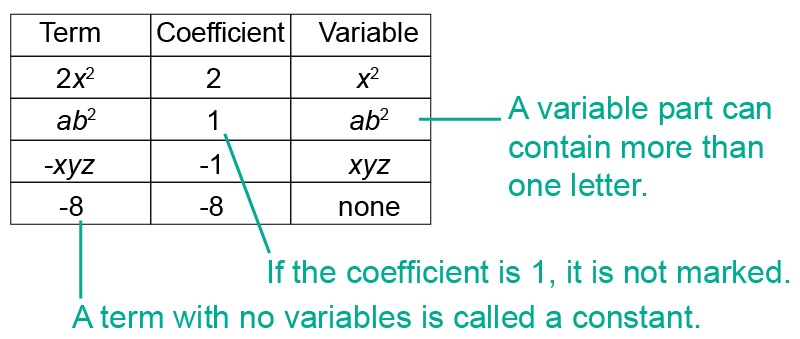
Terms
The product of a coefficient and a variable is called a term.
The variables that appear in a term stand for things that can receive numerical values. These include things like hourly wage, temperature, car speed, etc. If, for example, a litre of strawberries costs € 2, we can describe the price of strawberries with the term 2x. The term 2x indicates the price formation according to the number x of strawberries. If you buy 4 litres of strawberries, you get a price of € 8 by placing the number 4 in place of the variable x.
Marking terms
- The coefficient (number) is written before the variable (letter).
- A multiplication sign is not marked in a product containing a number and a variable.
- A multiplication sign is not marked in a product containing several variables.
- When the coefficient is the number 1, the coefficient is not marked.
- The plus or minus signs are marked first.
Example 1
Simplify the following expressions.
a) [[$ 4 \cdot x = 4x $]]
b) [[$ b \cdot 3 = 3b $]]
c) [[$ 1 \cdot y = y $]]
d) [[$ -1 \cdot a = -a $]]
e) [[$ 5 \cdot (-x) \cdot y = -5xy $]]
Example 2
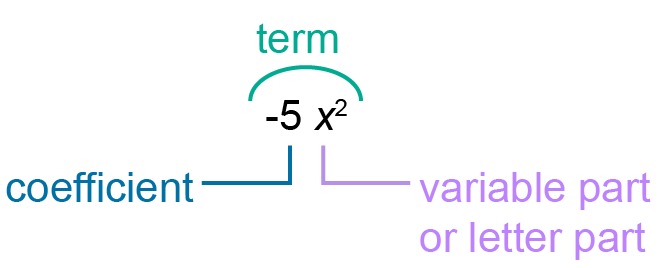
Let’s look which part of the term is a coefficient and which part of the term is a variable.