16. America
Contents
16.1 The American continents
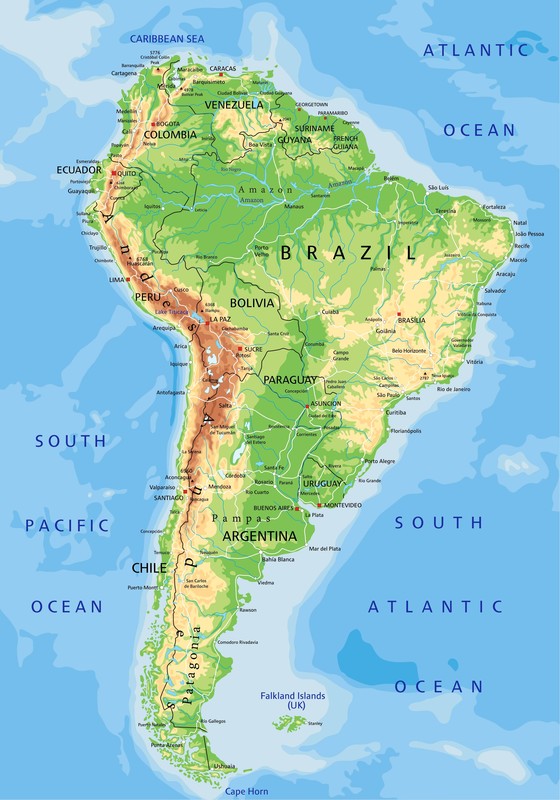
 North America and South America are separate continents. Together, they form an unified landmass known as the Americas. The most significant nations of the Americas include Canada, the United States, and Brazil. The first two are located in North America, whereas the latter is located in South America.
North America and South America are separate continents. Together, they form an unified landmass known as the Americas. The most significant nations of the Americas include Canada, the United States, and Brazil. The first two are located in North America, whereas the latter is located in South America.
Native Americans are the original inhabitants of the Americas. Their ancestors migrated to the two continents from Asia via the Bering Strait thousands of years ago. Native American tribes settled both of the two continents. Most of these tribes gained their livelihoods from fishing, hunting, gathering and agriculture. The Aztecs, Incas and Incas of South America built advanced civilizations that lasted until the 16th century, when they collapsed as a result of the arrival of European settlers and colonists.
Europeans, Africans and Asians have migrated to the Americas over the course of the last few centuries. This has resulted in the formation of the cultural regions of primarily English-speaking Anglo-America in North America and Spanish-speaking Latin America in Central and South America. The modern populations of American nations are also affected by the history of the slave trade in the 17th century. During this time, approximately half a million African slaves were brought by the European colonists to work in the fields and farms of the Americas. The descendants of these slaves comprise the basis for the modern Afro-American population.
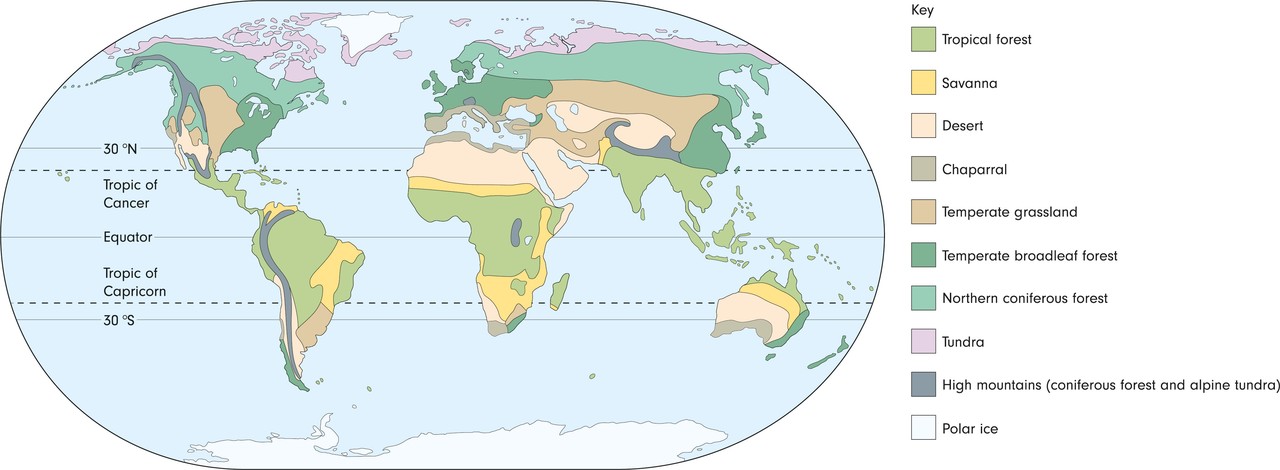
16.2 American vegetation zones
- The Americas encompass a large surface area from the shores of the Arctic Ocean in the north and nearing the continent of Antarctica in the south.
- The Americas have regions of varied elevation. These include lowlands, highlands and mountain ranges. The mountain range of the American Cordilleras (which is comprised of the North American Rockies and the South American Andes) has an especially significant effect on the climatic conditions found on the two continents.
- Tundra (grasses, mosses, lichens).
- Coniferous forest.
- Temperate grassland and broadleaf forest.
- Rainforest.
16.3 United States
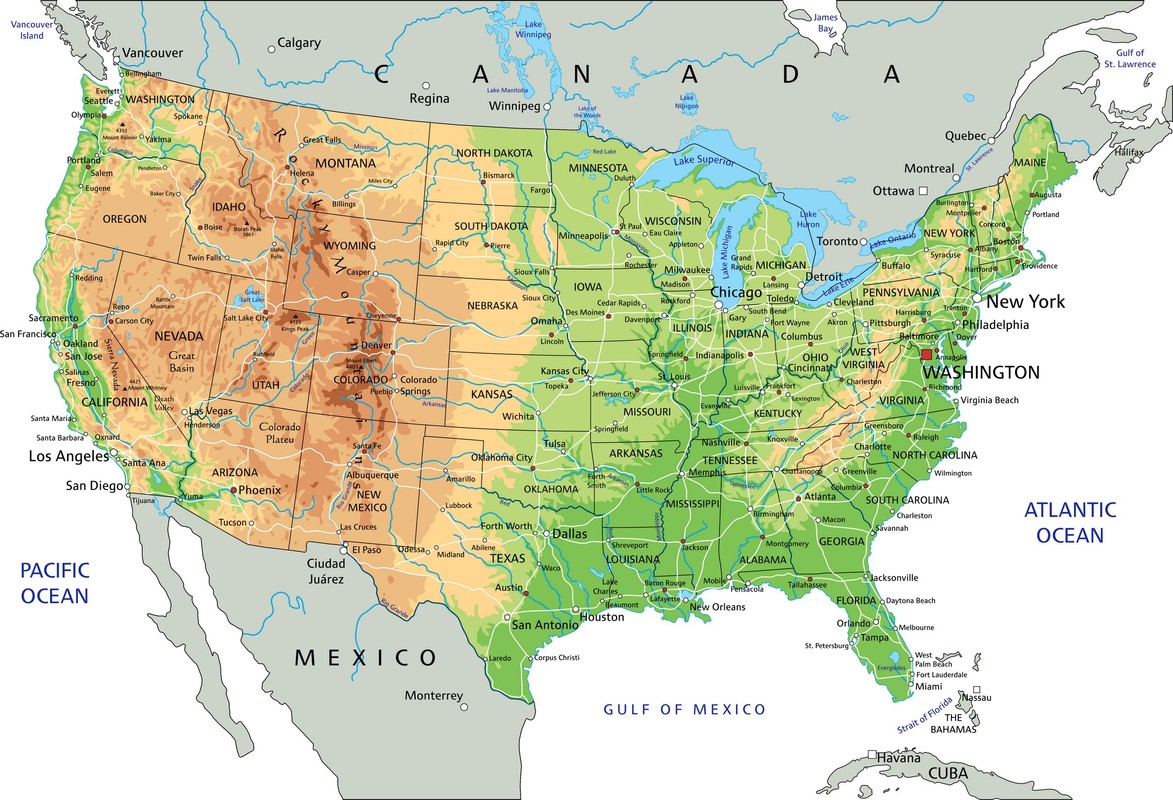
A map of the United States.
The United States is a federal republic that consists of different states. Its flag consists of 50 stars and thireen stripes, seven of which are red and six of which are white. The stars on the American flag represent the 50 modern states, whereas the stripes represent the orginal number of states and colonies.
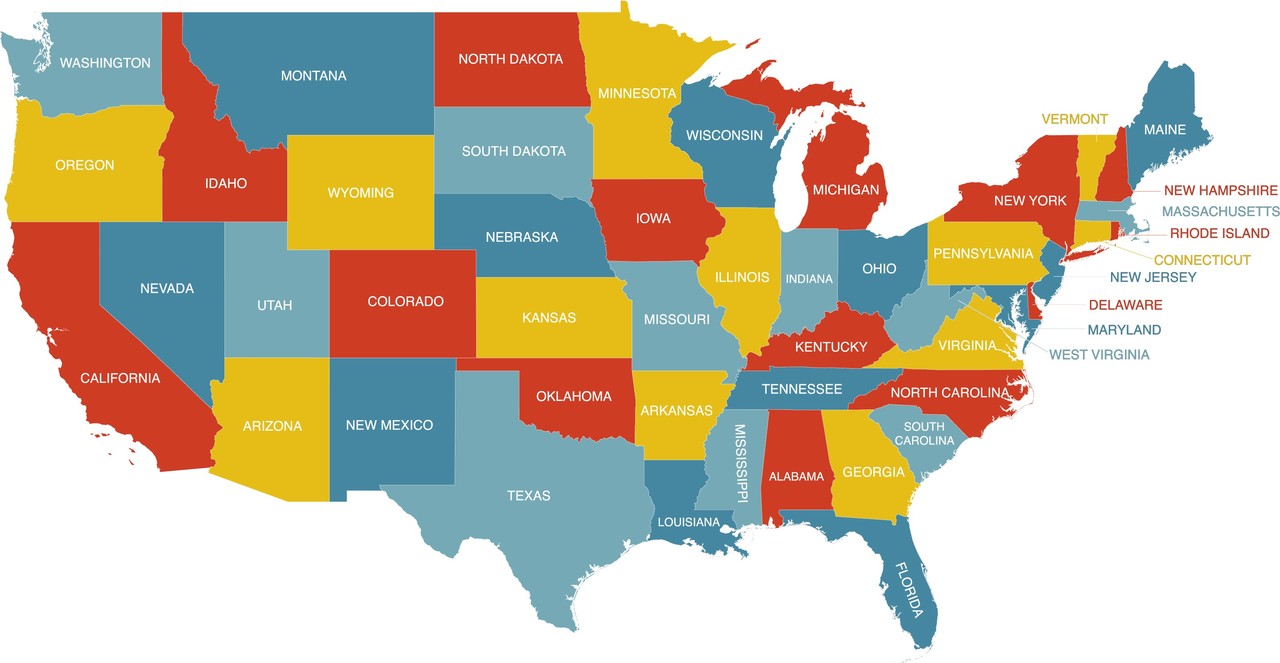
States. The states of Alaska and Hawaii are left outside the map.
Each state has its own legislation and government that is concentrated in the state capitals. The states are lead by governors. State legislations can often differ from each other significantly.
Washington D.C. is the capital of the United States. It is not part of any state. Instead, it is its own autonomous district. The official residence of the nation's president, the White House, is also located in Washington. The office of the President of the United States is one of the most influential in the world.

The President of the United States between the years 2017–2020 is the ex-businessman Donald Trump.
The bountiful natural resources of North America and the skilled workforce that has accumulated in the nation as a result of centuries of immigration have traditionally formed the basis of the United States' economy. The large supplies of energy and raw materials have made American industry globally significant, whereas the different climatic conditions in various parts of the nation have contributed to the development of large-scale agriculture, forestry and tourism.
16.4 Canada
Canada is a federal republic and a part of the Commonwealth of Nations. It is comprised of ten provinces and two Northern Territories.

A Canadian flag flying in the Rocky Mountains.
The provinces have large degrees of autonomy, whereas the territories are ruled exclusively by the federal government. Native Americans comprise only one percent of the nation's population.
Canada is known for its cultural diversity. This diversity can be seen in the nation's largest city, Toronto, the population of which is 40 % immigrants. Toronto has often been voted as the most diverse city in the world, as over a hundred different languages are spoken there. Most of the Canadian population comprises of the descendants of English and French settlers. During the past few decades, immigrants have arrived in Canada mostly from Asia.
Canada is a bilingual country. The majority of the population is English-speaking, but the province of Quebec is French-speaking. In Quebec, the status of the French language has been protected with legislation that limits the use of the English language in the region.

Canada is a federal republic that consists of ten provinces and two territories.
16.5 Latin America
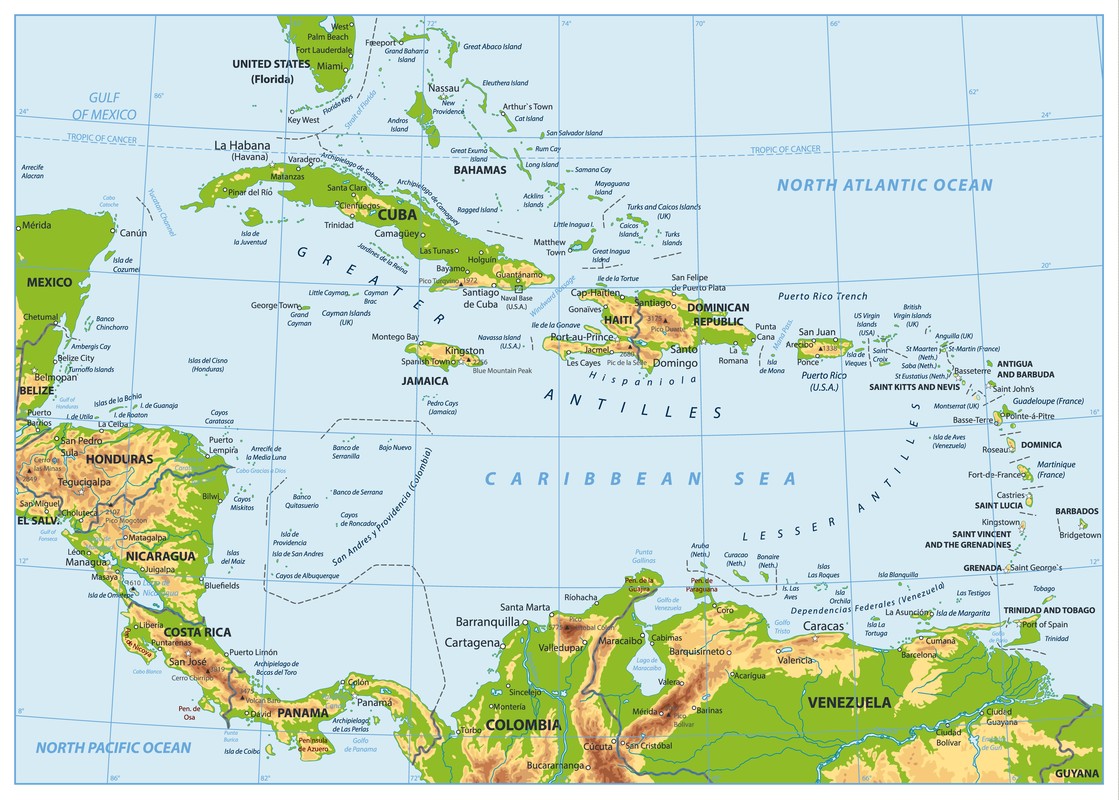 The region of Central America consists of the continental region that comprises Mexico and other Central American nations, as well as the archipelago of the West Indies.
The region of Central America consists of the continental region that comprises Mexico and other Central American nations, as well as the archipelago of the West Indies. The nations of Central America include
Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua and Panama.
The island nations of the West Indies include
Antigua and Barbuda, Bahama, Barbados, Dominica, Dominican Republic, Grenada, Haiti, Jamaica, Cuba, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines as well as Trinidad and Tobago.
The region of Latin America contains all of the nations above, as well as all of the countries of South America, such as Brazil and Argentina.
Most of Latin America is Spanish-speaking. Listen to the sounds of the language from the following textbook chapter: