6. Trigonometric area formulas *
Trigonometric area formulas
Trigonometric functions can also be used to calculate the areas of two-dimensional patterns if the patterns can be divided into parts consisting of right triangles.
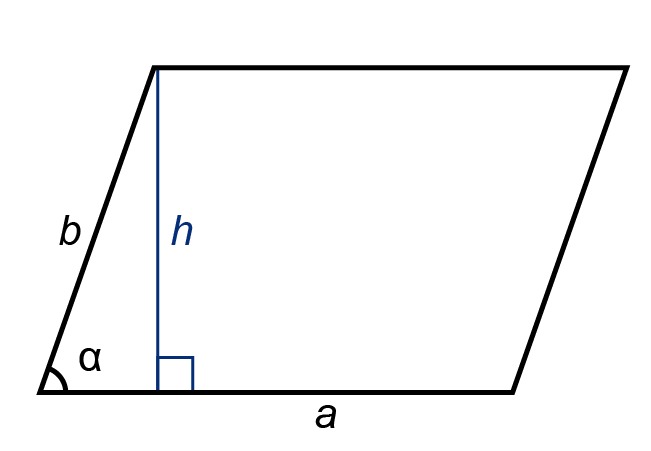
Example 1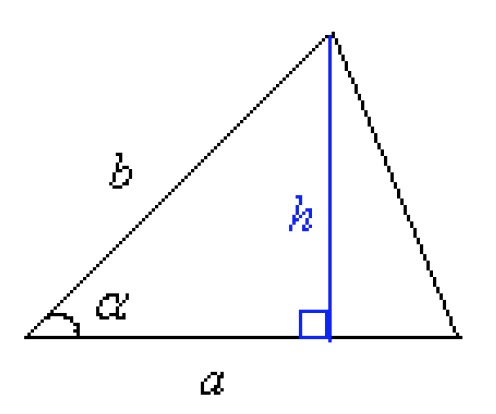
Derive a formula to calculate the area of a triangle from the lengths of two sides of the triangle [[$ a $]] and [[$ b $]] and the magnitude of the angle between them [[$ \alpha $]].
The height of a triangle is determined by sine:
[[$ \begin{align*}
\sin \alpha &= \displaystyle\frac {h} {b} \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; {\color {blue} {| \cdot b}} \\
b\sin \alpha &= \displaystyle\frac {bh} {b} \;\;\;\;\;\; {\color {red} {\text {Move}} \;\color {red} {h}\; \color {red} {\text {to the left of the equation and the others to the right}}}\\
-h &= -b\sin \alpha \; {\color {blue} {| \cdot \left( -1\right)}} \\
h &= b\sin \alpha \\
\end{align*} $]]
When [[$ h $]] is placed in a normal triangle area equation, a new area equation is formed. In this area equation, the height of the triangle does not have to be solved separately.
The area of a triangle
The area of a triangle is [[$ A = \displaystyle\frac {1} {2} ah = \displaystyle\frac {1} {2} ab \sin \alpha $]].
Note! The formula is applicable even when the angle [[$ \ alpha $]] is obtuse.
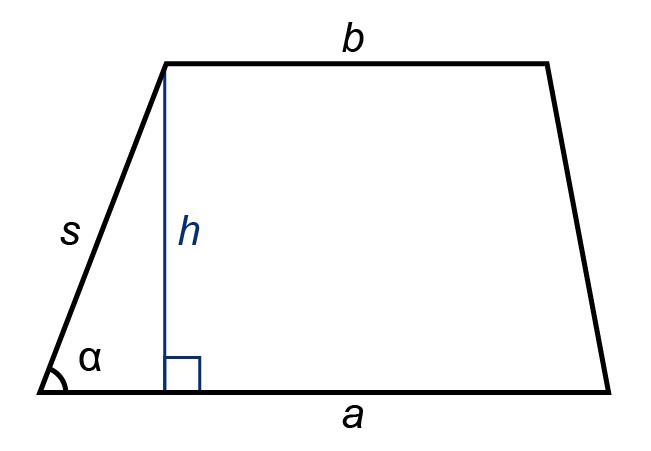
The corresponding surface area trigonometric formulas can also be derived for a parallelogram and trapezoid.
The area of a trapezoid
Area of a trapezoid is [[$ A = \displaystyle\frac {1} {2} \left(a + b \right) h = \displaystyle\frac {1} {2} \left(a + b \right) s \sin \alpha $]].
Example 2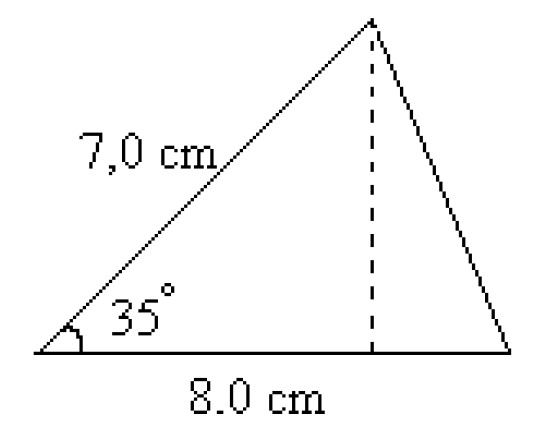
Calculate the area of the adjacent triangle.
Answer: The area of the triangle is [[$ 16 $]] cm[[$ ^2 $]].
Example 3
The lengths of a triangle's sides are [[$ 6,\!2 $]] cm and [[$ 8,\!5 $]] cm. How large is the angle between the sides when the area of the triangle is [[$ 24,\!8 $]] cm[[$ ^2 $]]?
Solution:
First, determine the sine of the angle between the sides:
[[$ \begin{align*} \displaystyle\frac {1} {2} ab \sin \alpha &= A \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\; {\color {blue} {| \cdot 2}} \\ \\ ab \sin \alpha &= 2A \;\;\;\;\;\;\ {\color {blue} {| :ab}} \\ \\ \sin \alpha &= \displaystyle\frac {2A} {ab} \\ \\ \sin \alpha &= \displaystyle\frac {2 \cdot 24,\!8 \;\text {cm}^2} {6,\!2 \;\text{cm} \cdot 8,\!5 \;\text {cm}} \\ \\ \sin \alpha &≈ 0,9412 \\ \\ \alpha &≈ 70,\!3° \\ \end{align*} $]]The calculator gives the acute angle that implements the equation. However, there is another solution to the equation, which is [[$ 180° - 70,\!3° = 109,\!7° $]].
The calculator can still check that [[$ 180° - 70,\!3° = 109,\!7° $]].
Answer: The angle is [[$ 70,\!3° $]] or [[$ 109,\!7° $]].
In general, the following rule applies:
Exercises
2/06. Submission folder for answers
Sinulla ei ole tarvittavia oikeuksia lähettää mitään.