Espanjan variantit
El meme

Espanja - Columbia - Meksiko - Argentiina
Teksti
1. SPANGLISH
Pohjois-Amerikassa englantiin sekoittunutta espanjaa kutsutaan nimellä "spanglish".
2. ESPANJAN ERI VARIANTIT
Espanjaa puhutaan äidinkielenä 21 maassa, joista suurin osa sijaitsee Etelä-Amerikassa. Tutki kartalta seuraavien maiden México (& Oaxaca y zapotecas), Cuba, Chile ja Argentina erilaisia ääntämissääntöjä espanjan kieleen. Ääntämissääntöjen päällä on video, josta pääset tutustumaan kyseisen maan matkailuun. Eli lue läpi ääntämissäännöt ja katso videot.
3. ÄÄNINÄYTTEET ESPANJAN ERI VARIANTEISTA
Katsoo seuraava video, jossa kuulet ääninäytteitä eri maiden espanjasta.
4. Meksikon alkuperäiskansojen vihellyskieli
Lisää aiheesta:
6 Different Spanish Dialects From Around the World
Many people think that Spanish can be broken down into two categories: Spain Spanish and Latin American Spanish.
But oh, have we got a surprise for you! There are actually a lot of different Spanish dialects out there.
Now, don’t worry. As a Spanish learner, this doesn’t mean you need to be able to sound like a native in every single dialect. In fact, many native Spanish speakers will tell you that they can’t even understand other Spanish dialects because of the heaviness of the accents!
But, it is important to be aware that there are different Spanish dialects out there. Not only will this help you learn more about the Spanish culture as a whole, but it will also help you recognize situations in which you encounter someone who speaks an unfamiliar dialect.
So, which Spanish dialects do you need to be aware of?
Read on to learn about 6 different Spanish dialects from around the world.
1. Castilian Spanish
Castilian Spanish is perhaps the most widely-known of all the Spanish dialects.
With Castilian Spanish, there are actually different verb conjugations than other Spanish-speaking countries.
The main difference is that Castilian Spaniards use the vosotros verb form. Vosotros is a way of saying “you guys”, but in an informal way. You can basically think of it as the plural of “tu”.
And of course, with a new verb form comes a new conjugation. Let’s take the verb estar, for example. If you want to say, “How are you?” using the vosotros form in Spanish, you would say, “¿cómo estáis?”
Another major difference with Castilian Spanish is in their use of the imperfect subjunctive. As you might already know, the imperfect subjunctive is used to talk about uncertainty in the past.
In most Spanish dialects, you will see the -ra ending being used with the imperfect subjunctive. However, with Castilian Spanish, you will often see an -se ending.
For example, the imperfect subjunctive form of llegar in other dialects would be llegara, whereas in Castilian Spanish it would be llegase.
Learn more about this in this video below! You’ll learn some Castilian pronunciation!
2. Andalusian
After Castilian, Andalusian Spanish is the second-most spoken Spanish dialect in Spain.
The big thing to remember about Andalusian Spanish is that it is very fluid sounding, and it is much softer than other Spanish dialects.
This is because Andalusians tend to emit the consonants “r” and “d”. They also tend to drop or soften the sound of final consonants at the end of words.
3. Rioplatense (Argentine)
Spoken in parts of Uruguay and Argentina, the Rioplatense dialect gets its name from the Río de la Plata, the river where the two countries border one another.
Because both of these countries saw a large influx of Italian immigrants in the 20th century, this dialect has a heavy Italian influence. For example, when saying goodbye, you will almost always hear people in these regions say “chau”, which is derived from the Italian word for goodbye, “ciao”.
In fact, both words sound the exact same. Another big distinction is that in place of the double l or y, the Rioplatense dialect will often substitute the sh.
For example, instead of saying, “¿Dónde están las llaves?” (Where are the keys?), you will hear, “¿Dónde están las shaves?”
You will often sometimes hear people in this region substituting tú for the word vos = el voseo. This can be especially tricky, as the word vos can sometimes have different conjugations.
For example, “you feel” in “regular” Spanish is, “tú sientes“. But, in Rioplatense, it would be “vos sentís“.
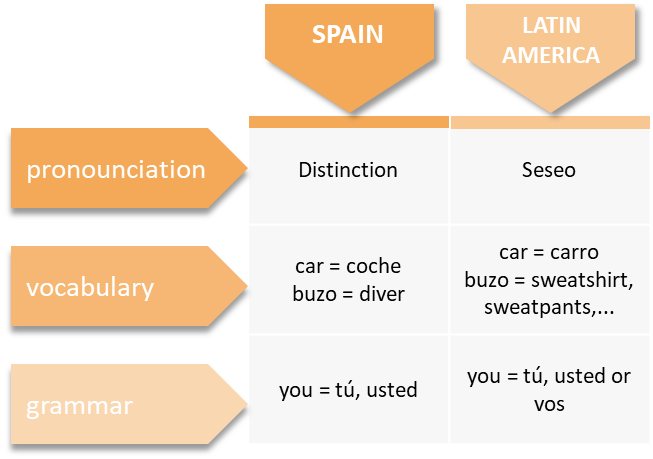
El seseo= the combinations of ce, ci, and z they pronounse "s".
However, most people of the Rioplatense understand these differences, so if you are speaking to someone from this region, they should have no problem accommodating to your dialect.
Here is a video below that will give you some tips on using Spanish from Argentina!
4. Caribbean Spanish
Caribbean Spanish includes the countries of Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Dominican Republic. And while they each have their own dialect, other Spanish speakers all lump these countries together as Caribbean Spanish.
You don’t hear about many Spanish language learners going to these countries to learn Spanish, and that’s perhaps in part because of the rapid pace at which they speak the language.
For example, Caribbean Spanish speakers will completely drop the “d” at the end of words. Instead of saying mitad, for example, they will say mita. Para, another very commonly used word which means “for”, turns to “pa” in Caribbean Spanish.
Caribbean Spanish speakers also tend to drop the “s” sound at both the middle and end of words.
Puerto Rican Spanish is especially unique because it is heavily influenced by the US. Because of this, you will often hear Puerto Ricans stressing the “r” sound like American English speakers do.
Dominican are perhaps the most difficult to understand by other native speakers, as they are famous for their word cutting, in which they will cut huge chunks off of a word. For example, instead of saying “esta”, they will just say “ta”.
It really doesn’t get more Caribbean than the Dominican accent! Check out this video below of a couple of young ladies, one teaching the other some Slang.
5. Andean
Andean Spanish is the dialect that is spoken by city-dwellers in Bolivia, Colombia, Ecuador, Peru, and parts of Venezuela.
This dialect is influenced by its local indigenous languages as well as its European heritage. Many people find the Andean dialect one of the easiest to understand, as native speakers from this region firmly and clearly pronounce their consonants.
While there are small differences between the countries, there really isn’t anything major that should ever trip you up. For example, instead of using the “ito” at the end of the word to describe something cute or small, Colombians will say “ico”.
6. Mexican/ Central American
Last but not least, we have the Mexican and Central American dialects.
Mexico is the largest Spanish speaking country in the world, and it is also the heart of Spanish cinema and media.
This is great news for language learners, as Mexican and Central American Spanish is considered the easiest to understand due. Mexicans and Central Americans have a very clear pronunciation, and you will likely find yourself understanding a lot more in this region than you would in other parts of the world.
Fun with Different Spanish accents
We love this video below. She get a few people to repeat a phrase and you have to guess the accent. The Mexican accent and the one from Argentina & Spain are the ones that really stands out…