1.3 The cell
Plants and animals are comprised of one or multiple cells. The cell contains a lot of water. Therefore, water is essential for living cells.
Animal cell:- The cell is defined by the cell membrane. It regulates the movement of substances to and from the cell.
- The cell is filled with cytoplasm, where various important reactions take place.
- The nucleus comprises the "brains" of the cell. The nucleus contains the cell's genome in DNA form.
- The Golgi apparatus is involved in the production of materials.
- The mitochondrion is where the cell produces energy. Muscle cells, for example, contain a number of mitochondria.
- Unlike plant cells, animal cells do not contain a cell wall nor a vacuole.
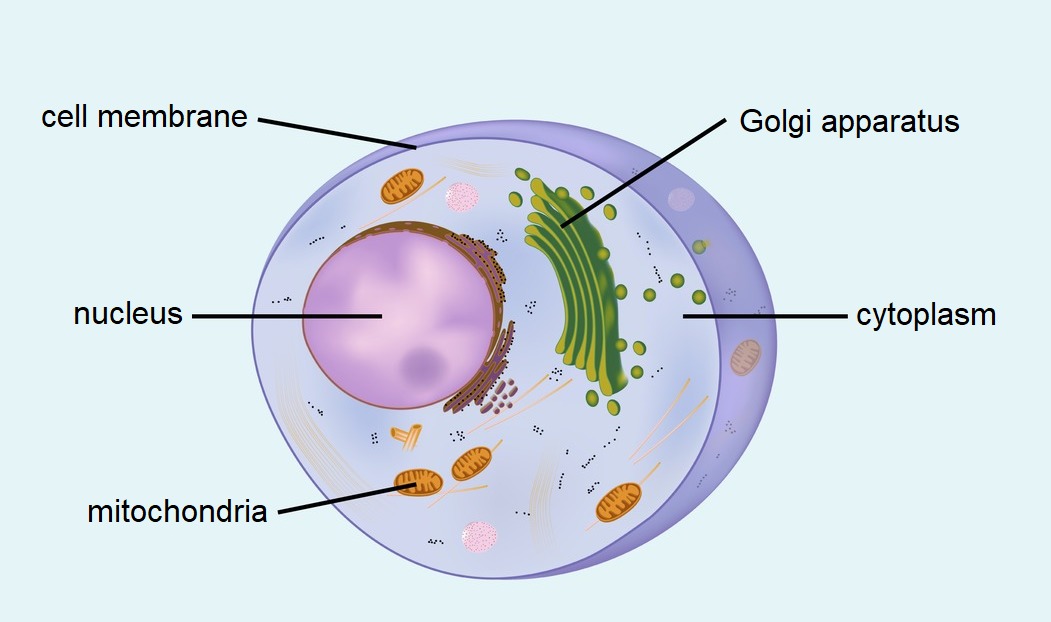
Animal cell.
The different parts of the plant cell have different functions:
- The nucleus comprises the "brains" of the cell. It contains the cell's genome in DNA form.
- The cell membrane regulates what substances can move to and from the cell.
- The cytoplasm is where various important reactions take place.
- The cell wall of a plant cell provides protection and support.
- The vacuole of the plant cell is used to store water.
- The chloroplasts of the plant cell are where photosynthesis takes place.
- The plant cell also has mitochondria, like the animal cell.
Cells form larger structures in both plants and animals. These structures are known as cell tissue. For example, the human muscle cells form muscular tissues, whereas the superficial cells of a plant's leaves form superficial tissues.
 Plant cell.
Plant cell.