7.3 Fish reproduction
 The process of fish reproduction is called spawning. It requires male fish sperm, or milt, and female fish eggs, or roe. The process of spawning involves females releasing ova (unfertilized eggs) into the water, while males simultaneously release sperm cells (milt) to fertilize the eggs. This process is known as external fertilization, as it does not take place inside the female fish.
The process of fish reproduction is called spawning. It requires male fish sperm, or milt, and female fish eggs, or roe. The process of spawning involves females releasing ova (unfertilized eggs) into the water, while males simultaneously release sperm cells (milt) to fertilize the eggs. This process is known as external fertilization, as it does not take place inside the female fish.
Depending on the species, the development of fertilised eggs into fish takes from a few days to several months. The eggs develop and hatch into larvae (baby fish) without any help from the parents.
The larvae are not able to feed themselves, and carry a yolk-sac which provides their nutrition. Before the yolk-sac completely disappears, the tiny fish must become capable of feeding themselves.
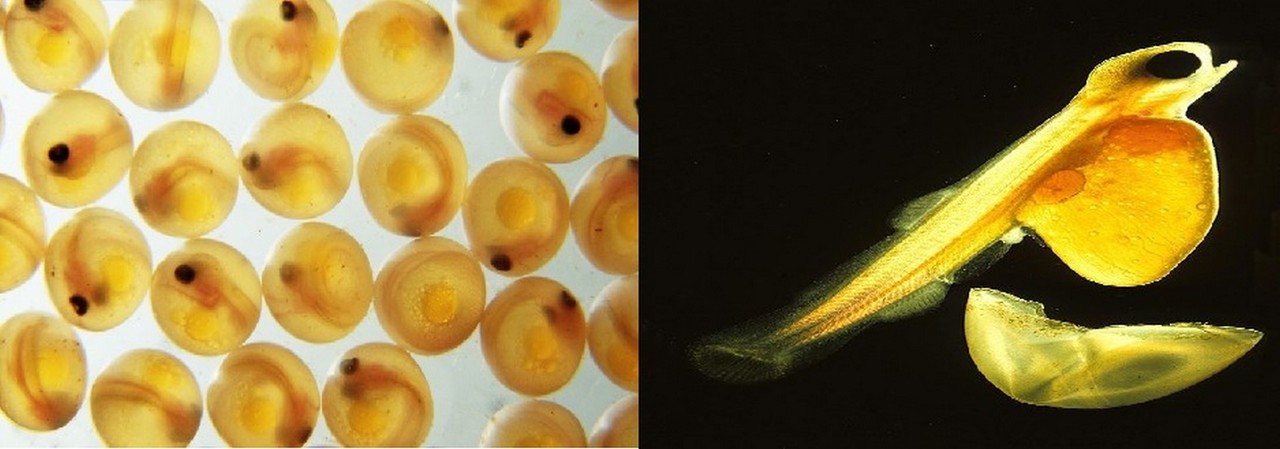
Left: Fertilized eggs. Right: Hatched salmon larva. It gets its energy from a yolk-sac.