1. The living cell
Contents
1.1 How do you recognize a living organism?
Pebble plants (also known as living stones) are plants that can be found in the dry areas of Southern Africa. As their name suggests, they resemble small stones found in the surrounding environment. Despite their appearence, pebble plants are still living organisms and the surrounding stones are lifeless.

Pebble plants are real, living plants.
Think about the different things that separate these plants from their non-living environment. Why are stones not considered living organisms? You can respond by commenting.
1.2 The basic requirements of life
What is required for life to be possible? The birth and existence of life requires:
- water in liquid form
- elements that render life possible, such as carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen and phosphorous
- a source of energy, such as the Sun.
There can be no life without energy. Energy is used to construct complex chemical compounds, to move, and to make different things happen. The life on our planet receives most of its energy from the Sun.
Plants need water and sunlight, among other things. Animals require water as well as energy produced by plants.
Plants, algae and some bacteria are capable of photosynthesis, which means that they can make use of light energy from the Sun to produce chemical energy, stored in chemical compounds. All other organisms are dependent on the chemical energy produced by plants.
The solar energy bound by green plants and other producers moves through the food chain and is used by consumers, such as herbivores and predators.
Life on earth is organic, which means that it is based on different carbon compounds. Carbon is an element that can form a variety of different chains and wheels.
The molecules that are significant for living organisms, such as carbohydrates, fats, and proteins, are comprised of carbon chains that have elements such as hydrogen, nitrogen and oxygen attached to them. Life as we know it also requires other elements, such as phosphorous, potassium, calcium, magnesium and iron.

Solar energy is bound by plants and transferred to herbivores and other consumers.
1.3 The cell
Plants and animals are comprised of one or multiple cells. The cell contains a lot of water. Therefore, water is essential for living cells.
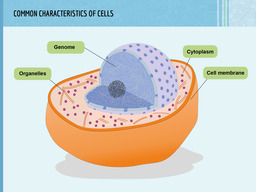
Animal cell:- The cell is defined by the cell membrane. It regulates the movement of substances to and from the cell.
- The cell is filled with cytoplasm, where various important reactions take place.
- The nucleus comprises the "brains" of the cell. The nucleus contains the cell's genome in DNA form.
- The Golgi apparatus is involved in the production of materials.
- The mitochondrion is where the cell produces energy. Muscle cells, for example, contain a number of mitochondria.
- Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not contain a cell wall nor a vacuole.
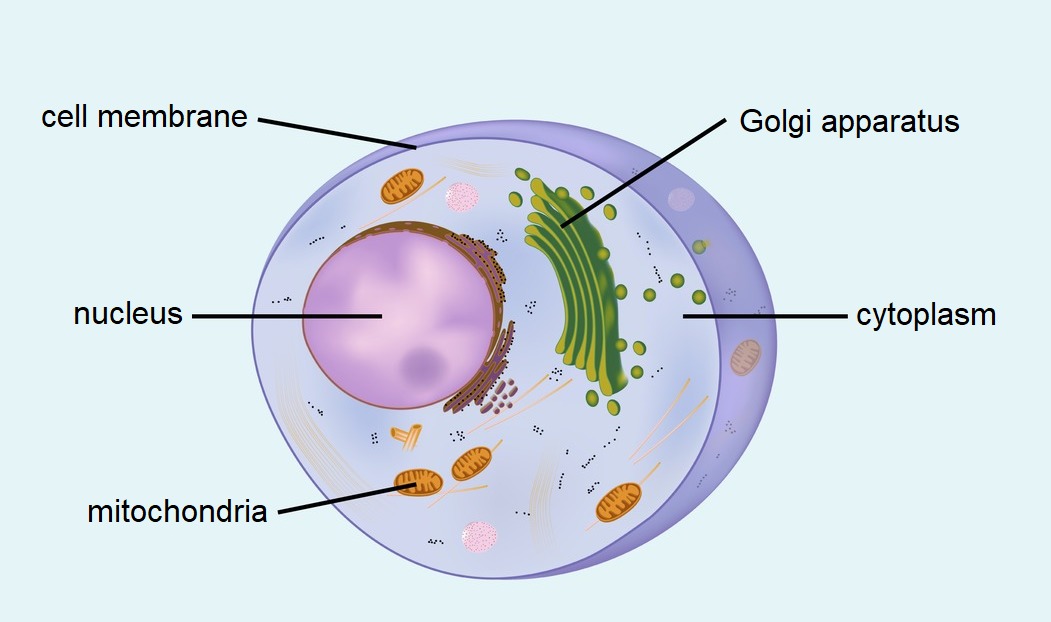
Animal cell.
The different parts of the plant cell have different functions:
- The nucleus comprises the "brains" of the cell. It contains the cell's genome in DNA form.
- The cell membrane regulates what substances can move to and from the cell.
- The cytoplasm is where various important reactions take place.
- The cell wall of a plant cell provides protection and support.
- The vacuole of the plant cell is used to store water.
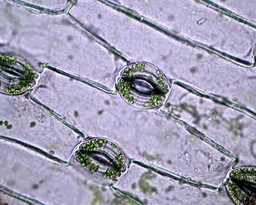
- The chloroplasts of the plant cell are where photosynthesis takes place.
- The plant cell also has mitochondria, like the animal cell.
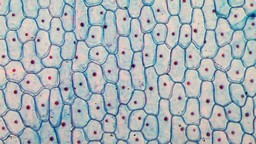
Cells form larger structures in both plants and animals. These structures are known as cell tissue. For example, the human muscle cells form muscular tissues, whereas the superficial cells of a plant's leaves form superficial tissues.
 Plant cell.
Plant cell.
Learn the parts of the cell
Animal cell.
Plant cell.