The number notation system
The number notation system we use is considered a positional system. In it, the meaning of a digit is affected by its place in the figure. The number zero usually signifies nothingness, but if it is placed after one, the value of the number one will increase tenfold. There are several different positional number notation systems. Each of these systems has a specific base number. The system we use is called the decimal system. It has a base number of 10.
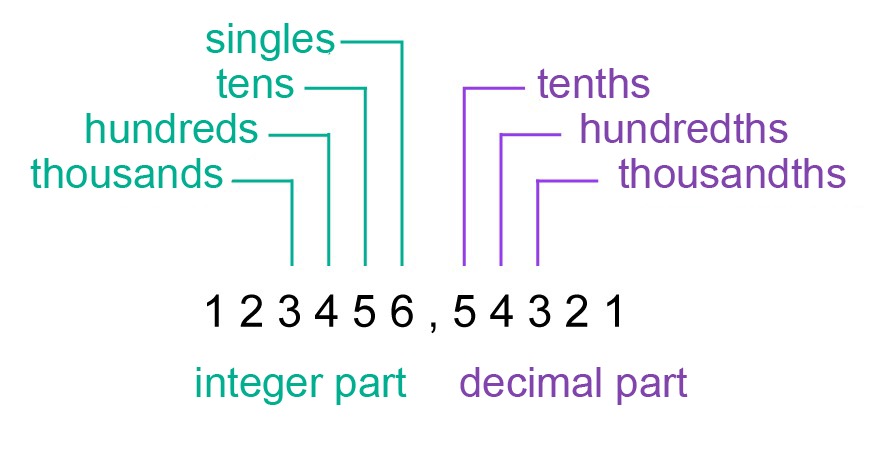
Example 1
Express the following decimals as fractions.
a) 0.32
b) 0.845
c) 3.4
The last number means hundredth parts, so [[$ \text{0.32} = \dfrac{32}{100}$]].
b) 0.845
The last number means thousandth parts, so [[$ \text{0.845} = \dfrac{845}{1000}$]].
c) 3.4
The last number means tenth parts, but there is also a whole part in the number, so [[$ \text{3.4} = 3 \dfrac{4}{10} = \dfrac{34}{10}$]].