The Pythagorean theorem
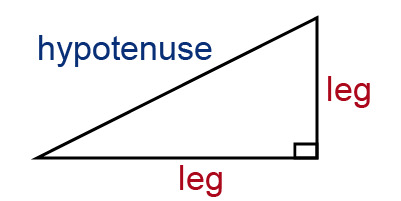
In a right triangle, the hypotenuse is the side opposite to the right angle. Sides adjacent to the right angle are called legs.
NB! The hypotenuse is always the longest side of a right triangle.
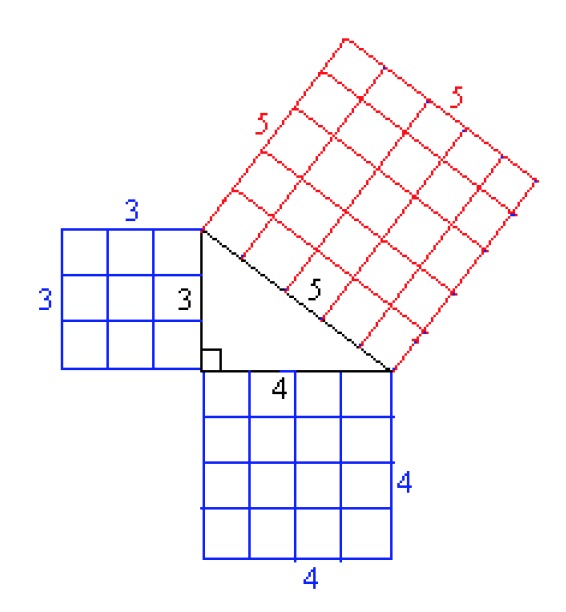
Consider a rectangular triangle with legs of [[$ 3 $]] and [[$ 4 $]] and a hypotenuse of [[$ 5 $]].
Draw squares on the sides of the triangle with side lengths that are equal to the triangle's side lengths.
The areas of the leg squares are
[[$ 3^2 = 9 $]] and [[$ 4^2 = 16 $]].
The area of the hypotenuse square is [[$ 5^2 = 25 $]].
If the areas of the leg squares are added together [[$ 9 + 16 = 25 $]], the area of the hypotenuse square is obtained.
This property is valid for all rectangular triangles and is known as the Pythagorean theorem.
The Pythagorean theorem
In a right triangle, the sum of the squares of the two legs equals the square of the hypotenuse.
[[$$ a^2 + b^2 = c^2 $$]]
The Pythagorean theorem can be used to examine whether a triangle is a right triangle.