Mitosis
- This is a type of cell division in which a cell divides into two daughter cells each having the same numberof chromosomes as the parent cell.
- This takes place in all body(somatic) cells of an organism to bring about increase in number of cells, resulting in growth and repair.
- Mitosis is usually described as a series of stages for convenience of explaining the process involvrd in a logical manner. These stages are, Interphase, Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase.
- These stages of cell division occur in a smooth and continuous pattern so that one stage merges with the next without interfering with the activities of the cell.
Interphase
The term interphase is used to describe the state of the nucleus when the cell is just about to divide.
During this time the following take place:
- Multiplication of genetic material so that daughter cells will have the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
- Manufacture of cell organelles such as mitochondria, golgi bodies, centrioles, ribosomes and centrioles.
- Energy for cell division is synthesised and stored in form of Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) to drive the cell through the entire process.
During interphase, the following observations can be made:
- Chromosomes are seen as long, thin, coiled thread-like structures.
- Nuclear membrane and nucleolus are intact.

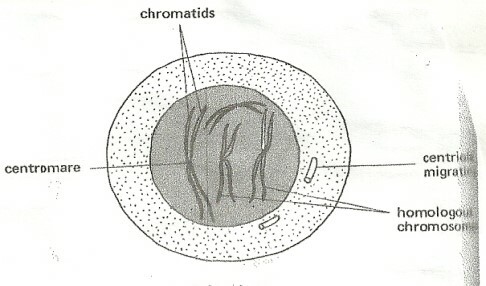
Prophase
- The chromosomes shorten and thicken.
- Each chromosome is seen to consist of a pair of chromatids joined at a point called centromere.
- Centrioles (in animal cells) separate and move to opposite poles of the cell.
- The centre of the nucleus is referred to as the equator.
- Spindle fibres begin to form, and connect the centriole pairs to the opposite poles.
- The nucleolus and nuclear membrane disintegrate and disappear.
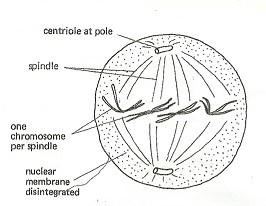
Metaphase
- The nuclear membrane disappears hence chromosomes are free in the cytoplasm.
- The spindle fibres lengthen. In animal cells they attach to the centrioles at both pole
- Each chromosome moves to the equatorial plane and is attached to the spindle fibres by the centromeres.
Anaphase
The following events occur during this phase,
- Chromatids separate and migrate to the opposite poles due to the shortening of spindle fibres .
- Thespindleapparatusbegins to disappear.
- In animal cells, the cell membrane starts to constrict towards the end of the anaphase.

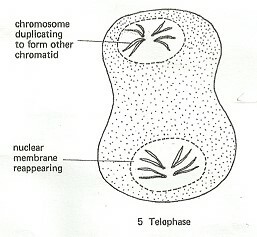
Telophase
This is the final phase ofcell division
- The chromatids collect together at the two opposite ends of the spindle.
- A nuclear membrane forms around each set of chromatids andare nowreferred to as chromosomes.
- The cytoplasm divides into two leading to the formation of two daughter cells.
- Chromosomes later become less distinct.
Significance of Mitosis
- It brings about the growth of an organism:
- It is a basis of asexual reproduction.
- Ensures that the chromosome number is retained.
- Ensures that the chromosomal constitution of the offspring is the same as the parents.