23.5 Many factors contribute to evolution
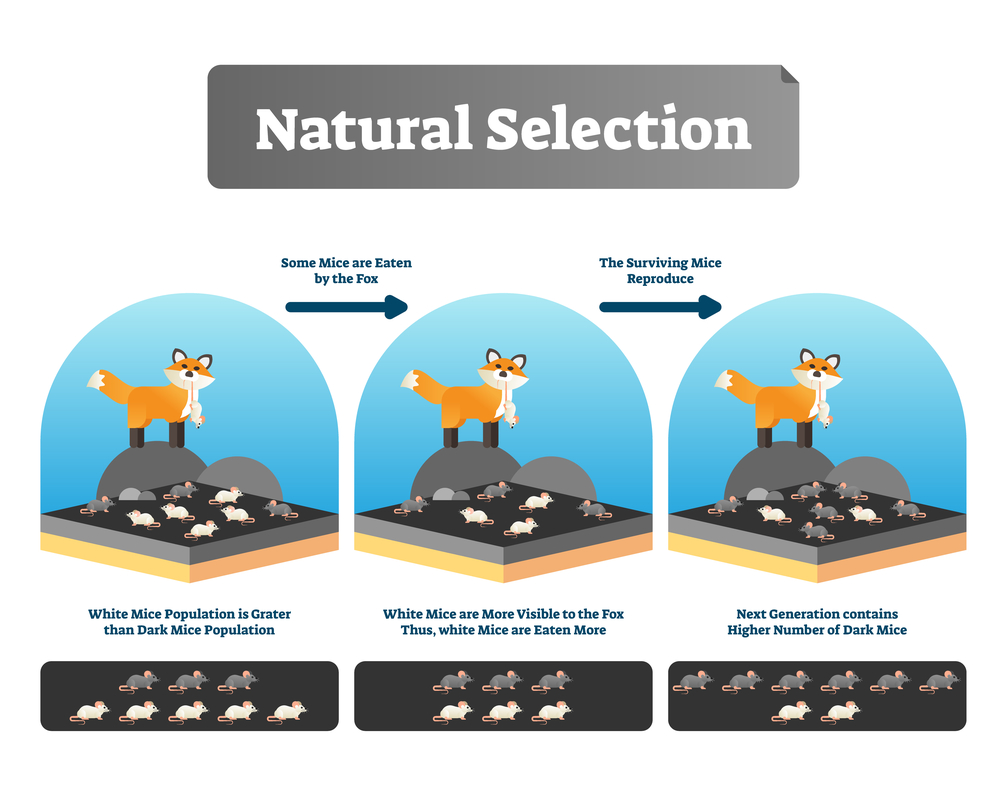
 What causes the changes in organisms? Natural selection is the most important factor influencing evolution. Natural selection is based on the fact that individuals of the species produce more offspring than sustainable in their habitat. Individuals of each species that are best adapted to the natural conditions at the time are most likely to survive. They are most successful and produce the most offspring, passing on their genes to the next generation. Genes carry genetic traits.
What causes the changes in organisms? Natural selection is the most important factor influencing evolution. Natural selection is based on the fact that individuals of the species produce more offspring than sustainable in their habitat. Individuals of each species that are best adapted to the natural conditions at the time are most likely to survive. They are most successful and produce the most offspring, passing on their genes to the next generation. Genes carry genetic traits.
Natural selection can only work if individuals are different. Indeed, there are differences between individuals in the traits that affect their success. Genetic changes, i.e. mutations, and modification through sexual reproduction bring about differences. For example, mutations make it possible that seeds can produce different colour leaves to their parent tree. Leaves of a certain colour, photosynthesise better than others. Such plants produce more seeds than others: there has been natural selection.
Individuals of the same species living in the same place and reproducing with each other form a population. In a population, basically all individuals of a species can reproduce with each other. If, for some reason, a population finds itself in a situation where a factor prevents individuals from reproducing with each other, individuals may evolve in different directions over time, resulting in different forms, subspecies, and over time, even different species. This speciation is the evolutionary process by which populations evolve to become distinct species.
Speciation can also occur in such a way that individuals of the same species are exposed to different habitats, where environmental factors slowly modify the species. The species adapts to the prevailing conditions and natural selection takes place.
The survival of a species, subspecies, or population under changing environmental conditions is affected by how much difference there is in their inheritance between individuals — that is, how much they differ genetically. Because an individual’s inheritance provides an individual’s traits, a genetically diverse population is also diverse in traits. In this case, as the habitat changes, individuals will be found whose traits contribute to survival in the new conditions and the species or population will be able to adapt to these new conditions. If we want to protect species and populations, we need to make sure that their genetics remain diverse.
In modern life, evidence of evolution is provided by bacteria that have evolved to be resistant to a variety of antibiotics. Thus, bacteria have evolved into strains in which antibiotics used as drugs are no longer effective. These so-called nosocomial bacteria are the biggest threats to health care.