5.2 Plant reproduction
Flowering plants have flowers that produce seeds when pollinated.
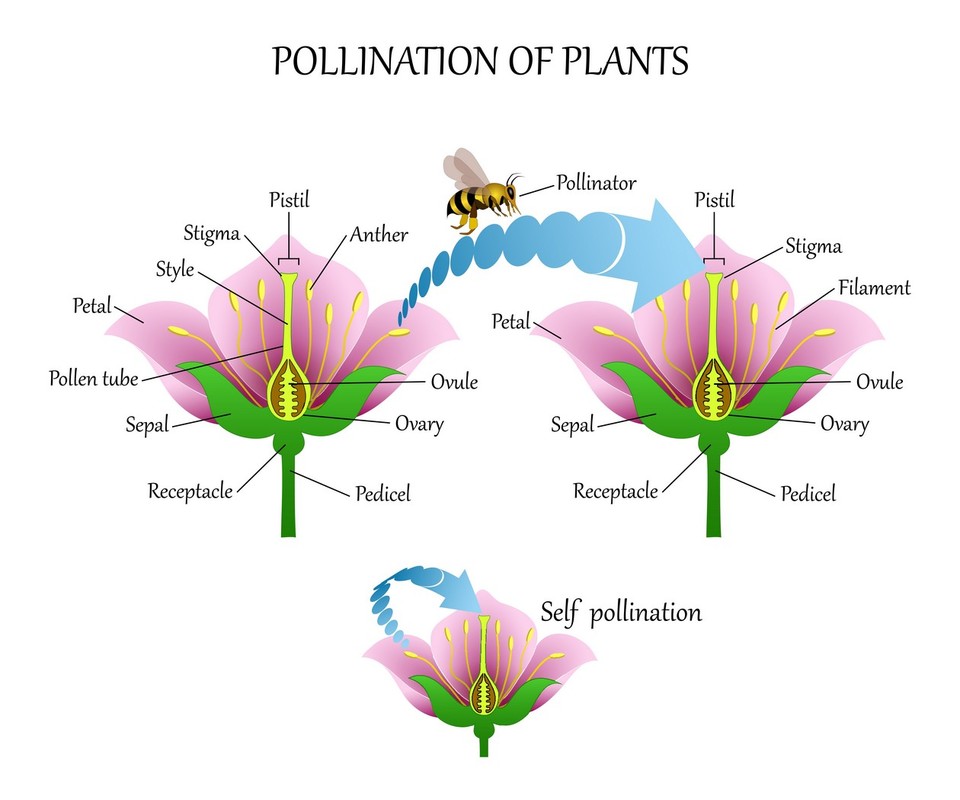
Flowers contain structures called stamens and pistils. Stamens produce pollen. Pistils are where the seeds are produced.
A colorful flower attracts insects, such as bees and butterflies. Insects arrive at the flower in order to drink its sweet nectar. At the same time, pollen from the flower is caught to these insects and travels with them from flower to flower.
The process where pollen is transported from one flower to another is called pollination. It can occur with the help of the wind, insects, or birds. When pollen from one flower reaches the egg cell (ovule) located in another flower’s pistil, the process of fertilization occurs. As a result of fertilization, a seed is produced.
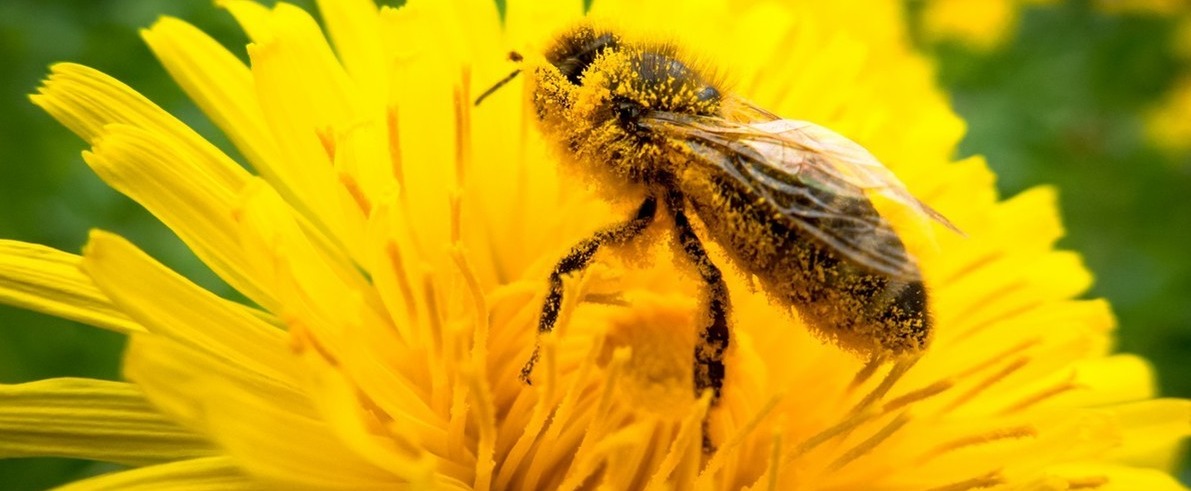

Bees are common pollinators.
Flowering plants are also called seed plants. Their reproduction is an example of sexual reproduction, because it includes the fertilization of two gametes (sex cells).
The seed contains a small embryo of a new plant. The seed contains a large amount of extra nutriment, which the plant uses when growing its first photosynthetic leaves.
Plants can also reproduce without the help of seeds and flowers. For example, the strawberry plant can produce runners that grow into new individuals. This kind of reproduction is considered asexual, because it does not make use of gametes.
Many plants can also begin their growth from small plant fragments. For example, a piece of a dandelion root can grow into a new plant. You can even try growing plants in this way by yourself. For example, when you place a ruler-length willow branch into soil, it can grow into a new willow tree!

Strawberry plants spread into new areas by growing runners. This is an example of asexual reproduction.
Sporiferous plants do not have flowers. Instead, they use spores to reproduce asexually. They produce large amounts of spores in their sporangia and release them to the environment. Each of these spores can grow into a new plant if the conditions are right. Ferns, horsetails, and club mosses are all sporiferous plants.
| Part or process | Significance |
|---|---|
| Stamen | Produces pollen. |
| Pistil | Produces the egg cell (ovule). |
| Pollination | The process where pollen is transported from one flower to another flower’s pistil. |
| Fertilization | The nucleus of the pollen is combined with the nucleus of the egg cell. → The seed begins to develop. |
| Sexual reproduction | Reproduction that takes place with the help of gametes (pollen and egg cell). |
| Asexual reproduction | Reproduction that takes place without the help of gametes, for example with runners or spores. |