21. Bones and muscles
What are bones?
 Bones are the structures that comprise our skeletal system. The skeletal system is the body's internal supporting structure.
Bones are the structures that comprise our skeletal system. The skeletal system is the body's internal supporting structure.Bones are living tissue. This means that they contain living bone cells, blood vessels and nerve cells.
Bones can feel pain. If a bone breaks, this pain will be excruciating. When this happens, a doctor must place the broken ends of the bone back together. A cast can be placed over the broken bone to make sure that the ends of the bone stay in place.
In a couple of weeks, the bone cells will gradually duplicate. When this happens, the ends of the bone grow back together, and the bone heals.
The ends of bones contain cartilage. Blood vessels transport energy and oxygen to the bone cells.
Nerve cells transmit information in and out of the bone. The central part of a bone consists of bone marrow. New blood cells are produced in the marrows of certain bones.
The space between bone cells is mostly comprised of calcium-rich medial substance. Our bones need calcium to stay healthy. Calcium can be gained by eating milk products, for example. To transmit calcium to the bones, we also need plenty of vitamin D.
The skeletal system
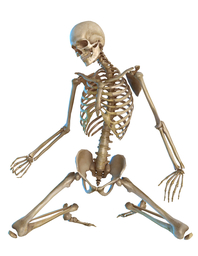
 The human skeletal system is consisted of over 200 different bones. The longest bones of the body are found in the legs, whereas the smallest bones of the body can be found in the inner ear.
The human skeletal system is consisted of over 200 different bones. The longest bones of the body are found in the legs, whereas the smallest bones of the body can be found in the inner ear. Our head is protected by our skull bones. The skull bones of a young child are separate, but they grow together as the child develops. This is why the body of an adult contains fewer bones than that of a child.
The arms and hands contain a large number of bones. The bone that extends down from your shoulder is called the scapula.
The crook of your arm contains a joint. Joints are places where two bones connect with each other. The elbow joint makes it possible for us to bend and rotate our arms. It also prevents the arm from bending backwards.
Below the elbow joint, the arm continues in the form of two bones: the ulna and the radius. The radius is the bone that is found on the thumb side of your arm. By feeling your hand with your fingers, you can also locate your wrist bones, metacarpal bones and finger bones.
The backbone consists of vertebrae. The space between the vertebrae is filled with cartilage, which helps to absorb the shock the bones receive during movement.
The vertebrae of the backbone protect the spinal cord. The spinal cord contains long nerves that transport information to and from different parts of the body.
The rib cage protects your lungs and your heart. The rib cage is connected to the breastbone.
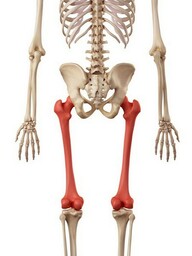
The pelvis protects your intestines. The large leg bones are called the femur, the tibia and the fibia. They are joined together by the knee joint, which is protected by a bone called the patella.
Gallery: Bones
What are muscles?
 Muscles are structures that make our body move. This is achieved in co-operation with the skeletal system.
Muscles are structures that make our body move. This is achieved in co-operation with the skeletal system.
A muscle consists of several long muscle cells, that have joined together into structures called fascicles.
Muscles are connected to bones with tendons. For example, the upper part of the calf muscle is connected to the tibia by a tendon, whereas the lower part of the same muscle is connected to the heel via the Achilles tendon.
Some of our muscles
 Our movement ability is based on our muscles.
Our movement ability is based on our muscles.The human body contains tens of different muscles. For example, the thigh contains a number of different muscles.
The largest muscles in your arm are called the biceps and the triceps. These muscles make your arm bend and stretch out, respectively.
The largest muscles in your leg are the called the quadriceps and the gastrocnemius, commonly known as the calf muscle.
How can we bend our hands?
 We control our muscles with messages we transmit from our brain. These messages are quickly transmitted to the muscles through nerves and the spinal cord. When the muscle receives the message, it begins to contract.
We control our muscles with messages we transmit from our brain. These messages are quickly transmitted to the muscles through nerves and the spinal cord. When the muscle receives the message, it begins to contract. If we want to bend our hand towards our shoulder, our brain sends a message to the biceps muslce through the nervous system. The biceps muscle is connected to the radius and the shoulder. When the cells of the biceps muscle contract, the hand begins to move towards the shoulder.
If we want to stretch our hand back to its regular position, our brain must send a message to the triceps muscle, which is located on the other side of the arm as the biceps. When the muscles of the triceps muscle contract, the arm straightens.
Gallery: Muscles
Terminology
| Term | Explanation |
|---|---|
| bone | Hard and durable structures that protect and support the body. Made of bone cells. |
| cartilage | A structure made of resilient tissue that is found between bones and vertebrae. |
| nerve | A structure that is made of nerve cells and transmits information through the body. |
| joint | A structure that joins two bones together, making movement possible. |
| tendon | A strong, cartilage-like tissue that connects bones with muscles. |