2. Scale
Scale
A map is a reduced image of the area it portrays. This means that the shapes seen on a map are the same as they are in reality, but their size is different. Conversely, when studying small organisms with a microscope, an enlarged image of a figure is produced.
Reducing and enlarging are uniformity descriptions. In uniformity descriptions, the shapes of a pattern remains the same but its size changes. In order to be able to determine the actual length of a distance on a map, it is therefore necessary to find information about the map's scale.
Scale
The ratio of the corresponding sides of patterns is called the uniformity ratio, or scale.
Scales are usually expressed in a form in which one of the members is signified by the number one. In reductions, the number one in placed in front of the colon that indicates the scale's ratio. In enlargements, on the other hand, the number one is placed after the colon.
Since a scale is a ratio without a unit, the units can be chosen freely. However, the numbers on both sides of the ratio must have the same unit. For example, a map scale [[$ 1 : 1000 $]] can be interpreted as meaning that [[$ 1 $]] m on the map corresponds [[$ 1000 $]] m in real life, or that [[$ 1 $]] mm on the map corresponds to [[$ 1000 $]] mm in real life. However, centimeters are usually the most practical units when it comes to most maps.
Example 1
A guide map of Helsinki has been made at a scale of [[$ 1 : 20 000 $]]. The distance from the Parliament House to the Presidential Palace along Mannerheimintie and the Esplanade is [[$ 8 $]] cm on the map. How long is the distance in real life?
Solution:
The ratio of [[$ 1 : 20 000 $]] means that a distance of one centimeter on the map corresponds to a distance of [[$ 20 000 $]] cm in real life. The [[$ 8 $]] cm distance on the map is then in nature [[$ 8 $]] cm [[$ \cdot 20 000 = 160 000 $]] cm [[$ = 1,6 $]] km
Answer: The distance is 1,6 km in real life.
Example 2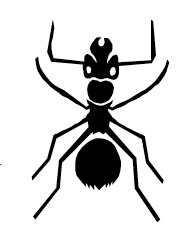
Calculate the actual size of the ant when the image is on a [[$ 6 : 1 $]] scale.
The length of the central part of the ant in the picture is [[$ 20 $]] mm. The actual length is obtained by creating a comparison as follows:
Answer: The length of the ant is [[$ 3,3 $]] mm in real life.
Example 3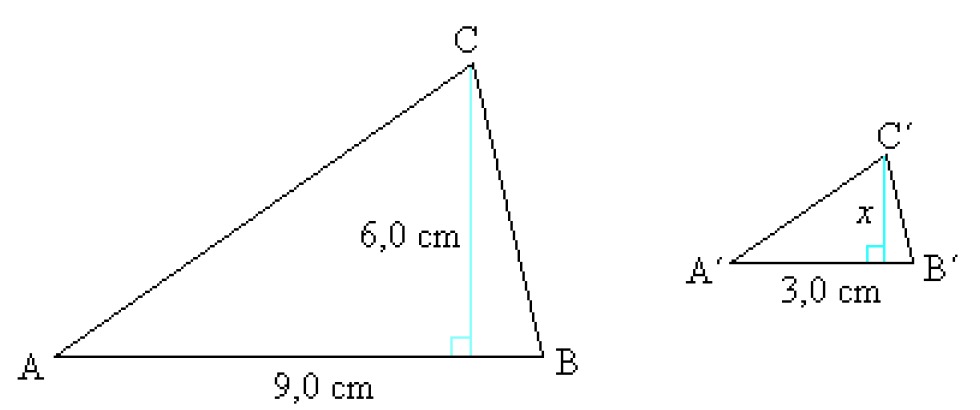
The triangles ABC and A´B´C´ are similar. What is the scale used, and what is the height of the triangle A'B'C?
Solution:
The scale is the ratio of the corresponding sides AB : A’B’ [[$ = 9,0 $]] cm [[$ : 3,0 $]] cm [[$ = 3 : 1 $]]
Since the ratio of the corresponding sides remains the same, a comparison can be made in order to determine the height of the triangle.
Answer: The scale is [[$ 3 : 1 $]], and the height of the smaller triangle is [[$ 2,0 $]] cm.
Exercises
Basic exercises
Applied exercises
Challenging exercises
3/02. Submission folder for answers
Sinulla ei ole tarvittavia oikeuksia lähettää mitään.

