39. Vertebrates
Fish
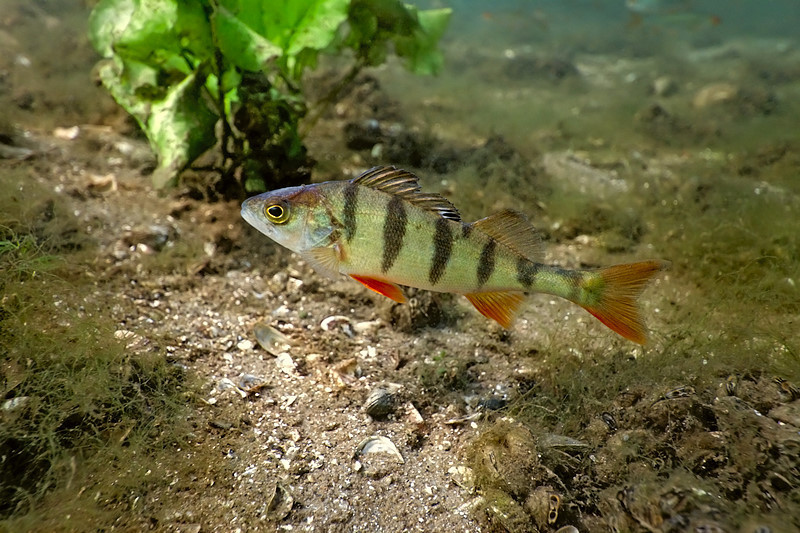 Fish are water-dwelling vertebrates. They move in the water by using their fins. They filter oxygen from the water with their gills.
Fish are water-dwelling vertebrates. They move in the water by using their fins. They filter oxygen from the water with their gills.Fish reproduce by spawning. During spawning, a female fish lays down its spawn (egg cells), and the male fish fertilizes them with its milt (sperm cells). This means that fish reproduce sexually.
Fish are poikilothermic animals. This means that their body temperature changes depending on the temperature of the water around them. As a result, fish are rather inactive during the cold winter months.
Fish have simple circulatory systems. The heart of a fish contains only one atrium and one ventricle, whereas the heart of mammals contains two of each.
Fishes can be divided into cartilagenous and bony fishes, depending on the material from which their skeletons are made out of. Most fish species are bony fishes, whereas sharks are examples of cartilagenous fishes.
Amphibians
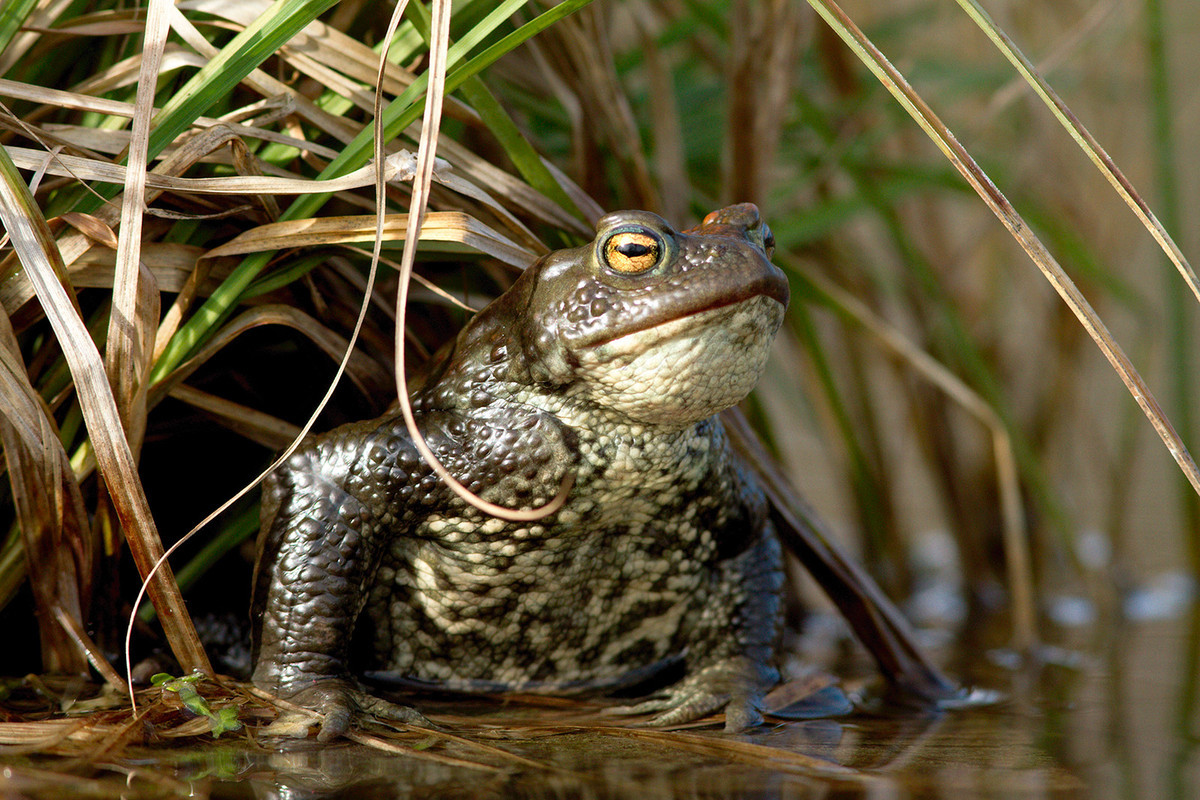 Amphibians are not as dependent on water as fishes are. They have four legs, which they use to move on dry land.
Amphibians are not as dependent on water as fishes are. They have four legs, which they use to move on dry land.Frogs are examples of amphibians. They are predators that eat insects and other small invertebrates.
Frogs reproduce by spawning. This means that they need water environments in order to reproduce. The frog egg develops into a water-dwelling larva, known as a tadpole. The tadpole gradually grows and develops into an adult frog.
Reptiles
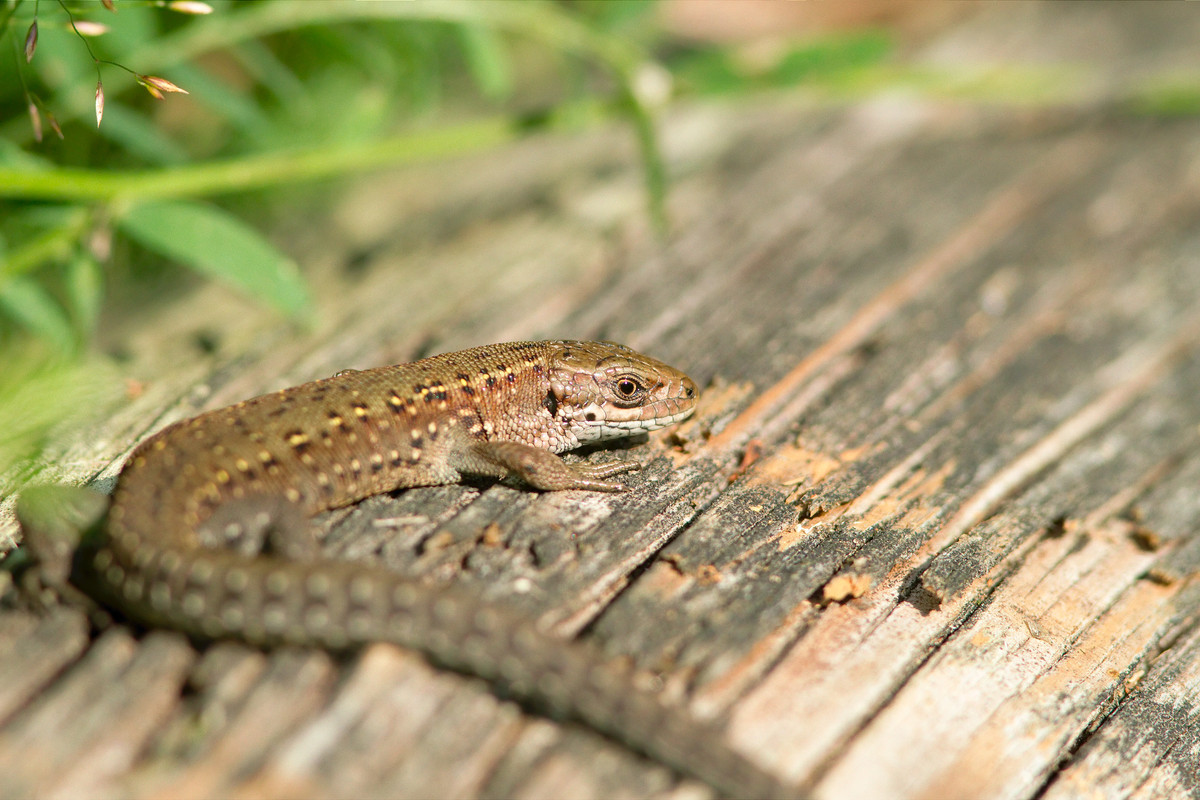 Reptiles are fully adapted to life on land. Their skin is dry and hard, unlike the soft and moist skin of amphibians.
Reptiles are fully adapted to life on land. Their skin is dry and hard, unlike the soft and moist skin of amphibians. Reptiles reproduce by laying eggs. Eggs that are laid on warm ground eventually hatch and reveal small reptile individuals that are already capable of living on land.
Snakes, lizards, turtles and crocodiles are the best known groupsof reptiles.
Because reptiles are poikilothermic organisms, they can only move when the weather is warm enough.
Different kinds of reptiles
Birds
 Birds are vertebrates with feathers, wings and a beak. This makes birds easy to distinguish from other vertebrates. However, distinguishing one bird species from another is a different matter: there are over 9 000 bird species in the world.
Birds are vertebrates with feathers, wings and a beak. This makes birds easy to distinguish from other vertebrates. However, distinguishing one bird species from another is a different matter: there are over 9 000 bird species in the world. Birds have adapted to flying. They have light, hollow bones, as well as effective circulatory and respiratory systems. Their wing feathers help them to stay in the air, whereas their down feathers protect them from the cold.
Birds only have two legs, as their front limbs have developed into wings.
Female birds lay eggs and brood over them in their nests. The egg develops into a young bird that grows into a flying, adult bird over the course of several weeks or months.
Characteristics of birds:
 Different bird species have different legs: flamingoes have long legs, whereas swifts have short legs.
Different bird species have different legs: flamingoes have long legs, whereas swifts have short legs.- Birds apply oil to their feathers. This protects them from water.
- Many bird species have excellent eyesight and hearing.
- The structure of a bird's beak depends on what kinds of things it eats.
- Birds sing in order to mark their territory and to attract mating partners.
- Some birds, such as the crow, are very smart animals. Many bird species are quick learners.
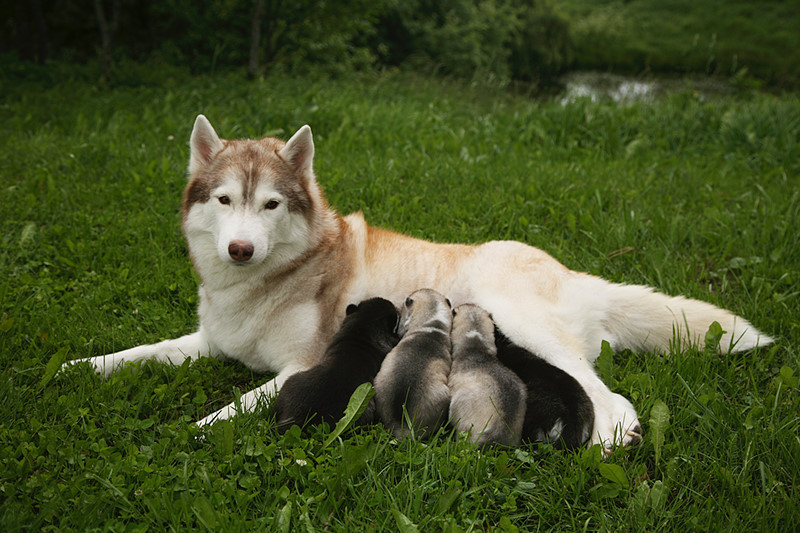
Mammals
- Like birds, they are warm blooded or homeothermic.
- They have efficient respiratory and circulatory systems.
- They have highly developed senses.
- They are quick learners.
Mammals have adapted to life everywhere in the world. The most common groups of mammals include bats, whales, canines, felines, rodents, cloven-hoofed animals and primates.
Mammals: Platypus
Mammals: Kangaroos and other marsupials

- No womb or placenta: instead, the young marsupial develops inside its mother's pouch.
- After being born, the young marsupial climbs into its mother's pouch.
- The mother's mammary glands are found inside the pouch.
- The young marsupial lives in its mother's pouch for up to a year, before it becomes independent.
- Kangaroos are herbivorous marsupials.
Mammals: Bats
Mammals: Whales

- Marine mammals: fin-like front limbs and tail, vestigial back limbs.
- Homeothermic or warm-blooded organisms, like all other mammals.
- Suckle their young with their mammary glands
- Whales come up for air to breathe: they have no gills, which means that they cannot breathe under water.
- Baleen whales (such as the blue whale) eat plankton and small animals.
- Toothed whales (such as sperm whales) are predators.
- Large animals: blue whales can grow over 30 meters long!
Terminology
| Term | Explanation |
|---|---|
| spawning | A method of reproduction where a female animal lays its egg cells for the male animal to fertilize. |
| reptiles | A group of land-dwelling, poikilothermic vertebrates. E.g. snakes, lizards and turtles. |






