4. Sine and cosine
Sine and cosine
In addition to the tangent, two other trigonometric functions can be defined. These are the sine and the cosine.
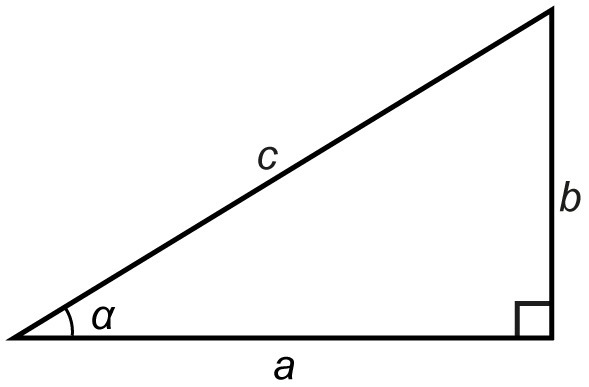
[[$ \cos \alpha = \displaystyle\frac {\alpha \; \text {'s adjacent leg}} {\text {hypotenuse}} = \displaystyle\frac {b} {c} $]]
Example 1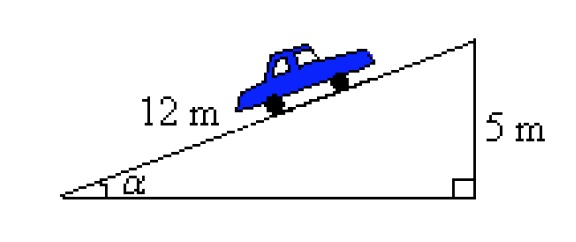
Calculate angle [[$ α $]] of the hill's slope.
The angle could be calculated using a tangent. However, the length of the second leg should be solved with the Pythagorean theorem first. The angle can now be calculated more easily with the help of the sine.
[[$ \begin{align*}
\sin \alpha &= \displaystyle\frac {5 \; \text m} {12\; \text m} \\
\\
\sin \alpha &= 0,\!4167 \\
\alpha &≈ 25°
\end{align*} $]]
The angle is obtained by calculating the inverse of the sine with a calculator

Answer: The slope of the hill is [[$ 25° $]].
Example 2
Calculate the length of the kite's string [[$ x $]] in two different ways.
Method I
In a right triangle, the sum of the acute angles is [[$ 90 ° $]]. This means that the acute angles are one another's complementary angles. The complementary angle of [[$ 35 °$]] is [[$ 55 ° $]]. The following equation is obtained:
[[$ \sin 55° = \displaystyle\frac {23 \; \text m} {x} $]]
This equation can be solved using regular methods.
[[$ \begin{align*}
\sin 55° &= \displaystyle\frac {23 \; \text m} {x} \;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\color {blue} {|| \cdot x}} \\
\\
\sin 55° \cdot x &= 23 \text m \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\color {blue} {|| : \sin 55°}} \\
\\
x &= \displaystyle\frac {23 \; \text m} {\sin 55°} \\
\\
x &≈ 28 \; \text m \\
\end{align*} $]]
The length of the side is obtained by entering the following calculation into the calculator:
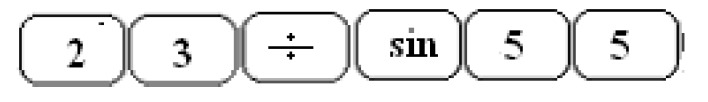
Method II
If we look at a right triangle from another sharp angle, the length of the hypotenuse can be solved with the help of the cosine.
[[$ \begin{align*} \cos 35° &= \displaystyle\frac {23 \; \text m} {x} \;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\color {blue} {|| \cdot x}} \\ \\ \cos 35° \cdot x &= 23 \text m \;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;\;{\color {blue} {|| : \cos 35°}} \\ \\ x &= \displaystyle\frac {23 \; \text m} {\cos 35°} \\ \\ x &≈ 28 \; \text m \\ \end{align*} $]]The length of the side is obtained by entering the following calculation into the calculator:

Answer: The length of the kite's string is [[$ 28 $]] m.
Note! Trigonometric functions can only be applied to right triangles. Since the Pythagorean theorem is also valid, the same angle can eventually be calculated using tangent, sine, and cosine. However, one of these usually gives the most straightforward answer, depending on the situation.
Exercises
Basic exercises
Applied exercises
Challenging exercises
2/04. Submission folder for answers
Sinulla ei ole tarvittavia oikeuksia lähettää mitään.