4. The skeletal system
Contents of the chapter
4.1 Bones make up the skeletal system
The function of the skeletal system is to protect other parts of the human body, such as the brain and the heart.
Bones also form the body's backbone, which enables movement in conjunction with muscles.
Red blood cells, the cells that transport oxygen in our bodies, are also produced in the bone marrow.
4.2 Bone structure
Bones are made up of 70% minerals, the most important of which are calcium and phosphates. The minerals make our bones very durable. The rest of the bone consists is collagen protein. Collagen protein has a structure similar to a triple-stranded rope. It makes the bone longitudinally flexible.
Bones contain blood vessels, nerve cells and living bone cells known as osteocytes. These are held together by a framework of hard, non-living material that contains calcium and phosphorous. The blood vessels nourish bone tissue and supply oxygen. Bones also feel pain through their nerve cells, which are connected to the nervous system.
A thin membrane called the periosteum covers the bones. New cells grow in periosteum as the bone grows. Cancellous bone is the layer beneath the dense periosteum that contains durable trabeculae.
Running along the centre of long bones, such as your femur (thigh bone), is a cavity filled with bone marrow. Red bone marrow is a soft tissue that produces blood cells, whereas yellow bone marrow is used to store fat.
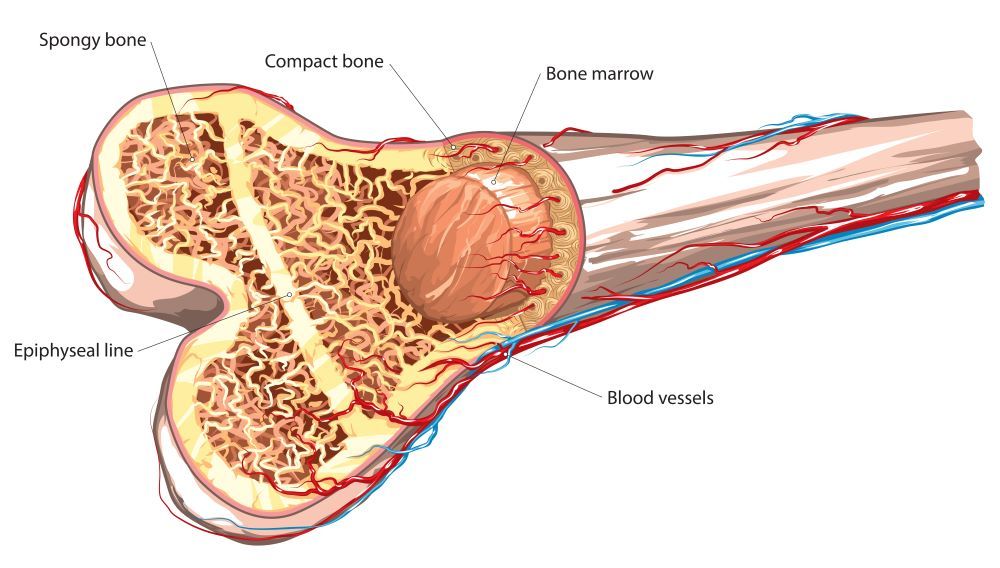
Parts of the bone.
4.3 Functions of the skeletal system
 The skeletal system protects the body's vital organs. The skull bones protect the brain as well as the auditory and visual senses. The spinal cord, the most important nerve bundle, is located within the vertebrae of the neck and spine. The heart and lungs are protected under the ribs. Hip bones protect our genitals.
The skeletal system protects the body's vital organs. The skull bones protect the brain as well as the auditory and visual senses. The spinal cord, the most important nerve bundle, is located within the vertebrae of the neck and spine. The heart and lungs are protected under the ribs. Hip bones protect our genitals.
The skeletal system also forms the body's backbone. Cartilage and joints support and connect bones with one another. Muscles are needed to keep our bodies in the desired position and to help with movement in conjunction with the skeletal system. Muscles are attached to bones, and their function is to move the bones and thus the body as a whole. By doing so, bones and muscles allow us to move around.
Blood cells are produced in bone marrow. In children, round large bones, such as the femur, produce red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets in their bone marrow. In adults, blood cell production is concentrated to flat bones, as the round bones of adults have been filled with adipose tissue.
Bones give our body its basic form. For example, facial bones determine many of our facial features. However, things like our diet and lifestyle influence our appearance, as well.
4.4 Bones are living tissue
Human bones contain bone cells which are constantly in need of nutrients, building materials and oxygen.
Blood vessels that supply calcium and other essential substances pass through the bones.
Bones also feel pain. For example, when you hit something on your tibia or when your bone is damaged, you will feel intense pain. The nerves found in our skeletal system carry messages to and from the brain.
The picture on the right displays the porous, spongy structure of a bone. There is enough space between the calcium- and phosphate-containing parts of the bone to accommodate bone cells, nerves and blood vessels.
4.5 Bones
 A newborn baby has more than 350 bones, but adults have just over 200. The skull of an infant or a young child is made up of bony plates that allow for growth. As a result, the baby's head is able to flex inside the narrow maternal birth canal.
A newborn baby has more than 350 bones, but adults have just over 200. The skull of an infant or a young child is made up of bony plates that allow for growth. As a result, the baby's head is able to flex inside the narrow maternal birth canal.
Bones merge during childhood, which is why adults have fewer bones than infants. The merging of bones can be seen in the tight seams between the bones of our skulls. Bone growth in childhood and adolescence indicates that bones consist of living tissue.
Find out about the different bones in the body from the following website. Study the names of the bones.
4.6 Types of joints
Bones are connected with one another with joints. The hip and the shoulder are both examples of ball and socket joints. They allow you to swing your arms and legs in many different directions. In the ball and socket joint, the oval-shaped condyle of one bone fits into the elliptical cavity of the other bone.
There are several hinge joints in the limbs. All fingers, elbows, knees, and toes have hinge joints that also allow movement back and forth, movement similar to the opening and closing of a hinged door.
The only saddle joints in your body are found in your thumbs. The bones of a saddle joint can rock back and forth and from side to side, but they have limited rotation. Condylar joints are found at the wrist, connecting the radius and carpal bones, and at the base of the index finger.
The pivot joint in your neck allows you to turn your head from side to side. This joint would even allow for a complete rotation but other factors, including muscles, prevent that from happening. One pivot joint in your neck allows sideways rotation only, whereas another pivot joint allows the head to move back and forth.
The picture on the right shows various types of joints found in the human body.
- A. Ball and socket joint (shoulder joint)
- B. Hinge joint (forearm)
- C. Condylar joint (joint near the wrist)
- D. Saddle joint (joint between thumb and palm).
4.7 Teeth
The hardest substance in the human body is found in the mouth. It is enamel, which is found on the surface of teeth. However, enamel can also be damaged: especially flavored waters and carbonated drinks can cause enamel erosion. Dentine is found under the enamel. The inside of the tooth contains cementum and pulp. Pulp is made up of connective tissue, blood vessels and nerve fibres. Its function is to supply nutrients to your teeth. The pulp cavity extends into the root of your teeth, forming the root canal.

4.8 A bone can fracture
Bones can break or fracture. Most fractures heal over time. If the bone is broken, its ends need to be realigned. The broken bones are then immobilized, often with a plaster cast, so they can start healing themselves. Bones are capable of repairing themselves. Bone remodeling allows bones to adapt by becoming thicker and stronger when subjected to stress.
Basketball and volleyball players have to jump high. During physical activity, the ankle may twist inward as a result of landing unwantedly. This may cause one or more ligaments around the ankle to stretch. Proper rest and an ankle support are often enough to heal damage to the ligaments that help support the ankle joint. If the ligament injury is more severe and the ligaments have been torn, an operation is required.
The hinge joint of the knee can withstand only one kind of back-and-forth movement. When the knee is twisted, there is a risk of damage to the ligaments and the joint. In most cases, knee injuries require a prolonged period of rest, and they often keep the person from exercising for several months.
When lifting heavy loads off the ground, the lifting position must be taken into account. A vertebral disc can slip out of place while you are twisting or turning when trying to lift an object. Due to displacement, the disc can press on the spinal nerves, resulting in a risk of losing leg function.