Examples
Example 1
Calculate the area of the parallelogram.
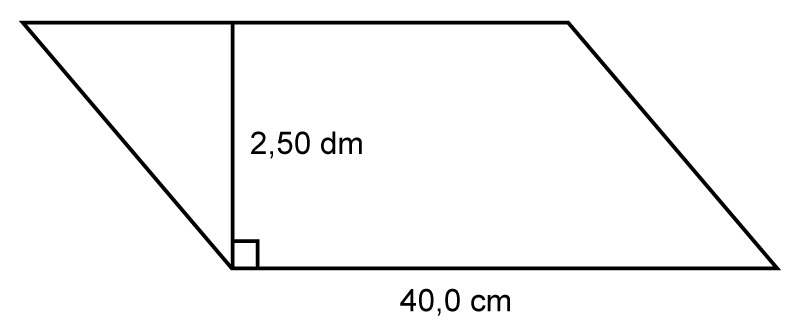 Before placing the dimensions in the formula, they must be converted into the same unit. The decimeters must therefore be converted into centimeters.
Before placing the dimensions in the formula, they must be converted into the same unit. The decimeters must therefore be converted into centimeters.[[$ \text{2.50 dm} = \text{25.0 cm}$]].
[[$ A = a \cdot h = \text{40.0 cm} \cdot \text{25.0 cm} = 1 000 \text{ cm}^2 $]]
Answer: The area of the parallelogram is [[$ 1 000 \text{ cm}^2$]].
Example 2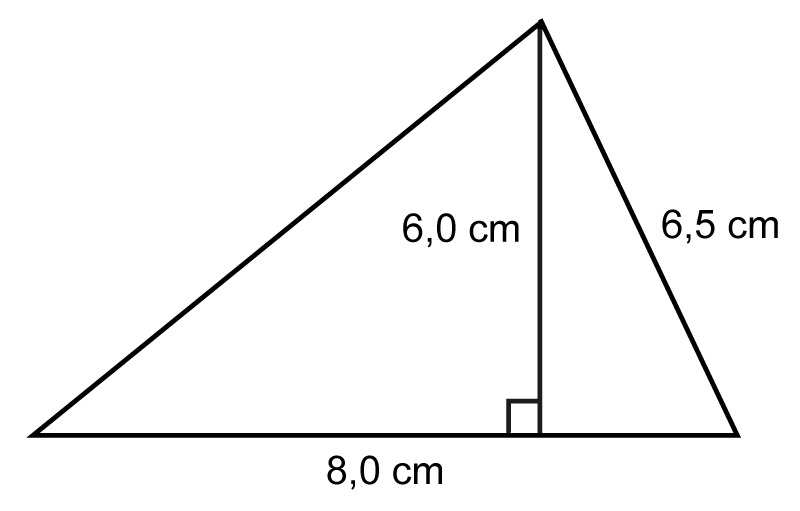
Calculate the area of the triangle.The length of the triangle's side is given in the problem, but it is not needed to calculate the area.
[[$ A = \dfrac{a \cdot h}{2} = \dfrac{\text{8.0 cm} \cdot \text{6.0 cm}}{2} = \dfrac{48 \text{ cm}^2}{2} = 24 \text{ cm}^2 $]]Answer: The area of the triangle is [[$ 24 \text{ cm}^2$]].
Note! In parallelograms, triangles and trapeziums, the altitude of the figure is different from its side lengths. Because of this, the side lengths cannot be used to calculate the areas of these figures.
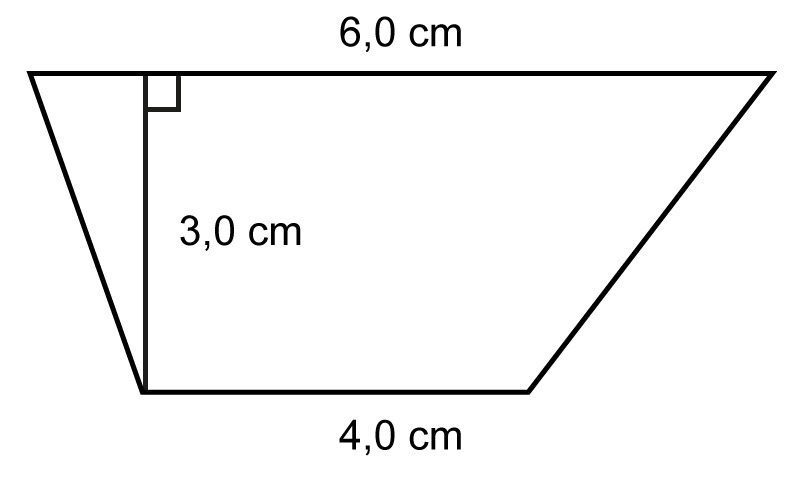
Example 3
Calculate the area of the trapezium when its bases are [[$\text{4,0}$]] cm and [[$\text{6.0}$]] cm long and the distance between them is [[$\text{3.0}$]] cm.It is a good idea to start solving the verbal problems of geometry by drawing a picture of the situation, marking all the given dimensions.
Place the values in the trapezium area formula:
[[$ A = \dfrac{a + b}{2} \cdot h = \dfrac{\text{4.0 cm} + \text{6.0 cm}}{2} \cdot \text{3.0 cm}= \dfrac{\text{ 10.0 cm}}{2} \cdot \text{3.0 cm} = 5 \text{ cm} \cdot \text{3.0 cm} = \text{15 cm}^2$]]Answer: The trapezium has an area of [[$ 15 \text{ cm}^2$]].