14. The tangent angle of a circle
The tangent angle of a circle
A tangent is a line that passes through a point on the circle's circumference and is perpendicular to the circle's radius. Thus, the tangent is lateral to the circle at only one point, and its distance from the center of the circle is the same as the length of the circle's radius.
Two tangents can be drawn to a circle so that they intersect at a point outside the circle. An angle whose sides lie on the two tangents is called the tangent angle. The distance between the points where the tangets touch the circle and the point at which they intersect is equal.
The tangent angle
The sum of the tangent angle and its corresponding central angle is always [[$ 180° $]].
Example 1
Calculate the magnitude of the central angle when the magnitude of its corresponding tangent angle is [[$ 40 ° $]].
The sum of the tangent angle and the corresponding central angle is always [[$ 180 ° $]], which means that the magnitude of the central angle is [[$ 180 ° - 140 ° = 40 ° $]].
Example 2
The sighting basket of a sailing vessel is located at a height of [[$ 40 $]] m. Calculate how far you can see from the sighting basket in calm weather. The radius of the globe is [[$ 6378 $]] km. Please note that the dimensions of the picture below are incorrect.
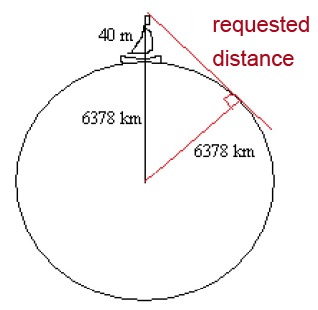
As you can see from the picture, a right triangle is formed, with one of its legs being the distance we want to find out. The length of the hypotenuse is [[$ 6378 $]] km + [[$ 0,040 $]] km = [[$ 6378,040 $]] km.
The requested distance can be deduced by completing the following calculation:
[[$ \sqrt {(6378 \text {km})^2 – (5885,22 \text {km})^2} = 22,5885 … \text {km} ≈ 23 \text {km} $]]
NB! In reality, the distance is measured along the surface of the Earth. In other words, the length of sector's arc should be calculated. However, since the central angle of the sector is very small compared to the size of the Earth, the result is the same in both cases at the accuracy of kilometers.
Exercises
Basic exercises
Applied exercises
Challenging exercises
3/14. Submission folder for answers
Sinulla ei ole tarvittavia oikeuksia lähettää mitään.
