19. Energy
Contents
19.1 A lot of energy is consumed in Finland
| Source | Share of the total energy consumption |
|---|---|
| Wood fuels | 27 % |
| Oil | 24 % |
| Nuclear power | 18 % |
| Coal | 8 % |
| Water power | 5 % |
| Exported electricity | 5 % |
| Natural gas | 5 % |
| Peat | 4 % |
| Other (wind, solar, etc.) | 5 % |
Like natural resources, energy sources can be divided into two broad groups depending on whether or not they are renewable. The supplies of non-renewable energy sources are limited, and they will run out the more we use them. Non-renewable energy sources include all fossil fuels: crude oil, natural gas, coal and shale gas. Nuclear power produces energy from radioactive uranium, which is a metallic element and therefore also a non-renewable energy source.
Renewable energy sources include solar power, water power and wind power. Various forms of biomass, such as wood, are also renewable energy sources. The advantage of these energy sources is that they will always renew themselves. Most renewable energy sources originally gain their energy from the Sun.
| Use | Share of the total energy consumption |
|---|---|
| Industry | 47 % |
| Heating | 25 % |
| Traffic | 16 % |
| Other | 12 % |
However, the largest source of Finnish energy consumption is industry. Industrial production is responsible for approximately half of the planet's total energy consumption. The refining of metals and the production of goods such as paper are examples of industrial processes that consume large amounts of energy.
19.2 Fossil fuels
Like their name suggests, fossil fuels were originally formed when the remains of ancient organisms decomposed in anaerobic conditions under layers of rock and soil. The formation of fossil fuels has occurred over a long period of time. Because of this, fossil fuels are considered practically non-renewable.
Oil, natural gas, and shale gas have formed from the remains of ancient marine organisms. Some concentrations of these resources are still located in the bottom of the oceans, while some have remained inside bedrock as a result of plate tectonics. Oil and natural gas are extracted by drilling into oil or gas pockets that are buried deep under the ground. Shale gas is extracted from rocks that contain organic substances with the help of pressurized water.
Oil is the most important energy source in the world. Approximately one third (33 %) of the total energy consumed on the planet is produced with oil. Crude oil contains a number of different hydrocarbons, and it can be refined into various kinds of fuels, lubricants, plastics and bitumen. In addition to its versatility, it is also easy to transport and store. Oil is especially important fuel in traffic and transportation. In contrast, natural gas covers approximately one quarter (24 %) of Earth's total energy consumption.
Approximately one fourth of Finland's total energy comes from crude oil. It is used as fuel for transport, as well as in heating and electricity production. Almost all of the crude oil used in Finland comes from Russia.
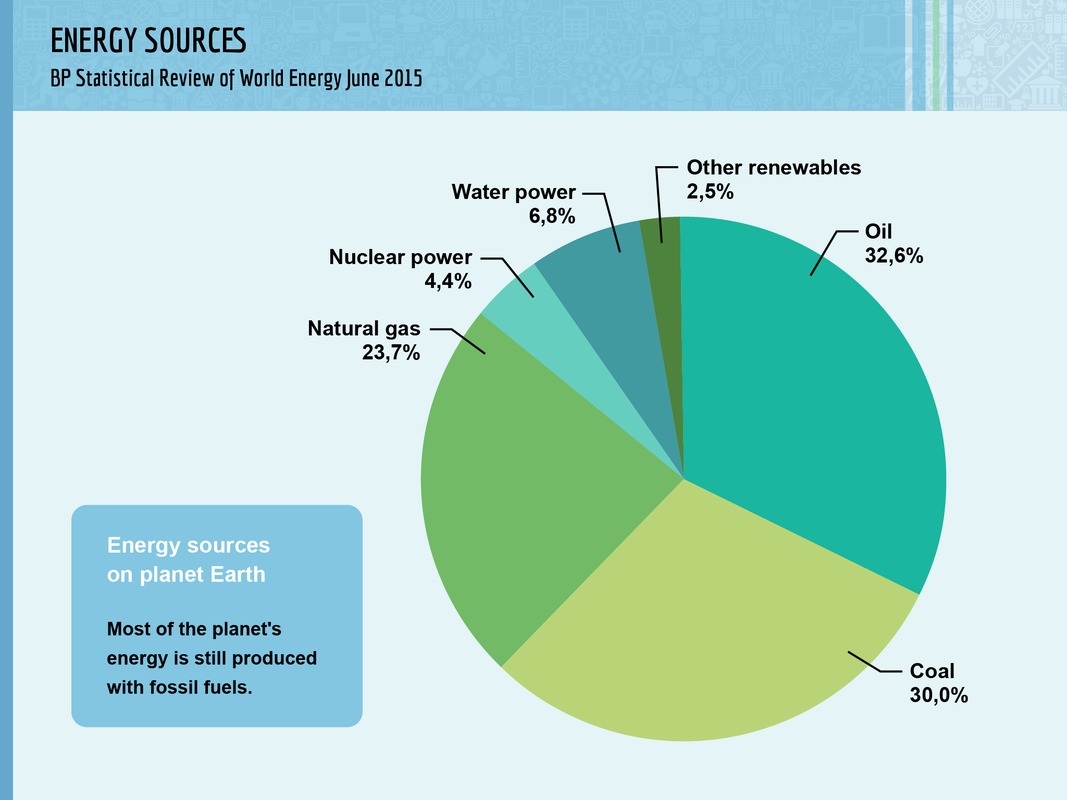
Natural gas is formed through similar processes as crude oil. It, too, is mostly imported into Finland from Russia, which is home to the largest natural gas deposits on the planet. It is mainly used to produce heating and energy for population centers and industrial production. It is also used in some cars. Natural gas is mainly comprised of methane, and it is by far the least harmful of all fossil fuels.
The planet's coal supplies were formed when the thick peat layers of ancient fern forests decomposed in anaerobic conditions. It is a solid fuel that is mined from bedrock. Coal is a lasting, cheap and easy energy source. It is used especially in heavy industry and electricity production. In Finland, coal is usually used as a reserve energy source for heating during the winter. It is one of the most environmentally harmful fossil fuels.

A coal power plant.
Like other fossil fuels, peat is also formed from the decomposed remains of ancient organisms. Peat is produced in bogs and is technically renewable, but this renewal occurs at such a low rate that it cannot be considered a renewable energy source. Peat collection is an important source of employment in Finnish regions where other jobs are in low supply. It is also easy to process and use. However, burning peat produces a lot of greenhouse gases, and its collection destroys bog ecosystems.
19.3 Nuclear power
Nuclear powerproduces energy by splitting the cores of uranium atoms in a process known as fission. This process releases heat that is used to warm up water, which in turn creates vapor that runs a turbine. Although the process itself is relatively simple, the radioactivity of the fuel used and the isotopes produced during the process create a number of technical challenges for nuclear power plants.
Nuclear power has many advantages. The production of nuclear energy is both efficient and stable, which means that it not reliable on external processes such as weather. As a result, the price of nuclear energy is always the same. Unlike fossil fuels, nuclear energy does not release combustion gases such as carbon dioxide. This is one reason why nuclear power is often championed as the answer to the planet's energy needs.
However, nuclear power also has its disadvantages. First, uranium is a relatively rare element in bedrock. Second, uranium is also a radioactive element. This means that uranium atoms have a tendency to break off by themselves, which can release harmful radiation into the environment. Nuclear power also has a risk of nuclear accidents, which can be devastating for the areas that are located near nuclear power plants.

Nuclear power produces energy by splitting the cores of uranium atoms in a process known as fission.
19.4 Renewable energy sources
Bioenergy is the most important renewable energy source in Finland. In bioenergy, heat or electricity is produced by burning plant-, animal-, or microbe-based materials. Burning wood in a fireplace is a well-known example of bioenergy. Biogenic materials or biomass can nowadays be refined into other forms, as well. For example, biomass can be used to produce liquid fuels such as biodiesel. Biogas is produced in landfills and sewage treatment plants. It is used especially in heating.
In water power or hydropower, running water is directed through electricity-generating turbines. This process is based on solar radiation, as rivers are formed when the Sun causes water to evaporate and rain back down to the surface of the Earth. Water power is currently the most significant renewable energy source in the world. Approximately 7 % of the planet's total energy consumption is covered by water power. It is the second most important renewable energy source in Finland, providing almost one fifth of the nation's total energy production.
In wind power, electricity is produced with generators. These generators are rotated by the wind, which itself occurs as a result of solar radiation. In Finland, wind power is popular especially in shore regions. Wind power plants are easy and cheap to build, but they are not dependable alone, as they are reliant on wind.

Wind power plants in Jokioinen, Finland.
Geothermal heat and other similar forms of energy are also based on energy that has originally arrived on the planet from the Sun. In these methods, heat from water or air is used to produce heat energy. Geothermal energy, on the other hand, uses the heat contained inside the planet to produce energy. Geothermal energy has traditionally been used especially in volcanic areas, such as Iceland, but its popularity is steadily growing in other regions, as well.
Most forms of renewable energy gain their energy from radiation from the Sun. This radiation can be directly transformed into electricity or used in heating water for service use. The use of solar radiation in energy production is called solar energy. Only one percent of global energy production is currently based on solar energy, but it is the fastest-growing form of energy production in the world. Finland is not the best place in the world for solar energy production because of the long, dark winter. However, solar panels are popular mode of energy production in many Finnish summer houses. They can also be installed on top of buildings to heat up water for domestic use.

Solar power is the fastest-growing renewable energy source in the world.
19.5 The problems of energy production
The simplest solutions for the problems posed by global energy production are saving energy and using renewable energy sources efficiently. Renewable energy sources can be favored by increasing taxation on non-renewable energy production, by giving benefits for renewable energy producers, and by changing legislation to support the efficient use of renewable energy sources.
All of us can lower our energy consumption by making conscious choices about what we consume and how we move. Industry also has to become more efficient and conserve more energy. This can be achieved by developments in industrial technology.