5. Migration
Contents
5.1 Where and why?
- Where would you like to live the most if you could live anywhere on Earth? Why?
- What do you like about the place you chose?
- Think of good reasons to move to three different countries, and reasons not to move to three other countries. What are these reasons, and why did you choose them?
5.2 The concentration of populations
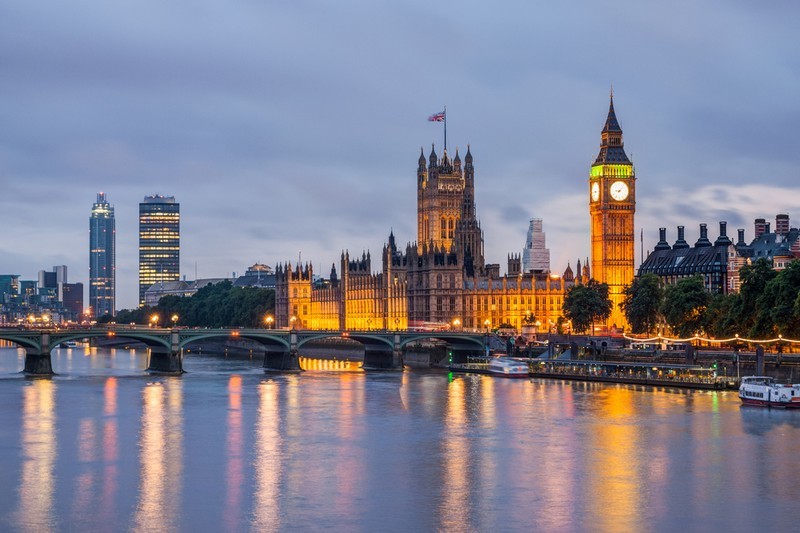

Throughout human history, seas and rivers have been important channels for the movement of people and the transportation of goods. As a result, many large cities have formed either on the shore of a sea or an ocean or connected to a sea or ocean by a river. Many significant cities, such as London (pictured), Cairo, and New York, have formed along the shores of rivers.
In addition to access to seas and oceans, climatic conditions and the fertility of soil have also been important factors that have affected human decisions about where to settle.
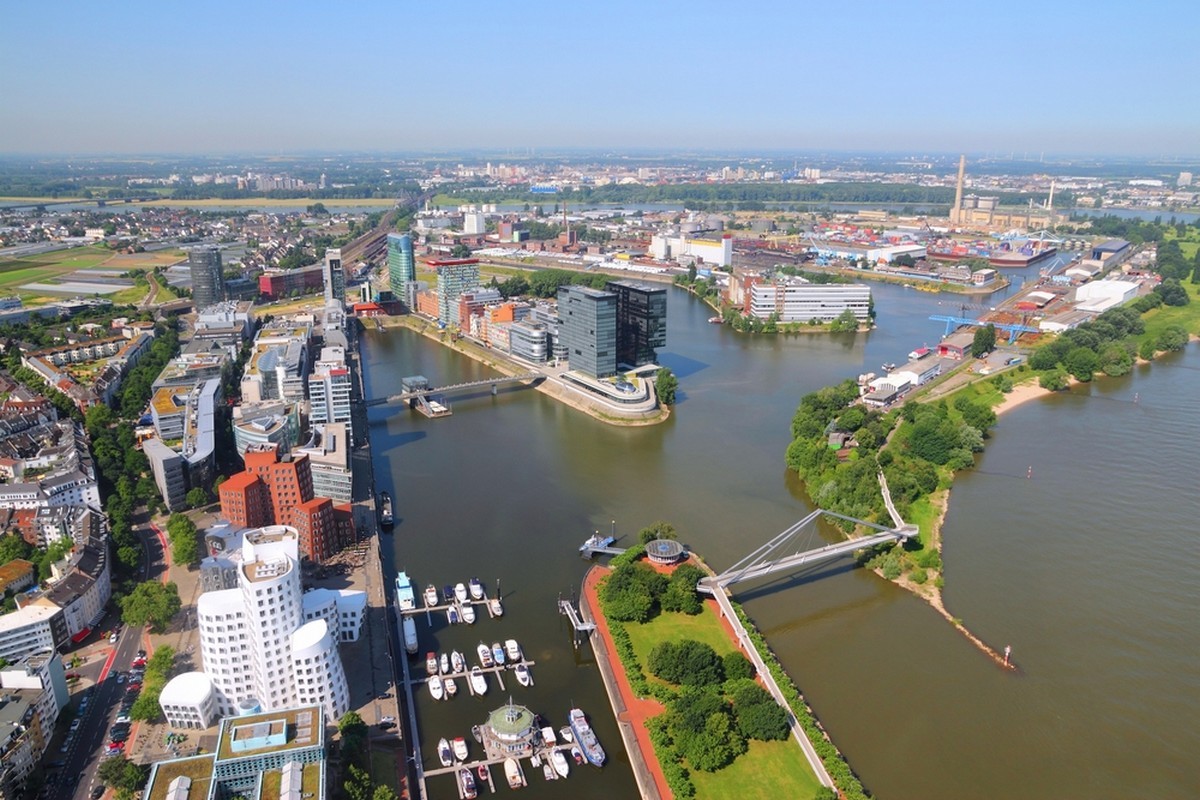 After the emergence of the industrial revolution during the 19th century, cities have also begun to form near different natural resources. For example, the German industrial cluster in Ruhr (pictured) makes use of the region's bountiful ore supplies.
After the emergence of the industrial revolution during the 19th century, cities have also begun to form near different natural resources. For example, the German industrial cluster in Ruhr (pictured) makes use of the region's bountiful ore supplies.
Topographic features also have a significant effect on human movement and food production. Mountain ranges are usually difficult to traverse, and food production is often ineffective on the slopes of mountains. As a result, humans have preferred low elevation areas for their villages, towns, and cities.
Nowadays, the most densely populated areas in Europe are concentrated in the central and western parts of the continent. However, the population density of even these areas is relatively small when compared to the extremely densely populated cities in Asia and Africa.
5.3 Europe is full of migrants
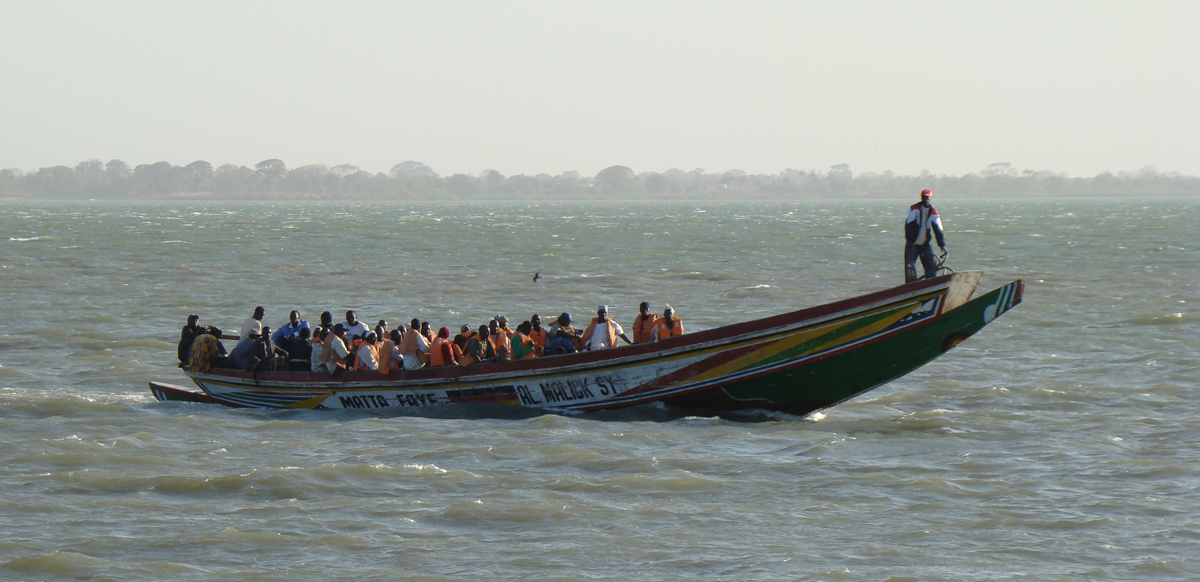

Migration is a term that describes the movement of populations between two areas. When a person moves to a new country permanently, they are called a migrant. People often choose to migrate to a new country because they are searching for a better job, livelihood, or services, or because of family reasons. This kind of migration is considered voluntary migration.
Refugees are people that have to leave their home country because they are in danger of persecution because of their ethnicity, religion, nationality, or political opinion. The difference between voluntary migrants and refugees is that the latter do not necessarily want to leave their home country, but have to do so to protect their safety or the safety of their friends or families.
Different nations have set quotas that are used to determine how many refugees each country will accomodate each year. These quotas are in place to divide the amount of refugees between different nations so that no single nation has to accommodate the large influx of refugees that have to leave their home nation during a conflict or epidemic.
An asylum seeker is a person who seeks for asylum, or protection and a right of permanent residence, in another country. People often seek asylum because they are escaping political persecution in their home nation. A refugee and an asylum seeker are therefore not the same thing.
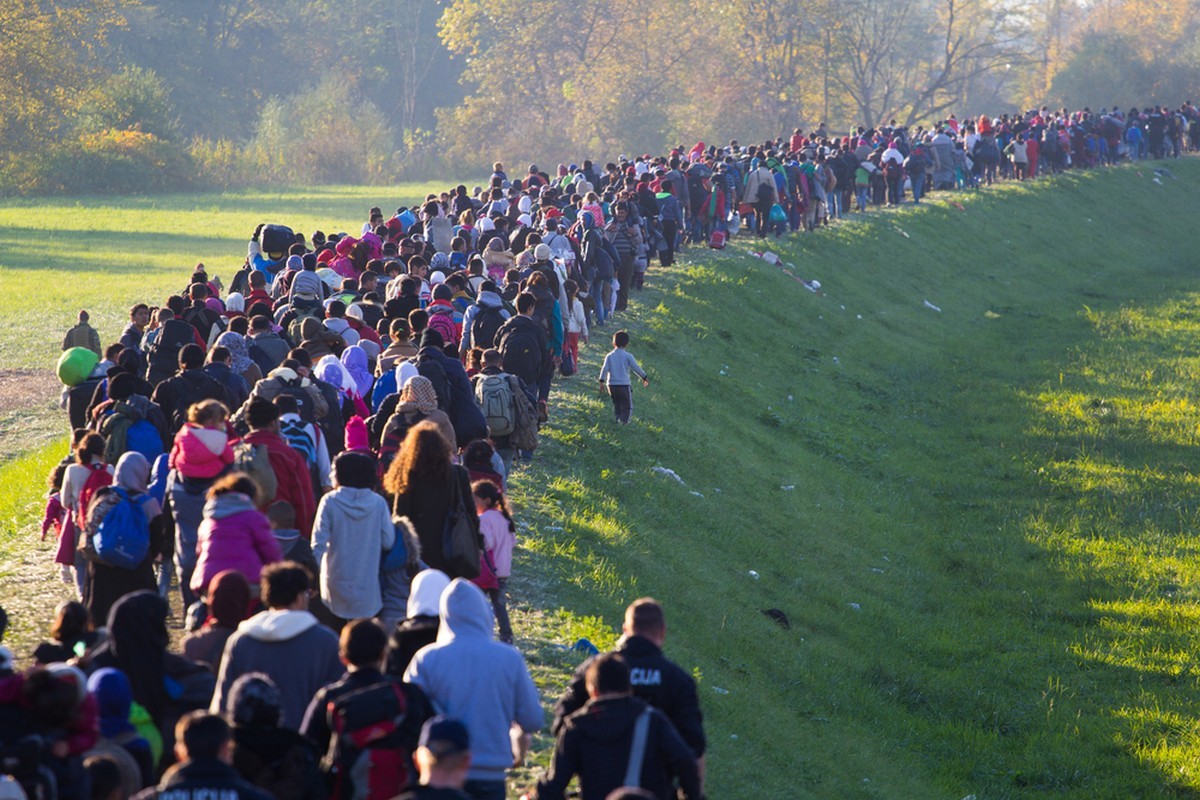

Europe received a large wave of refugees in 2015 due to the devastating conflicts in Syria and the Middle East .
5.4 The amount of refugees has grown
During the year 2015, Europe faced a large increase in refugees and asylum seekers. This was explained by the devastating conflicts that took place in Syria, Afganistan, Iraq, and Somalia. Another significant stream of refugees is between Africa and Mediterranean Europe, where refugees try to complete the difficult sea journey from Africa to Italy and Greece in search of a better life, often on unsafe vessels.
| Africa | 6 million |
| Asia | 9 million |
| Europe | 2 million |
| Latin America & Caribbean | 300 000 |
| North America | 400 000 |
| Oceania | 60 000 |
| Total | 17 million |
5.5 Why leave your home country?
People migrate from their home country for a variety of reasons. These reasons are often connected to difficult economic, social, or political situations in the home country. Mass unemployment or unstable conditions are also common reasons for leaving.
Things that attract migrants to their destination nation include a higher quality of living, better job markets, personal connections, or the opportunity to create a better life for one's family.
In addition to these factors, different laws, permits, and regulations also affect the amount of migration between two countries.
Can you come up with other factors that influence migration?
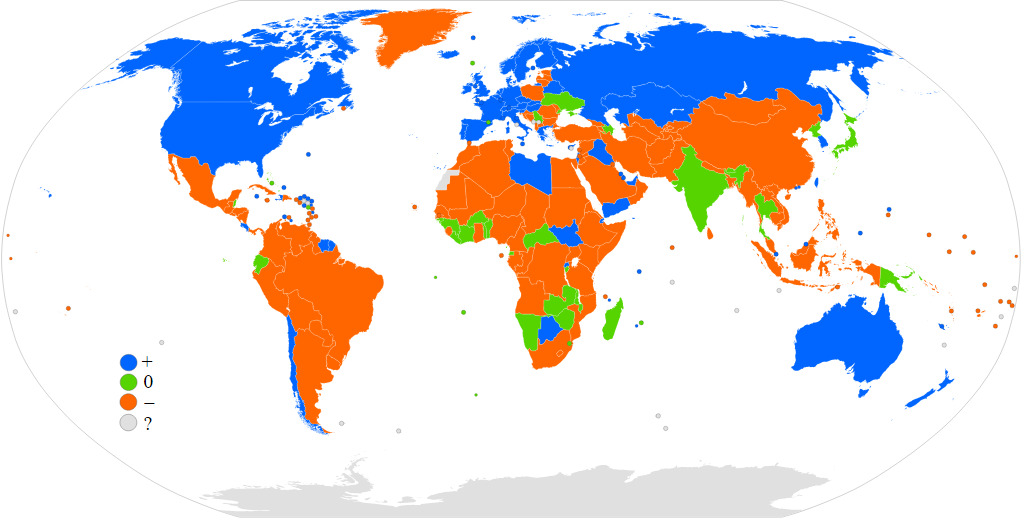
The map shows the direction of migration between different countries. Nations where the amount of immigration is higher than that of emigration is shown in blue. In contrast, the red areas display nations where the amount of emigration is higher than that of immigration.
Summary
- Populations have traditionally concentrated in areas where the conditions for transportation and food production are good.
- Migration means the movement of populations between different regions. When a person moves from one country to the next, they are called a migrant.
- Refugees have to leave their home country to avoid persecution.
- Asylum seekers are people who search for asylum, or protection and a permission of residence, from a certain country.