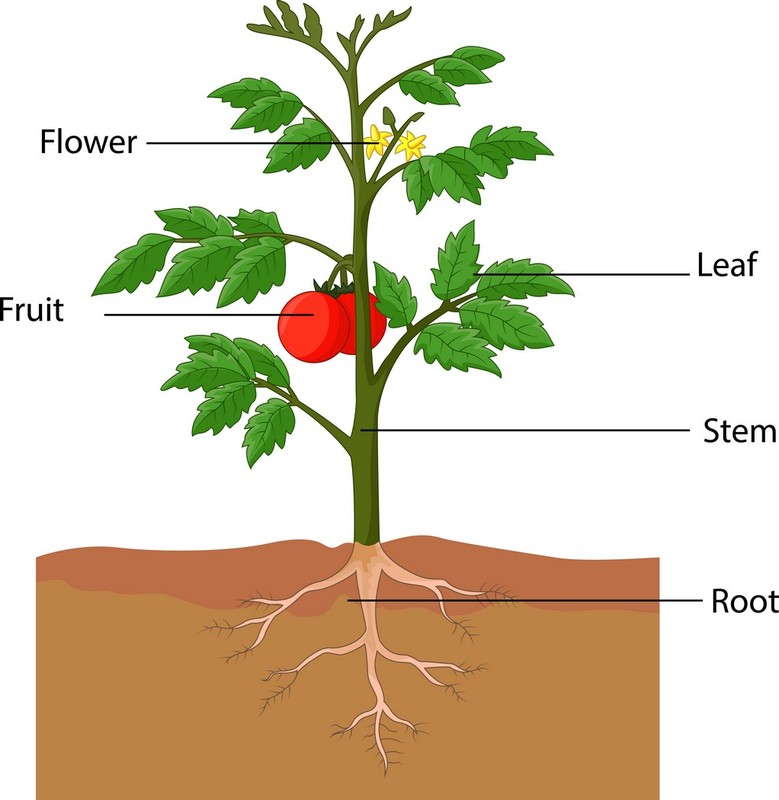
5.1 Plant structure
The main structures of a plant are the root, the stem, and the leaves. The root of a plant is attached to the soil. The plant uses its root to gather water and nutrients.
Conducting tissue begins at the plant’s roots and continues through its stem all the way up to its leaves. The conducting tissue transports water and nutrients from the plant’s roots to its leaves. In addition to this, the conducting tissue also transports the sugars produced in the plant’s leaves back down to its roots.
The plant uses its stem to reach out towards sunlight.
The leaves of the plant are where photosynthesis takes place. During photosynthesis, the plant uses the energy from sunlight to make sugar and oxygen out of water and carbon dioxide.
The plant uses sugar to grow and reproduce. The plant uses some of the oxygen it produces during photosynthesis itself, and the rest of the oxygen is released into the environment. There it is used by other organisms.
Illustration: The parts of the plant.