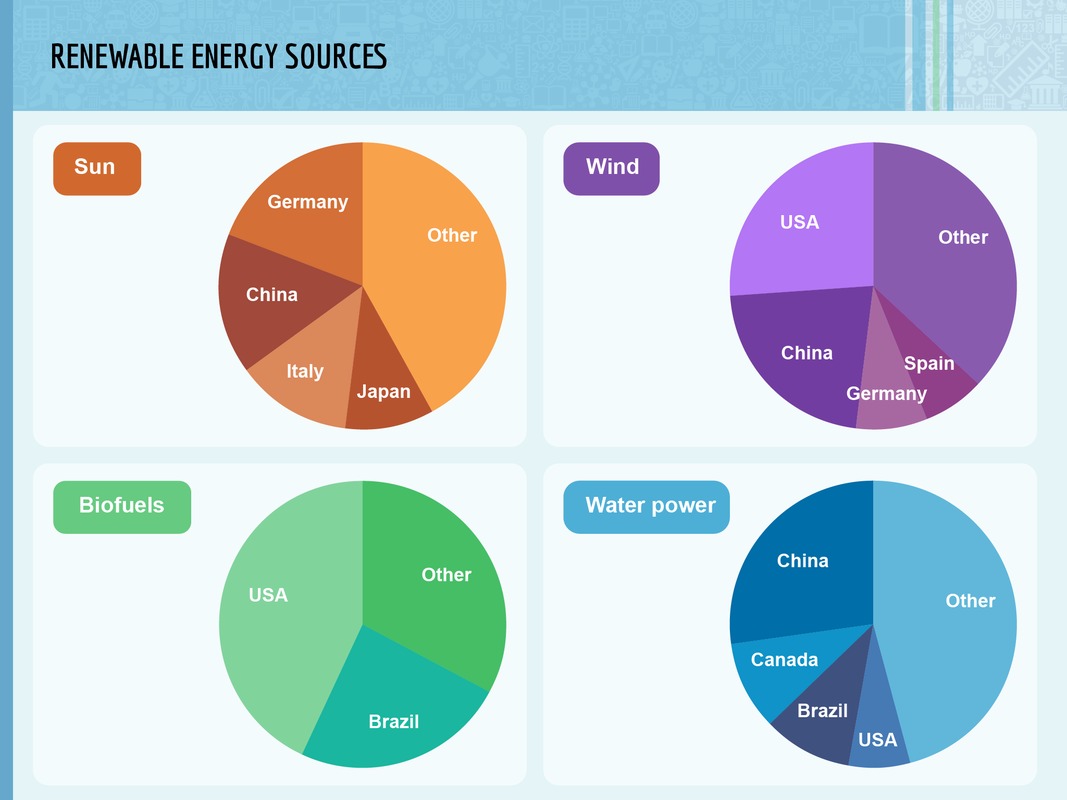
The most important producers of renewable energy sources.
9.6 Gallery: Renewable energy sources
Summary
- Energy can take the form of electricity, heat, movement or radiation.
- Energy sources can be divided into renewable and non-renewable.
- Most of the planet's energy is produced with fossil fuels.
- Fossil fuels include oil, coal, natural gas, and shale gas.
- Fossil fuels cause climate change.
- Nuclear power is an effective energy source, but it also has its risks.
- Renewable energy sources include solar energy, wind power, water power, bioenergy, geothermal energy and geothermal heat.
- The largest energy consumers in the world include China and the United States.
- The largest energy producers in the world include the United States, Russia, Saudi Arabia and China.
- Key words: renewable energy sources, non-renewable energy sources, fossil fuels, climate change, oil, coal, natural gas, shale gas, nuclear power, water power, solar energy, wind power, bioenergy, geothermal heat, geothermal energy.








