17. Symmetry
Symmetry
Every object has a center of gravity. If an object is supported from its center of gravity, it will remain in balance in any position. The entire mass of an object can be thought of as being located at its center of gravity. Because of this, the center of gravity is often referred to as the center of mass.
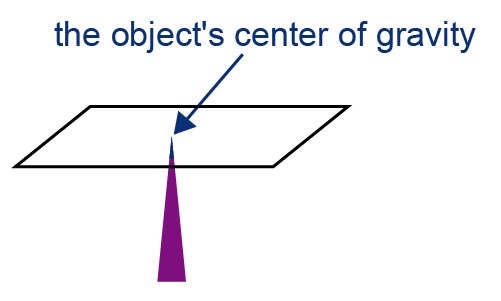
The center of mass of a symmetrical object is located at its center of symmetry, on the axis of symmetry or in the plane of symmetry when the mass of the object is evenly distributed. The axis of symmetry is the line in relation to which the pattern or object is symmetrical. A pattern or object symmetrical with respect to a point is described is mirrored with respect to its center of symmetry. Three-dimensional objects can also have planes of symmetry that, like a normal mirror, depict the other side of the object.
Example 1
A right triangle has three axes of symmetry that pass through the centers of symmetry of opposite faces. The center of symmetry of a right triangle, in turn, is located at the point of intersection of its axes of symmetry.
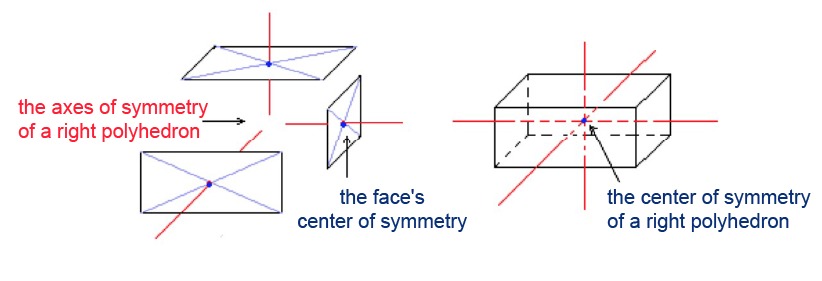
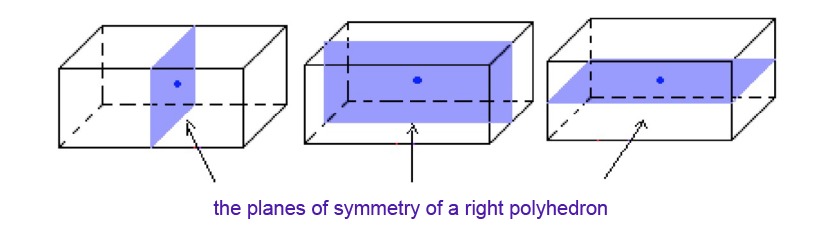
The planes of symmetry of a right polyhedron are at the center of symmetry of its body. They are parallel to the polyhedron's faces
Exercises
2/17. Submission folder for answers
Sinulla ei ole tarvittavia oikeuksia lähettää mitään.