Variable expressions
In most countries, temperatures are reported in degrees Celsius, but in some countries, such as the United States, degrees Fahrenheit are used. There is a certain relationship between the different temperature scales, which can be expressed as a mathematical expression. Degrees Celsius can be converted to degrees Fahrenheit by using the expression [[$ F = \dfrac{9}{5}C + 32 $]], where [[$ F $]] is the temperature in degrees Fahrenheit and [[$ C $]] is the temperature in degrees Celsius.
The Fahrenheit expression can be used over and over again by placing different temperatures in place of [[$ C $]]. Therefore, it is an example of a variable expression. The letter [[$ C $]] represents a variable that can have different values. In variable expressions, the multiplication sign is omitted when the product of a number and a variable or several variables are entered. However, the sign must be marked when placing a numeric value in place of a variable. In addition, if the value of the variable is negative, it must be enclosed in brackets. Two calculation signs cannot occur in a row without brackets.
Example 1
Calculate what a Fahrenheit scale thermometer shows if the outside temperature in degrees Celsius is a) 5 °C, b) –15 °C?a) Place the number 5 in the place of the variable [[$ C $]] and calculate the value of the expression.
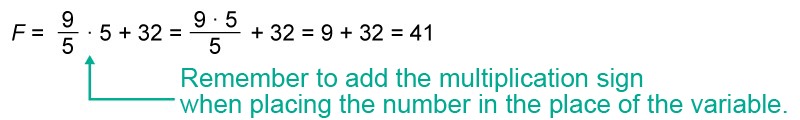
b) Place the number -15 in the place of the variable [[$ C $]] and calculate the value of the expression.
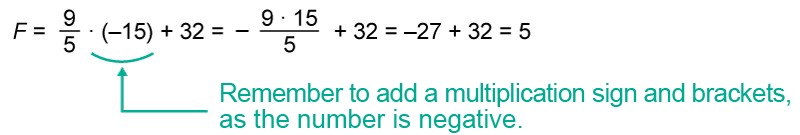
Answer: a) 5 °C is 41 °F in Fahrenheit. b) –15 °C is 5 °F in Fahrenheit.
Typical errors when placing variable values
Place values [[$ x=3 $]] and [[$ y=4 $]] in the expression [[$ 2xy $]].

a) Incorrect!
You forgot the multiplication signs.
b) Correct!
Place values [[$ x=-2 $]] and [[$ y=-5 $]] in the expression [[$ 2xy $]].

a) Incorrect!
You forgot the multiplication signs.
b) Incorrect!
You forgot the brackets!
c) Correct!