24. The heart and the circulatory system
What is blood?
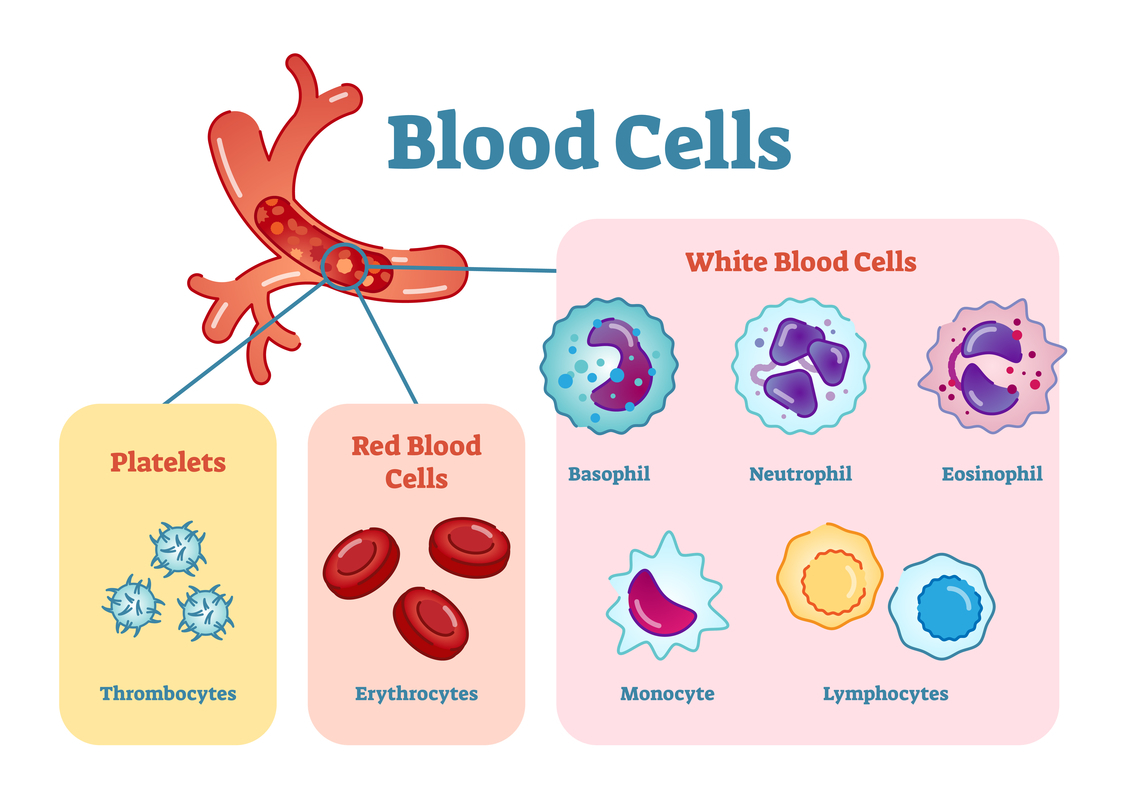
Blood is a fluid that contains various cells.
Blood's red color comes from red blood cells. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin. Their function is to transport oxygen from the lungs to the heart and to the rest of the body. Red blood cells also transport carbon dioxide to the lungs.
The funtion of white blood cells is to destroy disease-causing pathogens, which are bacteria and viruses. Some white blood cells can transform themselves into memory cells, which protect you from catching the same illness twice.
Vaccines are also based on memory cells. Vaccines contain things like dead viruses, which help to produce memory cells against these viruses. If the same virus arrives in the body at a later time, the memory cells quickly destroy the virus. As a result, the human does not become ill at all.
Blood also contains small blood platelets. Their function is to help blood coagulate. For example, when a wound appears on the body, the blood platelets help to stop it from bleeding.
Blood also contains water, nutrients and hormones.
How does blood travel through the body
After leaving the heart, the blood travels through the aorta. The aorta is divided into smaller blood vessels known as arteries. Arteries transport blood from the heart into all parts of the body: into the brain, into the legs and into the arms. Blood returns to the heart by travelling through veins.
Before travelling to the rest of the body, the blood must first travel through the lungs. There, the blood loses all of the carbon dioxide it has collected during its journey. The carbon dioxide is replaced with oxygen, which is then transported to different parts of the body.
The circulatory system is important to our bodies. It transports oxygen and nutrients to the body's cells and tissues. At the same time, it transports carbon dioxide and other harmful substances away from the cells and tissues.
Blood vessels
 Blood travels in the body through a network of blood vessels. They are empty tubes with flexible walls.
Blood travels in the body through a network of blood vessels. They are empty tubes with flexible walls. You can see some of your body's blood vessels through your skin. Other blood vessels are located deep inside your body.
Inside blood vessels, blood travels in only one direction. Arteries are blood vessels that transport blood from the heart to the rest of the body, whereas veins are blood vessels that transport blood towards the heart.
The smallest blood vessels are called capillaries. Capillary vessels transport blood between cells and arteries or veins.
Capillary vessels are so small, that red blood cells can only barely travel through them.
The heart
The heart is a hollow muscle that is located between the lungs. The heart's function is to pump blood into different parts of the body.
 The heart consists of four parts: two atria and two ventricles.
The heart consists of four parts: two atria and two ventricles.
The blood travels through the atria into the ventricles. The walls of the ventricles contain strong muscle cells. When these muscle cells contract, the blood is pumped at a great speed into the blood vessels of the body.
The aorta is the largest blood vessel in our body. Its purpose is to transport blood from the heart into the arteries.
Veins bring blood from the body into the heart's atria.
The heart is covered with coronary arteries. These arteries transport oxygen and energy to the cells of the heart itself.
The heart rests briefly between each heartbeat.
The rate at which the heart beats or contracts is called the heart rate. It can be measured by using your hands or a specialized heart rate meter. The heart can pump blood to the body over 100 times per every minute.
The heart pumps blood into the body in four stages:
1. Blood arrives at the atria.
2.–3. Blood moves from the atria to the ventricles.
4. The muscle cells of the ventricle contract, and the blood is pumped into the body.
Terminology
| Term | Explanation |
|---|---|
| blood | A fluid that travels through the circulatory system. It contains cells and transports various substances. |
| blood vessel | Hollow, flexible tubes that transport blood in the human body. |
| the heart | A muscle that pumps blood in to the body. |