FY1-2 in English 2022
SCHEDULE
| date | lesson | Topic | module |
| 15.8. | 1 | School photo and laptops | FY1 |
| 16.8. | 2 | What is physics | FY1 |
| 18.8. | 3 | Four Fundamental Forces | FY1 |
| 22.8. | 4 | Quantities | FY1 |
| 23.8. | 5 | Significant numbers | FY1 |
| 25.8. | 6 | Micro- and macrocosmos | FY1 |
| 29.8. | 7 | Measuring | FY1 |
| 30.8. | 8 | Graphical model | FY1 |
| 1.9. | 9 | (Linear model) Student happening in Kirjurinluoto | FY1 |
| 5.9. | 10 | Linear model | FY1 |
| 6.9. | 11 | Studying motion | FY1 |
| 8.9. | 12 | 1. Energy in Physics, lesson | FY2 |
| 12.9. | 13 | 2. Sources of Energy and Power plants, preparation of a presentation | FY2 |
| 13.9. | 14 | Practise test in Abitti | FY2 |
| 15.9. | 15 | 3. Sources of Energy and Power plants, slide show or similar | FY2 |
| 19.9. | 16 | Preparing the presentations of different types of energy sources | FY2 |
| 20.9. | 17 | Preparing the presentations (first presentations?) | FY2 |
| 22.9. | 18 | Presentations | FY2 |
| 29.9. | 19-21 | Final exam | FY1 |
Grading will be based on the course activities and what students should know at the end of the course.
Roughly: Final exam and active participation +1, 0 or -1
Exam 80% of your grade
Presentation 20% of your grade
For example: exam 9- and presentation 7 will give you 0,8*8,75 + 0,2*7 = 8,4 -> 8
Lesson 01
FY01-02 Physics as a natural Science
Teacher: Susanna Hietanen
Today we are going to get to know each other and then
we will go to Vellilä to get you your laptops.
If you think your guardian has not given the permit in Wilma,
please send them a message!
Take a pair and find out a few things about them
(name, where are from, hobbies etc.)
Tell me and the other class about your pair
Write these questions in your notebook
1) What is physics?
2) What do we study in physics?
3) How has physics influenced the development of society?
4) Who needs physics? Give at least five examples.
Then find the answers with your pair
Next task is to go and get you your laptops in Vellilä
If you think your guardian has not given the permit in Wilma,
please send them a message.
************
Physics is a natural science that studies different phenomena in nature. We can divide it in two groups: theoretical physics and applied physics. Do you know the difference between these two? We can also divide it in two groups: classical physics from 1600 until 1900 and modern from 1900.
We study what happens between objects in nature: we can study different objects (humans, cars, balls, buildings, atoms) and forces (gravity, electromagnetic force, strong and weak nuclear force)
Teacher: Susanna Hietanen
Today we are going to get to know each other and then
we will go to Vellilä to get you your laptops.
If you think your guardian has not given the permit in Wilma,
please send them a message!
Take a pair and find out a few things about them
(name, where are from, hobbies etc.)
Tell me and the other class about your pair
Write these questions in your notebook
1) What is physics?
2) What do we study in physics?
3) How has physics influenced the development of society?
4) Who needs physics? Give at least five examples.
Then find the answers with your pair
Next task is to go and get you your laptops in Vellilä
If you think your guardian has not given the permit in Wilma,
please send them a message.
************
Physics is a natural science that studies different phenomena in nature. We can divide it in two groups: theoretical physics and applied physics. Do you know the difference between these two? We can also divide it in two groups: classical physics from 1600 until 1900 and modern from 1900.
We study what happens between objects in nature: we can study different objects (humans, cars, balls, buildings, atoms) and forces (gravity, electromagnetic force, strong and weak nuclear force)
Lesson 02
Course schedule and evaluation:
Notice that this course has two parts
FY1 is 8 lessons and FY2 is 7 lessons.
FY1 you will have final exam on examweek
FY2 you will make presentations
Lets work in groups:
Write these four questions in your notebook and find the answers
1) What is physics?
Math based natural science to describe speed and mass and to calculate them.
The study of how things work around us and the study of natural forces.
A fundamental science that studies natural occurences and object.
The study of actions and reactions.
Studies the interactions between objects.
Study of electricity.
2) What do we study in physics?
motions, energy, electricity, heat and mechanics, different formulas and math, speed of things like light, constants, gravity, force, work, matter, mass and density
3) How has physics influenced the development of society?
Valuable inventions, battery, radiation, speedometers, engings, cars
Understanding of different illnesses
Better technology
Improved space travel and environmental changes
Understanding of Gravity
Answers for the questions about world
4) Who needs physics? Give at least five examples.
physicist
astronomists
pilots
engineers
architects
astrophysicists
************
Käydään läpi ryhmien tuotokset (10 min)
Notice that this course has two parts
FY1 is 8 lessons and FY2 is 7 lessons.
FY1 you will have final exam on examweek
FY2 you will make presentations
Lets work in groups:
Write these four questions in your notebook and find the answers
1) What is physics?
Math based natural science to describe speed and mass and to calculate them.
The study of how things work around us and the study of natural forces.
A fundamental science that studies natural occurences and object.
The study of actions and reactions.
Studies the interactions between objects.
Study of electricity.
2) What do we study in physics?
motions, energy, electricity, heat and mechanics, different formulas and math, speed of things like light, constants, gravity, force, work, matter, mass and density
3) How has physics influenced the development of society?
Valuable inventions, battery, radiation, speedometers, engings, cars
Understanding of different illnesses
Better technology
Improved space travel and environmental changes
Understanding of Gravity
Answers for the questions about world
4) Who needs physics? Give at least five examples.
physicist
astronomists
pilots
engineers
architects
astrophysicists
************
Käydään läpi ryhmien tuotokset (10 min)
Lesson 03
Last time we were talking about what is physics and what do we study in physics.
Physics is a natural science that studies different phenomena in nature.
We can divide it in two groups: theoretical physics and applied physics.
Do you know the difference between these two?
We can also divide it in two groups:
classical physics from 1600 until 1900 and modern from 1900.
In physics we study what happens between objects in nature:
we can study different objects (humans, cars, balls, buildings, atoms) and
forces (gravity, electromagnetic force, strong and weak nuclear force)
Todays subject "Four fundamental forces"
Gravitation
Electromagnetism
Strong force
Weak force
Work in the same groups again and find out
1) Where can we find this force acting
2) Is it attractive or repulsive
3) What is the mediator
4) Is the force strong or weak
Then go back to your place and tell the others what you have learned
Book pages 18-25
Homework:
Chapter 2 exercises 7, 9, 13 and 17
Physics is a natural science that studies different phenomena in nature.
We can divide it in two groups: theoretical physics and applied physics.
Do you know the difference between these two?
We can also divide it in two groups:
classical physics from 1600 until 1900 and modern from 1900.
In physics we study what happens between objects in nature:
we can study different objects (humans, cars, balls, buildings, atoms) and
forces (gravity, electromagnetic force, strong and weak nuclear force)
Todays subject "Four fundamental forces"
Gravitation
Electromagnetism
Strong force
Weak force
Work in the same groups again and find out
1) Where can we find this force acting
2) Is it attractive or repulsive
3) What is the mediator
4) Is the force strong or weak
Then go back to your place and tell the others what you have learned
Book pages 18-25
Homework:
Chapter 2 exercises 7, 9, 13 and 17
Lesson 04
(Homework kappale 2: 7, 9, 13 ja 15 katsotaan ketkä ovat tehneet)
Four fundamental forces
Gravity = painovoima, between objects with mass
Electromagnetism = sähkömagnetismi between objects with charge ( + or -)
Strong force = vahva voima between
Weak force = heikko voima
Notebooks
QUANTITIES AND UNITS = SUUREET JA YKSIKÖT
Mathanticsin video yksiköistä ja SI-järjestelmästä: mathantics_intothemetricsystem
Tehdään välillä muistiinpanot
A quantity is something we can measure
In the SI system Base quantities are:
time, mass, current, temperature, substance, intensity and length
and their units are:
s, kg, A, K, mol, Cd and m
Vector quantity has direction and magnitude ex. velocity, force
Scalar quantity has magnitude but doesn't have direction ex. mass, length
This is how we write the unit of a quantity:
[t] = 1s ("the unit of time is second")
[m] = 1kg ("the unit of mass is kilogram")
[v] = 1m/s ("the unit of velocity is meter/second")
Jatketaan video loppuun
This is how we change the unit:
1h = 60 min = 60*60s = 3600s
1km = 1000 m
1km/h = 1000m/3600s =
Sometimes we have such a big numbers they are not easy to use
Esim. 2 s. 36
Alltogether ex. 2 and 8
Work with your pair and do ex. 5,6,7,10,11,17 use your books and/or internet
Vaihtoehtoisesti
Video (suureet, yksikkömuunnokset ja merkitsevät numerot 9 minuuttia)
Four fundamental forces
Gravity = painovoima, between objects with mass
Electromagnetism = sähkömagnetismi between objects with charge ( + or -)
Strong force = vahva voima between
Weak force = heikko voima
Notebooks
QUANTITIES AND UNITS = SUUREET JA YKSIKÖT
Mathanticsin video yksiköistä ja SI-järjestelmästä: mathantics_intothemetricsystem
Tehdään välillä muistiinpanot
A quantity is something we can measure
In the SI system Base quantities are:
time, mass, current, temperature, substance, intensity and length
and their units are:
s, kg, A, K, mol, Cd and m
Vector quantity has direction and magnitude ex. velocity, force
Scalar quantity has magnitude but doesn't have direction ex. mass, length
This is how we write the unit of a quantity:
[t] = 1s ("the unit of time is second")
[m] = 1kg ("the unit of mass is kilogram")
[v] = 1m/s ("the unit of velocity is meter/second")
Jatketaan video loppuun
This is how we change the unit:
1h = 60 min = 60*60s = 3600s
1km = 1000 m
1km/h = 1000m/3600s =
Sometimes we have such a big numbers they are not easy to use
Esim. 2 s. 36
Alltogether ex. 2 and 8
Work with your pair and do ex. 5,6,7,10,11,17 use your books and/or internet
Vaihtoehtoisesti
Video (suureet, yksikkömuunnokset ja merkitsevät numerot 9 minuuttia)
Lesson 05
What is a quantity in physics?
Tell me the base quantities in SI
Give me an example of
1) Vector quantity
2) Scalar quantity
In physics, a physical quantity is any physical property of a material or system that can be quantified,
that is, can be measured using numbers. A physical quantity can be expressed as a value,
which is the algebraic multiplication of a numerical value and a unit.
The present SI has seven base quantities: time, length, mass, electric current,
thermodynamic temperature, amount of substance, and luminous intensity
Vanhat Kotitehtävät 5, 6 ja 7 (kpl3)
Lets measure
the Area of the pin-up board:
Height (korkeus) = 1,26m
Width (leveys) = 2,70m
Area = 3,402 m^2 approx. 3,40m^2
When we measure, we don't always get exact numbers.
So we need to know the rules of significant figures:
Significant figures
Together: 8, 17
Homework: 2, 10, 12
Tell me the base quantities in SI
Give me an example of
1) Vector quantity
2) Scalar quantity
In physics, a physical quantity is any physical property of a material or system that can be quantified,
that is, can be measured using numbers. A physical quantity can be expressed as a value,
which is the algebraic multiplication of a numerical value and a unit.
The present SI has seven base quantities: time, length, mass, electric current,
thermodynamic temperature, amount of substance, and luminous intensity
Vanhat Kotitehtävät 5, 6 ja 7 (kpl3)
Lets measure
the Area of the pin-up board:
Height (korkeus) = 1,26m
Width (leveys) = 2,70m
Area = 3,402 m^2 approx. 3,40m^2
When we measure, we don't always get exact numbers.
So we need to know the rules of significant figures:
Significant figures
Together: 8, 17
Homework: 2, 10, 12
Lesson 06
Homework 2, 10 ja 12
Todays topic:
MICRO- AND MACROCOSMOS
Six groups
choose either micro or macro and make a short presentation (max. 5 min)
You can draw, make a poem, a short play or a poster!
Purpose:
to teach the others about the topic :)
to help us decide could a presentation be a part of evaluation in FY1+FY2
Todays topic:
MICRO- AND MACROCOSMOS
Six groups
choose either micro or macro and make a short presentation (max. 5 min)
You can draw, make a poem, a short play or a poster!
Purpose:
to teach the others about the topic :)
to help us decide could a presentation be a part of evaluation in FY1+FY2
-
the microcosm and its structures
-
the macrocosm and its structures
-
size classes of structures
-
interactions between structures
Lesson 09 and 10
Linear model
Lets look at the video in your book, where they measure
the volume V and mass m of two substances (sand and soil).
Make a table with Geogebra and then fit the line.
Find out the connection between mass and volume.
The assumption is that there is some mathematical relationship between the quantities being graphed.
What quantity is the physical slope in this case?
Kirjuriin!
Jatketaan seuraavalla tunnilla katsomalla video(t):
density
how to calculate density
Notebook:
Density
Density is a physical property, defined by mass over volume
d = m/V
[d] = [m]/[V] = kg/m^3
Chapter 7 exercises 5, 6, 7, 9, 10 (13)
HUOM Muista jakaa taulukkokirjalisenssit! Ja tarkastaa edelliskerran kotitehtävä :)
Lets look at the video in your book, where they measure
the volume V and mass m of two substances (sand and soil).
Make a table with Geogebra and then fit the line.
Find out the connection between mass and volume.
The assumption is that there is some mathematical relationship between the quantities being graphed.
What quantity is the physical slope in this case?
Kirjuriin!
Jatketaan seuraavalla tunnilla katsomalla video(t):
density
how to calculate density
Notebook:
Density
Density is a physical property, defined by mass over volume
d = m/V
[d] = [m]/[V] = kg/m^3
Chapter 7 exercises 5, 6, 7, 9, 10 (13)
HUOM Muista jakaa taulukkokirjalisenssit! Ja tarkastaa edelliskerran kotitehtävä :)
12 th lesson
How did you calculate your average speed from home to school?
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
New book and new topic
Energy
What does energy mean? Talk with your pair / group -> to the board
Do the "ennakkotesti"
Let's watch a video and fill in the paper
Energy can change its form but it never disappears!
We can divide energy also in two groups:
free energy (vapaa energia) and binding energy (sidottu energia)
FY02: Chapter 1
Read the text and do exercises
5, 6, 8, 9, 11,18
another video (work and energy explained)
What is the difference between speed and velocity?
New book and new topic
Energy
What does energy mean? Talk with your pair / group -> to the board
Do the "ennakkotesti"
Let's watch a video and fill in the paper
Energy can change its form but it never disappears!
We can divide energy also in two groups:
free energy (vapaa energia) and binding energy (sidottu energia)
FY02: Chapter 1
Read the text and do exercises
5, 6, 8, 9, 11,18
another video (work and energy explained)
Liitteet:
15 th lesson
Esitykset (n. 30 min)
1) mitä energian tuotantotapoja
2) mikä on niiden suhde
3) miten voimalaitokset toimivat
4) primääri ja sekundäärienergia
5) uusiutuva ja uusiutumaton
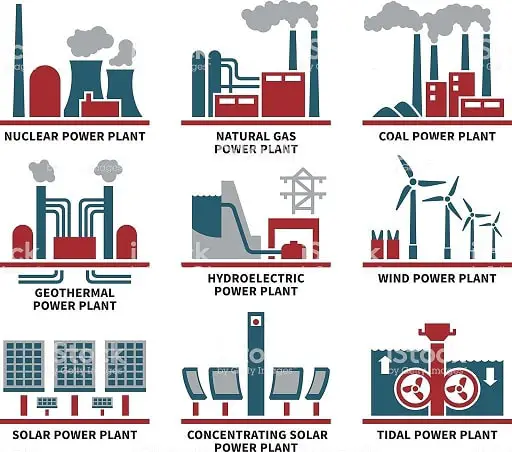
First three are thermal power stations, just using different fuel
Write down on your notebook, how does the thermal power station work:
lyhyt versio:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lh5_7sHyLU4
teknisempi versio:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IdPTuwKEfmA
s. 27 Lämpöarvo = Heat value
H = Q/m
s. 28 pictures: combined heat and power plant -> district heating (or heat networks)
What can be used as a fuel?
s. 29 What is good and what is bad in fossil fuel?
How does a nuclear power plant work?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_UwexvaCMWA
Chapter 3 Ex. 7, 9, 10, 11
1) mitä energian tuotantotapoja
2) mikä on niiden suhde
3) miten voimalaitokset toimivat
4) primääri ja sekundäärienergia
5) uusiutuva ja uusiutumaton

First three are thermal power stations, just using different fuel
Write down on your notebook, how does the thermal power station work:
lyhyt versio:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lh5_7sHyLU4
teknisempi versio:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IdPTuwKEfmA
s. 27 Lämpöarvo = Heat value
H = Q/m
s. 28 pictures: combined heat and power plant -> district heating (or heat networks)
What can be used as a fuel?
s. 29 What is good and what is bad in fossil fuel?
How does a nuclear power plant work?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_UwexvaCMWA
Chapter 3 Ex. 7, 9, 10, 11
linkkejä
Mittaamiseen liittyen
Suureita ja suuruusluokkia englanniksi
Lesson 16
FY1/2
Did you get your test results in your email?
If not, please ask a friend to forward it :)
I recommend that you look what went wrong and what is the correct answer!
Change in our schedule:
Monday and Tuesday preparing the FY2 presentations and
studying for FY1 test
Thursday presentations, max. 5 min each
Exam on 29th of September for two hours (10-12 or 9-11)How many groups? 14
(14*5 = 70 min)
Every group will have different topic but same questions:
1) How does this power plant work / Miten voimalaitos toimii
2) What are the good sides / Mitä hyviä puolia
3) What are the bad sides / Mitä huonoja puolia
max. 5 min!
Topics:
| 1. Hydroelectric power (vesivoimalaitos) | Adrian | ||
| 2. Wind power (tuulivoimalaitos) | Ella, Olivia, Elias | Iiris, Anna, Eppu | |
| 3. Solar collector (aurinkolämpö) | Helen and Hope | ||
| 4. Solar panel (aurinkosähkö) | Frans, Jasper, Einari | ||
| 5. Bioenergy (biopolttoaine) | Dijana | Esther | |
| 6. Geothermal energy (geoterminen energia) | Yeva | ||
| 7. Heat pump (lämpöpumppu) | Iida | ||
| 8. Hydrogen energy (vetyenergia) | Hayley, Maria | ||
| 9. Fusion (fuusio) | Fin | Tara | Dennis |
| 10. Modular Reactor (modulaarinen reaktori) | Emma |
FY1 videos and other useful links in English
Work, Energy and Power
Definitions of work, kinetic energy, potential energy and power
Powers of ten
Uudempi versio mikro- ja makrokosmoksen rakenteista ja mittasuhteista kympin potensseina
Interpolointi ja ekstrapolointi
How hot can it get
Chapter 14, part B
Chapter 14, part A
Chapter 15, part B
Chapter 15, part A
Galileos experiment about gravity
Galileon kokeet putoamiskiihtyvyyteen liittyen
Forces (friction, gravity, normal force...)
Hypertextbook:
Voimat (kitka, painovoima, normaalivoima...)
Voimat (kitka, painovoima, normaalivoima...)
Mass bending the space
Massan vaikutuksesta kaareutuva avaruus
Bowling ball and Feathers falling in a vacuum
Keilapallo ja höyhenet putoavat tyhjiössä
Lessons 7 and 8 Proportional constant
Proportional constant
kulmakerroin
kulmakerroin
Lesson 7 From Graphical Model to Mathematical Model (equation)
Miten kuvaajasta saadaan selville matemaattinen malli eli yhtälö
The Physics Hypertextbook
Fysiikan oppikirja, kattaa lähes kaikki lukiokurssit ja paljon muutakin.
You can find almost everything for our courses FY1-FY7 and more.
You can find almost everything for our courses FY1-FY7 and more.
Lesson 2 Significant figures
Merkitsevät numerot
Too much time? Watch this :D
Luento fysiikasta yleisesti - ihana :D
Lesson 8 Motion graphs
Liikkeen kuvaajia
The Four Fundamental Forces
Neljä perusvuorovaikutusta