6.6 Earthquakes
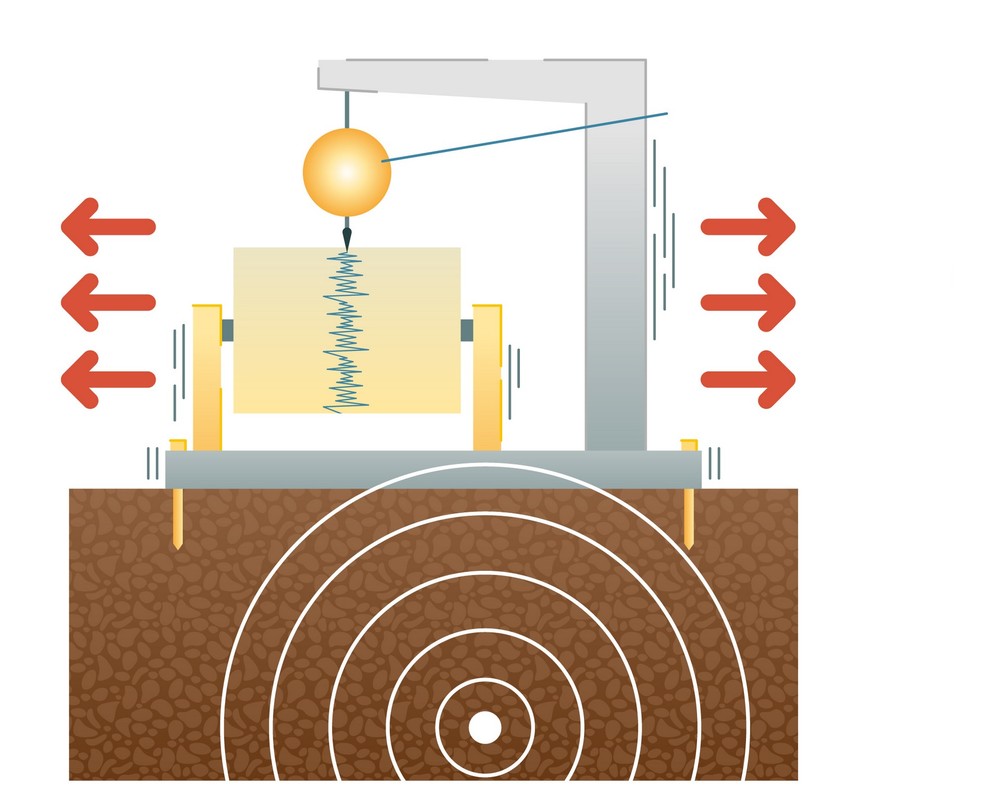 Earthquakes are caused by the movement of tectonic plates or the shaking of bedrock. Earthquakes mostly occur near the border zones of different lithospheric plates.
Earthquakes are caused by the movement of tectonic plates or the shaking of bedrock. Earthquakes mostly occur near the border zones of different lithospheric plates.
The strength or magnitude of an earthquake is measured on the Richter scale. An earthquake below the magnitude of two on the Richter scale can not be perceived by humans.
If the magnitude of an earthquake is over nine on the Richter scale, it will result in massive destruction that can cover an area of a few thousand kilometers. Thankfully, earthquakes of such magnitude occur only once in 20 years on average.
The consequences of earthquakes are not limited to structural damage, but they can also result in fatalities, injuries, and people losing their homes or livelihoods. An earthquake can also cause destructive storms called tsunamsis, as well as landslides.
Predicting earthquakes is difficult. In some areas, earhtquakes can occur between set time frames, but the precise time or location of an earthquake is impossible to predict.
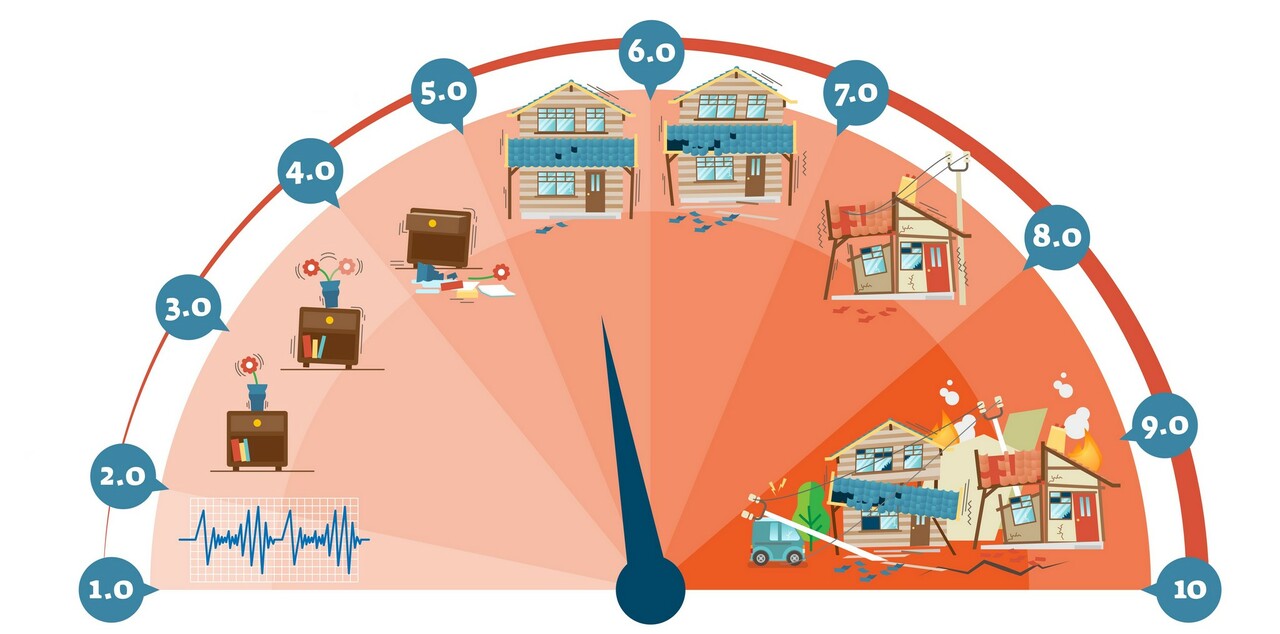
The magnitude of an earthquake is presented on the Richter scale.
| Event | Area | Date | Fatalities (estimate) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Earthquake | Haiti (Central America) | 12.10.2010 | 223 000 |
| Earthquake and tsunami | Sumatra (Indonesia, Asia) | 26.12.2004 | 220 000 |
| Earthquake | Pakistan, India, Afganistan | 8.10.2005 | 88 000 |
| Earthquake | Central China | 12.5.2008 | 84 000 |
| Earthquake | Iran (Asia) | 20.6.1990 | 40 000 |
| Earthquake | Iran (Asia) | 26.12.2003 | 26 000 |