24.7 The evolution of human characteristics
Many human traits serve as signs for various stages of human evolution. The DNA's of humans and chimpanzees are 99% identical. While there are many similarities in the structures of these two species, there are also many differences. Modern humans are the only primate species that walks upright. In humans, this is made possible by the structures of the spine, pelvis and legs.
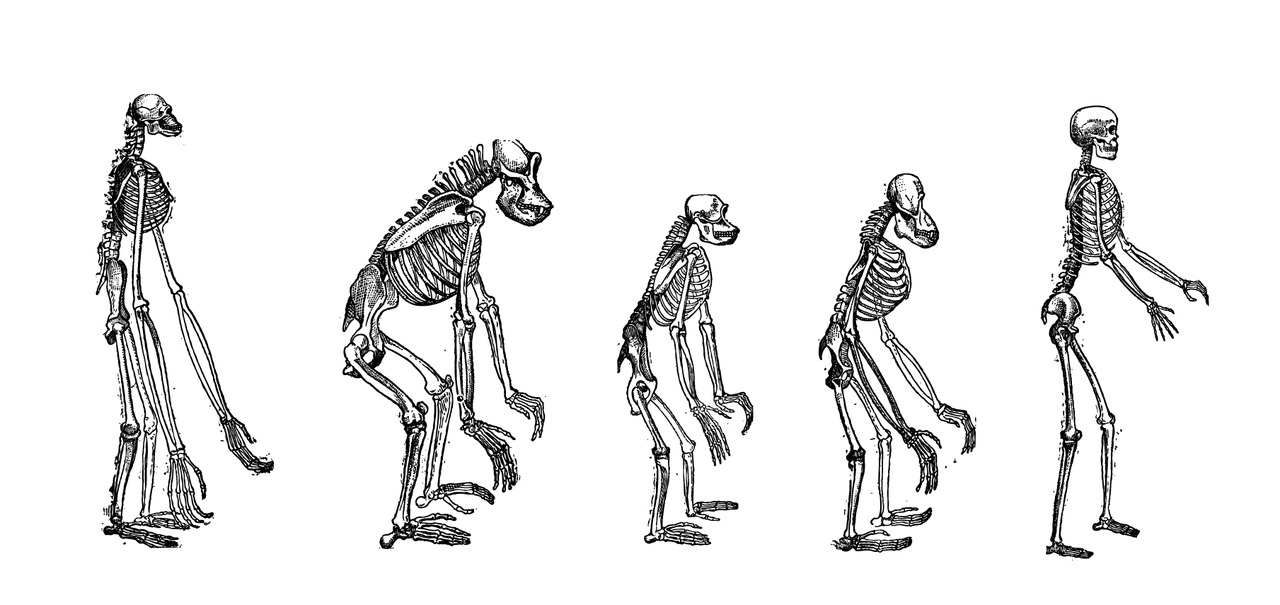 Skeletons of great apes. From left to right: gibbon, gorilla, chimpanzee, orangutan and human.
Skeletons of great apes. From left to right: gibbon, gorilla, chimpanzee, orangutan and human.The flexible and sturdy spine keeps the upper body upright. The forward-turned big toe of the legs and the curved arch of the foot allow for vertical walking.
There are similarities in the instinctive functions of humans and chimpanzees. Instinctive functions are inherited. The instinctive functions of newborn offspring are essential for survival. How would a newborn survive if instinctive functions did not guide him to fumble with his mother’s breasts and thus get milk for food?
The intensity of the gripping reflex is explained as a remnant of a time when a small offspring had to grip firmly on his mother’s fur and stay with the moving mother.
The human thumb and forefinger can touch one another, unlike those of a chimpanzee.
Humans are capable of fine motor skills that allow us to complete extremely meticulous tasks. Surgical procedures, drawing and various other kinds of work require the cooperation of different parts of the brain in addition to the senses of sight and touch. Three-dimensional vision and color vision are the most important characteristics in the development of human sight.
The structure of the human cerebrum makes it possible for us to produce speech. A small baby is capable of recognizing a familiar face and communicating with the people, animals, and objects around them with facial expressions and sounds. On average, a child learns to speak during their second year of life. When a child lives with other people, they learn to talk and communicate with the others in different ways. Along with social development, the skills and knowledge learned by individuals are passed on to the next generation through communication and learning.
Different character traits can be seen in the games played by young children. Belonging to a group is important for every person. Whether a group is a kindergarten circle of friends, a school class, a hobby circle, a group of co-workers, or whatever, it can be observed that sociality is one of the most important species-specific features of Homo sapiens.
